This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its authentic location you may go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s42003-025-08590-y
and if you wish to take away this text from our web site please contact us
TRPCA improves age prediction from intestine, oral, and pores and skin microbiome profiles
TRPCA (Fig. 1) improved MAE for host age prediction by as much as 28% in comparison with the opposite mannequin architectures (Support Vector Regression (SVR), Gradient Boosting Regression (GBR), Okay-Neighbors Regression (KNN), Neural Network Regression (NN), and RF), demonstrating the best enhancements in MAE for the pores and skin microbiome samples (Table 1, Fig. 2, Supplemental Data 1). Although TRPCA improved age prediction throughout datasets when grouping samples by topic ID, our analyses confirmed inferior age prediction for 16S pores and skin and oral microbiomes in comparison with RF fashions from Huang et al., on the identical datasets. To decide whether or not the discrepancy was due the distinction in how the practice/take a look at splits have been grouped and stratified, TRPCA fashions have been benchmarked with Huang et al. and evaluated for less than 16S pores and skin and oral samples following the very same stratification standards for samples denoted in Huang et al. (with out grouping by topic ID). The TRPCA mannequin had a median MAE of two.16 years for 16S pores and skin samples and three.86 years for 16S oral samples (Fig. S1), in comparison with the reported 3.8 years and 4.5 years, respectively. To additional examine the affect of samples from repeated measures within the 16S pores and skin and oral knowledge, we created two filtered datasets. One included the highest 40 topics with not less than two samples stratified by topic ID, and the opposite included just one pattern per topic. Using the filtered datasets, TRPCA outperformed the opposite fashions for host age prediction for the filtered datasets, suggesting that together with a number of samples from a person didn’t clarify the TRPCA mannequin’s benefit over different methods (Figs. S2–S3). When educated on the dataset together with a number of samples per host, TRPCA predicted host age with a MAE of 0.61 years for 16S pores and skin samples and 0.42 years for 16S oral samples (Fig. S2), outperforming the RF mannequin with a MAE of 1.84 years for 16S pores and skin samples and 1.31 years for 16S oral samples on this situation. Finally, we investigated the efficiency of TRPCA in comparison with the opposite mannequin architectures on the 16S pores and skin dataset with various pattern sizes. As anticipated for deep studying fashions, TRPCA carried out higher than standard fashions for bigger pattern sizes when predicting host age; nevertheless, TRPCA achieved related efficiency to standard fashions even for smaller pattern sizes (Fig. S4), demonstrating its utility for small datasets as nicely.
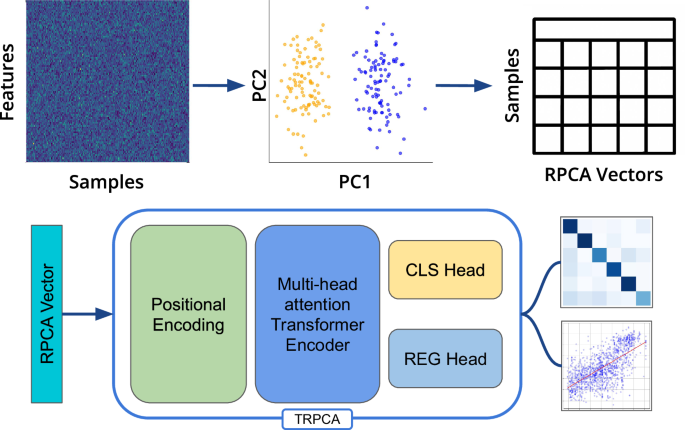
Samples represented as rely tables are visualized and transformed to RPCA vectors. RPCA vectors are enter as sequences right into a transformer encoder mannequin with multi-head consideration. The transformer mannequin outputs are supplied to a classification (CLS) or regression (REG) head for classification, regression, or Multi-task studying.
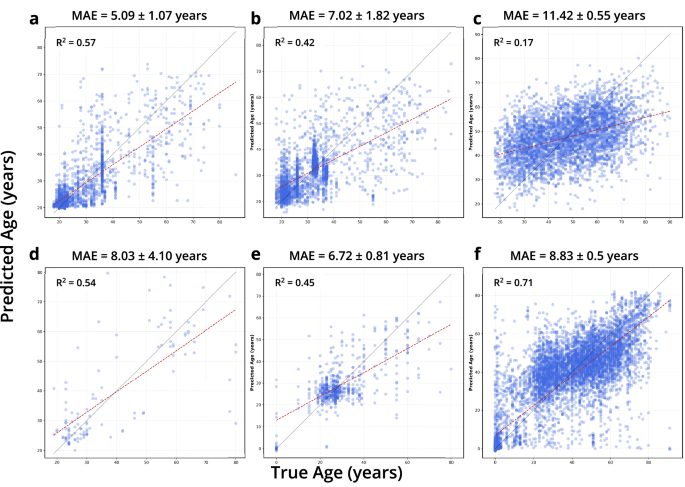
a–c are regressions for 16S knowledge and d–f for WGS knowledge. a, d, b, e, c, f point out regressions for pores and skin, oral, and intestine microbiome samples respectively.
MTL for grownup WGS intestine samples classifies nation of delivery and predicts host age
For the mixed process of classifying host delivery county and predicting host age, we took 270 samples from every of 5 nations (China:CHN, United Kingdom:BR, Japan:JPN, Netherlands:NLD, United States of America:USA) within the WGS grownup intestine dataset. To benchmark the standard fashions, we educated the fashions for classification and regression fashions individually. Then, we chosen the top-performing mannequin for every process to behave because the ensemble mannequin for comparability with TRPCA. TRPCA achieved a MAE of 10.21 years for host age prediction and an accuracy of 0.92 for nation of delivery prediction, in comparison with the most effective MAE of 10.90 years utilizing RF and the most effective accuracy of 0.80 utilizing RF (Fig. 3, Table 2). TRPCA improved host age prediction by 6% and delivery nation classification by 13% enchancment, in comparison with RF.
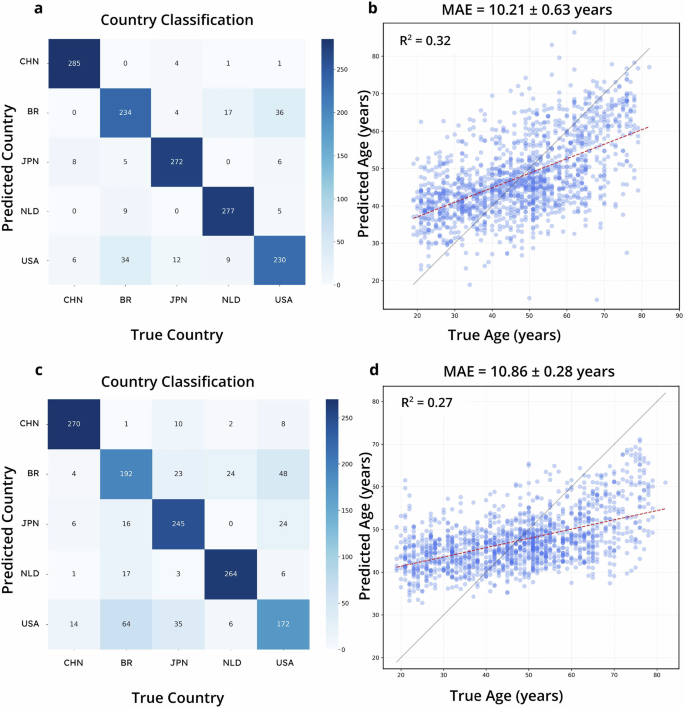
a, b are the confusion matrix and age prediction regression for the TRPCA MTL mannequin. c, d are RF fashions educated individually for a similar classification and regression duties because the TRPCA MTL mannequin.
Interpretable characteristic choice from TRPCA through SHAP values
After coaching every mannequin for regression duties, SHAP values have been calculated on the take a look at cut up of the information following prediction from the regression duties. From the SHAP values matrix and RPCA characteristic loading matrix, world imply importances (Figs. S5–S10) and pattern stage importances (Fig. 4, Figs. S11–S15) have been calculated. Global imply importances have been displayed as differentials to focus on options recognized for host age, with options of optimistic imply significance being related to older topics and options of unfavorable imply significance being related to youthful people (Figs. S5–S10). SHAP values on the pattern stage have been proven utilizing a normalized heatmap, highlighting the pattern stage options recognized by the TRPCA mannequin for age prediction. The prime 50 options recognized by TRPCA for 16S pores and skin have been prevalent throughout nearly all of take a look at samples and confirmed clustering patterns on a pattern and have foundation (Fig. 4). The pattern stage interpretation of the SHAP values supplied a high-resolution view of the characteristic importances, highlighting options which may be prevalent for many samples, in addition to options which will solely be essential for the age prediction of a subset of the information. The abundance of Enterococcus faecalis, for instance, was a globally important characteristic, as a result of most samples had a normalized characteristic significance better than 0.4 for this characteristic (Fig. S12). However, for the primary cluster of samples, E. faecalis abundance was a very powerful characteristic for age prediction, and different options had low characteristic importances. Global characteristic importances have been calculated by averaging the characteristic importances for every pattern. For the highest world options, correlations have been calculated between the log-transformed values for the characteristic versus host age (Figs. S16–S21). To additional validate the recognized options from TRPCA, we explored the person contributions of options for WGS pores and skin samples (Fig. 5). Using the pattern stage characteristic importances derived from TRPCA, we have been in a position to hone in on the person contribution of a single characteristic for the age prediction of a given pattern (Fig. 5a). Negative characteristic importances(coloured in blue) point out that the characteristic influenced the mannequin prediction in direction of a youthful prediction for that particular person, whereas optimistic characteristic importances(coloured in crimson) drove the mannequin prediction in direction of an older age. For instance, for the age group 28–35, we see people with compositions of Cutibacterium granulosum and Malassezia globosa which drive the fashions predictions in direction of a youthful prediction. Lastly, to research the derived characteristic importances from TRPCA, we in contrast the characteristic importances from every mannequin in a pairwise method utilizing Pearson correlation (Fig. 5c) and plotted normalized characteristic importances between TRPCA and RF for visualization (Fig. 5b, Fig. S22). TRPCA derived options present robust settlement with SVR, KNN, GBR, and RF fashions; nevertheless, TRPCA, SVR, KNN, GBR, and RF derived options demonstrated important divergence from the NN predictions, with the NN persistently underperforming for evaluations.
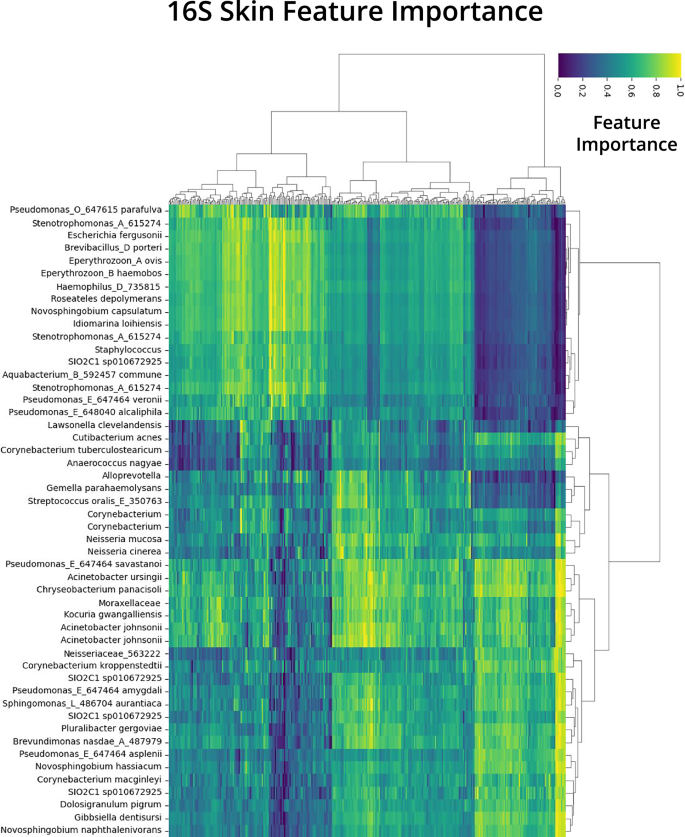
The characteristic importances are derived from the dot product of the PCA and SHAP matrices with rows as samples and columns as assigned taxonomy from influential ASVs. Redundant taxonomy values are indicative of AVSs which map to the identical taxonomy classification. Clustering of columns point out influential taxa groupings for age prediction, whereas clustering of rows spotlight people with related important options.
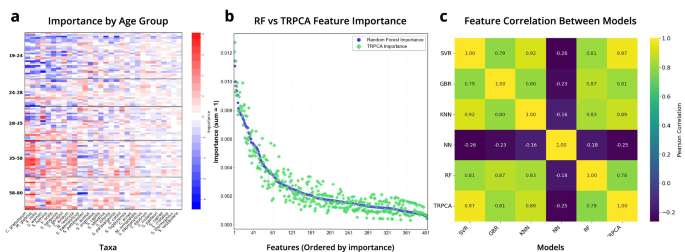
a Sample stage characteristic importances for WGS Skin microbiome samples. Features coloured in blue point out a characteristic that influences the prediction of that pattern to be youthful, whereas crimson is indicative of a characteristic that drives the prediction to be older. b Feature stage comparability of characteristic importances for WGS pores and skin between TRPCA and RF mannequin. c A pairwise comparability of the Pearson correlation between characteristic importances for every mannequin structure. SVR, GBR, KNN, RF, and TRPCA characteristic importances are extremely correlated for WGS Skin microbiome characteristic importances.
Paired microbiome samples exhibit consistency in age prediction error residuals
To additional discover the variations between 16S and WGS knowledge varieties, we educated TRPCA on paired 16S and WGS samples from the THDMI and FINRISK cohorts used for impact dimension comparisons in Greengenes2, the place every topic has a corresponding 16S pattern for every WGS pattern30. Models have been educated utilizing the default parameters and ten-fold cross-validation (Fig. 6). Age prediction for WGS confirmed a MAE of 8.68 years, in comparison with a MAE of 9.85 for 16S (WGS samples for this evaluation have been processed utilizing strategies described in Greengenes2, slightly than the curatedMetagenomicData pipeline). Although the host age MAEs differed considerably, we investigated the correlation between the prediction error residuals for every pattern. In line with prior impact dimension consistency reported with 16S and WGS knowledge, we report a excessive diploma of correlation within the age residuals from 16S and WGS prediction (R2 = 0.63)30. To decide whether or not samples from completely different physique websites from the identical topic exhibited the same sample, we chosen WGS samples from curatedMetagenomicData the place people had each intestine and oral microbiome samples. The ensuing dataset had 242 topics, with one pattern per physique web site. We ran TRPCA with default parameters on the dataset with a Cross validation(CV) = 10, stratifying the information splits by examine. The ensuing regressions confirmed no important distinction for age prediction between the oral (MAE = 9.11) and intestine samples (MAE = 9.5) for the 242 topics (Fig. 6). As for the age residuals, we discovered a reasonable correlation between the age prediction residuals for paired WGS oral and WGS stool samples (R2 = 0.34).
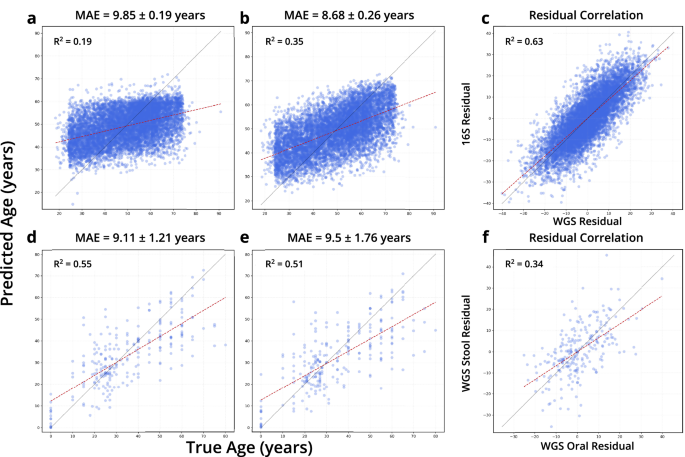
a TRPCA predictions for 16S stool samples from the THDMI and FINRISK cohorts. b TRPCA predictions for WGS stool samples from the THDMI and FINRISK cohorts. c The correlation between prediction errors in paired 16S and WGS stool microbiome samples (R2 = 0.632). d TRPCA predictions for WGS oral microbiome samples from curatedMetagenomicData. e TRPCA predictions for WGS stool microbiome samples from curatedMetagenomicData. f The correlation between prediction errors in paired WGS oral and WGS stool microbiome samples (R2 = 0.339). The error in mannequin prediction for paired samples (WGS Stool/16S Stool and WGS Stool/WGS oral) implies host related attributes could also be related to residual error.
Skin microbiome
TRPCA was in a position to establish a number of key bacterial species which have already been proven to be related to pores and skin well being, illness, and growing old31, together with Corynebacterium, Lactobacillus, Cutibacterium acnes, and Staphylococcus. Corynebacterium simulans has been proven to be extra plentiful in grownup pores and skin than childhood pores and skin, indicating a hyperlink with sebum secretion and a possible position within the growing old course of32. Lactobacillus, recognized as a characteristic related to youthful people, has been linked to pores and skin well being by means of antimicrobial exercise in opposition to pores and skin pathogens, highlighting their potential position in sustaining pores and skin well being and lowering pores and skin irritation32,33,34. Cutibacterium can also be essential for pores and skin well being, exhibiting correlations with chronological growing old and indicators of growing old18. Specifically, Cutibacterium acnes is a dominant bacterium on human sebaceous pores and skin, and specific clades are generally related to zits vulgaris35. Cutibacterium is most dominant throughout puberty on sebaceous pores and skin websites (together with face, scalp, higher again), and reduces in abundance as sebum secretions lower with older age36. Its larger abundance in youthful people makes it a well known marker for host age37,38. However, its over-proliferation has been implicated in contributing to zits, and particular strains of Cutibacterium acnes dominate the pores and skin microbiome of grownup zits sufferers, indicating that its involvement in pores and skin situations could complicate the age sign38,39. Cutibacterium acnes metabolic merchandise, equivalent to quick chain fatty acids, act on the dermis to advertise lipid synthesis and enhance barrier operate40. With TRPCA, we discovered that Cutibacterium has a unfavorable correlation with age from 18 years onwards, suggesting that the age sign is dominant over zits indicators within the normal inhabitants (Figs. S20 and S21). On the opposite hand, Staphylococcus epidermidis, one other prevalent pores and skin microbe contributing to pores and skin well being and infections, confirmed a optimistic correlation with age (Figs. S20 and S21). Staphylococcus epidermidis permits Cutibacterium acnes to type biofilms below sure situations41. Staphylococcus aureus, a serious human pathogen, in addition to Staphylococcus epidermidis, a commensal, have essential roles in pores and skin ailments whereas coagulase unfavorable Staphylococci, equivalent to Staphylococcus hominis, shield the pores and skin42,43,44. S. epidermidis has a optimistic correlation with age as of 18 years previous and up (Figs. S20 and S21).
Oral microbiome
Key bacterial taxa for TPRCA age prediction for oral microbiome samples equivalent to Actinomyces, Fusobacterium, Neisseria, Veillonella, Rothia mucilaginosa, and Prevotella have been beforehand recognized for his or her significance within the oral microbiome and its relationship with growing old. Actinomyces is a prevalent genus within the oral cavity related to oral well being45. Fusobacterium has been linked to varied oral well being and systemic well being situations together with periodontitis, acute pancreatitis and most cancers, and Fusobacterium abundance could enhance with age and impression oral well being outcomes46,47. Neisseria is related to the wholesome core microbiome of the human oral cavity and performs a job in sustaining oral well being, and sufferers with extra Neisseria have improved affected person outcomes within the context of adenoid cystic carcinoma and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma48,49.Veillonella and Rothia mucilaginosa could affect oral well being outcomes, growing old, and blood strain, by modulating nitric oxide bioavailability, with Veillonella showing as a genus to lower in abundance with age in our evaluation50. Prevotella species could assist preserve oral well being and be influenced by growing old, HIV standing, and nation of delivery49,51.
Gut microbiome
Among the taxa recognized by TRPCA, Akkermansia muciniphila, Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, Bacteroides, Bifidobacterium, and Roseburia have been extensively studied for his or her roles in influencing well being outcomes in growing old people. Akkermansia muciniphila, a mucin-degrading bacterium, has been related to numerous well being advantages, together with metabolic well being and anti inflammatory results. In settlement with the TRPCA characteristic significance, research have proven that Akkermansia muciniphila ranges have been elevated within the management group in comparison with people with particular well being situations, in addition to older people, indicating a possible protecting position in wholesome growing old52,53,54. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, recognized for its butyrate-producing capabilities, has been linked to intestine well being and immune modulation. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii abundance is negatively correlated with circulating branched-chain amino acids and insulin resistance, highlighting its potential metabolic implications55,56,57,58,59. As recognized by TRPCA as a prime characteristic for 16S stool samples, F. prausnitzi abundance decreases with age, suggesting implications in growing old1. Positive correlations between Bacteroides and age have been reported, suggesting a possible position within the charge of growing old60,61. Bifidobacterium ranges have been negatively related to age and illness severity, indicating its potential impression on well being outcomes62,63. Decreased ranges of Roseburia have been noticed in situations related to dysbiosis, suggesting a doable position in sustaining intestine homeostasis62,64,65.
Biological and technical insights from residual age predictions
Paired WGS microbiome samples from completely different physique websites confirmed solely a reasonable alignment in predicted growing old. Specifically, we noticed a modest correlation (R2 ≈ 0.34) between age predictions from oral versus stool WGS microbiomes. This stage of concordance doubtless displays elementary microbiome body-site variations. The oral and intestine communities are compositionally distinct, with over 90% of taxa in every habitat are distinctive and never shared with the opposite, limiting cross-site prediction settlement66. Prior research verify that microbiome growing old signatures are extremely site-specific: for instance, the pores and skin microbiome can predict age way more precisely than the intestine microbiome, doubtlessly obfuscating the correlation energy between the paired residuals20. Thus, a person’s oral and intestine microbiotas could every observe elements of host growing old, however variations in native setting, weight loss plan, and host elements at every web site dampen the correlation. Nonetheless, the reasonable correlation underscores that chronological age imprints on every body-site microbiome in a definite method, consistent with intensive proof that the microbiome is compartmentalized66.
In distinction, we discovered a a lot stronger residual correlation (R2 ≈ 0.63) between 16S rRNA gene versus WGS age predictions for the paired stool samples. This excessive correspondence signifies that when one sequencing modality’s mannequin over- or under-predicted an individual’s age, the opposite tended to point out the same residual. Several elements could clarify this alignment of residuals. First, it might replicate shared organic indicators captured by each strategies: the people who’re exhausting to foretell (or biologically uncommon for his or her age) through 16S are likewise outliers through WGS. In different phrases, method-independent growing old options drive the prediction errors in each instances. This is a promising situation, suggesting our fashions are detecting actual host-microbiome age relationships slightly than random noise. Alternatively, systematic biases in pattern processing or topic choice would possibly affect each 16S and WGS equally. For occasion, if sure subpopulations trigger microbiome age to deviate from chronological age, each sequencing strategies might establish these deviations. We additionally take into account the position of taxonomic decision with shotgun sequencing offering finer species stage element absent in 16S profiling. In principle this could enhance accuracy, and certainly shotgun fashions usually modestly outperform 16S67. However, the excessive residual correlation implies that, though the age prediction accuracy with WGS knowledge was decrease resulting from improved species decision, the related deviation in mannequin prediction stays constant, posing the age prediction residual as a reproducible measure. Such method-independent settlement helps the concept that the residuals replicate true organic variation in growing old tempo, versus method-specific artifacts. In abstract, whereas completely different sequencing applied sciences have inherent biases, the convergence of their age predictions in our examine suggests we now have recognized strong growing old signatures within the intestine microbiome that transcend technical platforms. This is encouraging for future efforts to develop microbiome-based age biomarkers, because it signifies an individual’s microbiome age is just not merely an artifact of the sequencing technique however slightly grounded in organic indicators.
Our evaluation of mannequin characteristic significance by age group revealed that sure microbial options disproportionately influenced mannequin predictions, notably in people aged 28–35 for WGS pores and skin knowledge (Fig. 5a). In this youthful grownup cohort, the mannequin tended to foretell decrease ages as a operate of a characteristic’s abundance. SHAP values highlighted two organisms particularly, Cutibacterium granulosum and Malassezia globosa, as drivers of skewed age estimates. By analyzing SHAP values, we recognized concrete microbial candidates which will function sentinels of accelerated or decelerated microbiome growing old in a person based mostly on the affect of the characteristic to drive mannequin prediction towards youthful or older ages.
Beyond these two taxa, our fashions recognized a broader panel of age-associated microbes throughout pores and skin, intestine, and oral websites, every with potential impacts on host well being. For occasion, a relative abundance of sure oral anaerobes (e.g., Fusobacterium) emerged as markers of an older oral microbiome in our fashions, according to literature exhibiting periodontal micro organism enhance with age in some people6. These organisms are well-known contributors to gum illness, which tends to worsen with age and may have systemic inflammatory results. Their prominence in age-prediction fashions means that oral well being standing is mirrored within the microbiome age sign. Likewise, within the intestine we famous that mannequin coefficients and SHAP values usually flagged depletion of helpful genera (e.g., Faecalibacterium) and enrichment of pro-inflammatory taxa (e.g., Escherichia/Shigella) in people predicted to be older than their years. The skill to foretell host age from microbiome knowledge carries a number of translational implications. In the realm of preventive and personalised drugs, a microbiome age mannequin might be developed right into a organic age indicator alongside different clocks (epigenetic, proteomic, and so on.). There are additionally clear alternatives within the skincare and beauty trade. The pores and skin microbiome was a powerful element of our fashions, and prior work reveals it to be a dependable mirror of chronological age18,20. Probiotic supplementation is one other path as our findings establish particular taxa (Faecalibacterium within the intestine, or Veillonella within the oral cavity) that decline with age6. Restoring fiber-degrading, butyrate-producing micro organism in an aged intestine microbiome won’t solely make the microbiome profile youthful but additionally confer advantages like improved colonic well being, diminished irritation, and higher metabolic regulation68.
Our microbiome growing old fashions display efficiency on par with, or exceeding, beforehand revealed microbial growing old clocks. For instance, Galkin et al. (2020) reported a deep studying mannequin for intestine microbiome age prediction with a MAE of ~5.9 years on an unbiased take a look at set7. The discovering on this examine is critical, because the mannequin carried out nicely on knowledge that was uncharacteristic and out of the coaching distribution, in addition to on topics that have been donors with sort 1 diabetes; nevertheless, as neural networks are steady operate approximators, well-regularized fashions can generalize on unseen knowledge. It also needs to be famous that the MAE metric of 5.9 years is predicated on a dataset with a number of samples from a given particular person, and with a median age task error of 9.27 years. To give context for our WGS stool evaluation, a median age task would yield a median error of twenty-two.45 years; nevertheless, given variations in cohort dimension and composition, our WGS stool age predictions accuracies are according to the literature. As seen in different age prediction modeling, easier fashions (e.g., RF) in prior research usually plateau at 7–10 years MAE for intestine microbiomes7. With TRPCA, the deep residual community outperformed such baselines for our datasets, lowering prediction error by a big margin. It is value noting that microbiome clock efficiency varies by knowledge sort: 16S profiles sometimes yield decrease accuracy than shotgun metagenomes, resulting from restricted taxonomic decision and the dearth of fungal indicators67. Consistent with this, our shotgun-based fashions outperformed 16S-based ones (as mirrored in decrease MAEs and better R2).
From a statistical standpoint, we took measures to make sure the rigor of our efficiency estimates. We used hold-out validation and cross-validation to substantiate that our MAE enhancements weren’t overfitting. Additionally, mannequin comparisons have been made to focus on efficiency enhancements for the assorted age prediction duties. TRPCA considerably outperformed all fashions for five out of 15 complete regression duties, with the KNN, SVR, and RF incessantly acting on par with TRPCA (Fig. S23). Still, we acknowledge that absolutely the R2 values are modest, particularly for 16S stool samples (Figs. 2c, 6a); nevertheless, these findings are constant throughout mannequin structure and two unbiased datasets, implying that 16S sequencing strategies present don’t resolve the human microbiome sufficient for growing old research. While TRPCA confirmed important numerical enhancements throughout datasets (Fig. S23) with a 28% MAE discount for pores and skin WGS knowledge (from 11.14 ± 2.65 to eight.03 ± 4.10), we acknowledge that overlapping uncertainty intervals in some instances point out variable statistical significance of those enhancements. These efficiency positive factors, although significant for computational modeling, doubtless supply restricted extra scientific relevance in comparison with standard ML approaches given our concentrate on chronological age in wholesome people, slightly than organic age between wholesome and unhealthy cohorts. Nevertheless, the constant efficiency sample throughout physique websites and sequencing strategies reinforces TRPCA’s worth as a methodological development for microbiome-based age prediction analysis. Our sensitivity evaluation of prediction residuals additional validates the robustness of those findings. For many demographic variables, together with intercourse and weight loss plan sort, we noticed no important results on age prediction residuals throughout most physique websites and sequencing strategies, suggesting our fashions are usually unbiased towards these elements. However, important associations between residuals and sure variables have been detected, notably study-specific results in 16S pores and skin and oral samples and Body Mass Index(BMI) results in WGS samples (Fig. S24, Supplemental Data 1–2). These findings spotlight potential methodological confounders and physiological elements that would affect microbiome-based age predictions. A notable limitation is the unfinished metadata throughout datasets, with variables like non-Westernized standing, weight loss plan, and BMI class incessantly lacking, stopping complete evaluation of all potential confounding elements throughout all physique websites and sequencing strategies. This metadata sparsity underscores the necessity for extra full demographic and life-style info in future microbiome growing old research to disentangle technical and organic influences on prediction accuracy. Given the outcomes of the evaluation, TRPCA is a promising instrument for exploring the microbiome organic clock and has supplied a considerable baseline for wholesome growing old. The evaluation additionally highlights suggestions for strategies and physique websites which greatest assist the investigation of the speed of growing old.
Our examine demonstrates that TRPCA considerably improves age prediction accuracy from microbiome profiles throughout numerous physique websites and sequencing strategies. We noticed substantial reductions in MAE for age prediction, with enhancements of 14% for pores and skin (16S) and 28% for pores and skin (WGS) in comparison with the most effective performing standard ML strategies (KNN for 16S and WGS pores and skin samples, Table 1). These findings underscore the potential of transformer-based approaches in capturing complicated patterns inside microbiome knowledge. The MTL strategy of TRPCA additional enhanced efficiency in simultaneous age prediction and delivery nation classification duties, attaining a 6% discount in MAE for age prediction and a 13% enhance in accuracy for nation classification. These outcomes display the flexibility of TRPCA in dealing with a number of associated duties effectively.
Our built-in TRPCA and SHAP evaluation revealed distinct age-related microbial signatures throughout physique websites. In the pores and skin, Corynebacterium simulans is extra plentiful in older people, whereas Lactobacillus species and Cutibacterium acnes are prevalent in youthful pores and skin, with Staphylococcus epidermidis rising with age. In the oral cavity, youthful people sometimes exhibit larger ranges of Actinomyces, whereas Fusobacterium is enriched with age and Veillonella tends to lower. For the intestine, helpful taxa equivalent to Akkermansia muciniphila and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii are frequent in youthful people; conversely, Bacteroides enhance with chronological growing old, and Bifidobacterium present diminished ranges in older populations.
In conclusion, TRPCA represents an development in microbiome knowledge evaluation, providing improved accuracy in age prediction and helpful insights into age-associated microbial options. This strategy paves the way in which for a extra nuanced understanding of the connection between the microbiome and chronological growing old, doubtlessly informing future interventions aimed toward selling wholesome growing old by means of microbiome modulation and the exploration of organic age from a microbiome perspective. Our findings assist the appliance of transformer-based strategies in microbiome analysis and recommend promising avenues for the adoption of state-of-the-art mannequin architectures in microbiome evaluation.
This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its authentic location you may go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s42003-025-08590-y
and if you wish to take away this text from our web site please contact us



