This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its unique location you possibly can go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://www.popularmechanics.com/space/deep-space/a65507137/betelgeuse-companion-star/
and if you wish to take away this text from our website please contact us
Here’s what you’ll be taught if you learn this story:
- The identical star that went viral in 2019 for being on the sting of going supernova (it didn’t) is now within the highlight once more for having a buddy.
- Because Betelgeuse ejected an enormous quantity of gasoline and dirt when it first made headlines, a companion—which was suspected for hundreds of years—wouldn’t have been detectable.
- Now, evidently the companion of Betelgeuse might have lastly been detected by way of a sophisticated imaging method, and can be extra seen when it orbits additional away from its host.
Betelgeuse wants no introduction. Besides having its identify borrowed by the ghost with the most, this 10-million-year-old crimson supergiant that mysteriously pulsates on the fringe of the Orion constellation is among the brightest stars within the evening sky. And it may not be alone.
Like its film doppelgänger, Betelgeuse is undead… type of. Having exhausted all of its hydrogen gasoline, it has now moved on to fusing helium atoms in its crimson large part, which explains its excessive dimension and brightness (the identical factor is predicted to occur to our Sun in about 5 billion years). It went viral in 2019 for an occasion referred to as the Great Dimming, throughout which the star grew so ominously darkish that many astronomers thought it was on the verge of going supernova. The actuality nevertheless, was much less last—the shadows obscuring the star weren’t a forecast of doom, however enormous gobs of gasoline and dirt it had belched out.
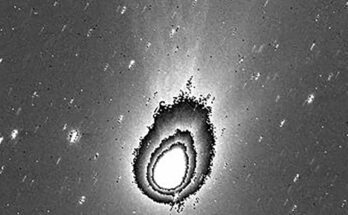
Though Betelgeuse has been thought to have a companion star for a whole lot of years, the monster’s intense luminosity (as much as 14,000 instances brighter than the Sun) blocked out something in its neighborhood. The fixed swirling of Earth’s thick environment can also be problematic—with the environment in the best way, objects in area can seem blurred when noticed from our planet’s floor. While Hubble was capable of observe what’s now referred to as the Great Dimming occasion from area and clear up fears of a supernova going off solely 700 light-years away, it was unimaginable to see a companion by way of the big ejection of star stuff.
Eventually, astrophysicist Steve Howell—a senior analysis scientist at NASA’s Ames Research Center—determined to watch Betelgeuse from the ground-based Gemini North telescope on the dormant Mauna Kea volcano in Hawai’i. Gemini’s massive aperture allowed for brighter photographs and made it superb for recognizing an object that may have beforehand been missed. Its hi-res digicam is named the ‘Alopeke speckle imager, and it uses an imaging technique based around ultra-short exposure times that freeze out atmospheric interference as the camera captures thousands upon thousands of images. Any remaining signs of turbulence can be removed when the images are processed.
Shifts in the velocity, angle, and brightness of Betelgeuse previously sparked the idea that a hypothetical companion star may be behind some of the perturbations scientists see when observing the star. Having had his eye on the red giant since the Great Dimming, Howell and his research team were insistent on finding an object that had eluded detection for so long. They were almost certain ‘Alopeke would be able to glimpse at least some possible evidence of the companion—if it existed.
“In a blind search for close stellar companions to bright stars, the results presented here would be marginal, but the correspondence between our detection and the predicted location of the companion adds credence to the result,” the team said in a study recently published in the journal The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
Howell’s outcomes confirmed potential proof for a stellar companion on the outer edges of Betelgeuse’s environment—proper in the identical location that had been predicted by astronomers and astrophysicists earlier than him. The faint companion appears to be orbiting on the identical distance and angle steered by these predictions. It can be extra detectable when it reaches the purpose in its orbit that’s the furthest away from the overwhelming brightness of Betelgeuse, which can be in November of 2027, so the follow-up observations ought to convey affirmation of the existence of this object a technique or one other.
The companion star additionally has a reputation (and no, it isn’t Lydia). “Betelgeuse” truly interprets from Arabic to “the hand of al-Jawza”, referencing a mythological determine which was absolutely articulated within the sky by historic astronomers. Her fingers, toes, head, hair, and different options are illustrated by stars within the Jawza celestial complex, often known as the Orion constellation. Howell felt it was solely acceptable to maintain with this theme in naming Betelgeuse’s companion, and as such, it’s now referred to as “Siwarha”, or “her bracelet.” Betelgeuse and Siwarha will finally merge.
While Betelgeuse isn’t anticipated to go supernova for at the least one other 10,000 years, it nonetheless is likely to be finest to not danger summoning something by saying its name three times.
Elizabeth Rayne is a creature who writes. Her work has appeared in Popular Mechanics, Ars Technica, SYFY WIRE, Space.com, Live Science, Den of Geek, Forbidden Futures and Collective Tales. She lurks proper outdoors New York City together with her parrot, Lestat. When not writing, she could be discovered drawing, enjoying the piano or shapeshifting.
This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its unique location you possibly can go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://www.popularmechanics.com/space/deep-space/a65507137/betelgeuse-companion-star/
and if you wish to take away this text from our website please contact us