This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its unique location you’ll be able to go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://theconversation.com/why-on-earth-is-the-planets-day-getting-shorter-260946
and if you wish to take away this text from our website please contact us
Earth will full a rotation 1.33 milliseconds sooner than standard on Tuesday, August 5. That makes it one of many shortest days of 2025 at 86,399.99867 seconds lengthy. How that occurs, and the way we will even measure it with such precision, may make your head spin quicker too.
On common, Earth bodily rotates in 23 hours, 56 minutes, 4 seconds and 90.5 milliseconds – that is referred to as a sidereal day. It is Earth’s “true” rotation relative to distant objects in deep area, like stars.
However, the type of day most individuals go by is 24 hours lengthy and that’s referred to as a photo voltaic day – it’s the time between two sunrises, or consecutive noons. The additional 4 minutes comes from the truth that Earth has to rotate 1 extra diploma, to 361 levels, for the Sun to seem in the identical place once more.
Both sorts of day are barely shorter on August 5 2025, largely due to what’s taking place with winds in Earth’s ambiance, fluid circulation within the ocean and magma – and even the Moon’s gravitational pull.
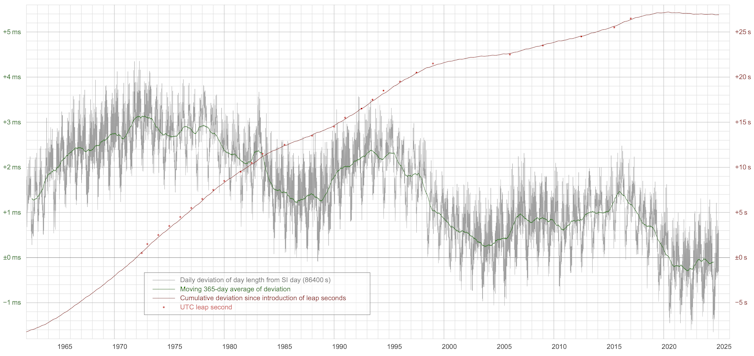
Deviations from 24 hours have been precisely measured because the Nineteen Seventies utilizing atomic clocks and astronomy. Over the course of a 12 months, these adjustments construct up: in 1973, for instance, the sum of deviations added as much as +1,106 milliseconds, that means that the Earth lagged behind in its rotation by simply over a second. Leap seconds had been launched in the identical 12 months to right for this, with one second added to the clock on the finish of the day – 23:59:60.
Absurd ranges of accuracy are wanted in time-keeping. Global positioning techniques (extra generally referred to as GPS) can pinpoint the place you’re in area, that’s no drawback. But if the planetary floor you’re on has bodily spun barely quicker or slower than anticipated that day, an uncorrected GPS received’t know that, and your place received’t match along with your map.
A 1.33 millisecond deviation interprets to a place error of about 62 cm on the equator, so 1973’s cumulative drift would have precipitated GPS errors of round half a kilometre if left uncorrected over the 12 months.
Why doesn’t the Earth keep nonetheless?
To learn the way quick the Earth is spinning in any respect, you have to discover a reference body by which, ideally, nothing is transferring. Everything in area strikes relative to every little thing else, however the farther we glance, the extra nonetheless issues appear; simply as distant hills seem to maneuver slower when you’re on a practice, and close by farms rush by.
Luckily, there are objects so magnificently vibrant that they outshine whole galaxies. These are quasars, and they’re seen throughout the universe from billions of sunshine years away.
Quasars are supermassive blackholes as much as billions of occasions the mass of our Sun, which emit between 100 and 10,000 occasions extra mild than our whole galaxy, the Milky Way. Quasars are detectable from billions of sunshine years throughout the universe, the place issues are basically stationary, in order that they act as cosmic beacons.
Radio telescopes measure our place relative to those, yielding values of Earth’s true rotation interval to sub-millisecond accuracy.

NOIRLab/NSF/AURA/J. da Silva
Those extremely‑exact observations are additionally the start line for computer models which embody actions of the ambiance, oceans, celestial motions and extra to foretell the size of day. This is how we all know, prematurely, when a day is shorter, and right GPS consequently.
Winds in Earth’s ambiance are the most important affect on the size of every day because of their collisions with the land floor, significantly once they hit mountain ranges. Incredible as it might sound, wind really slows the spin of the Earth this manner.
Earth’s prevailing winds are quickest within the northern hemisphere winter, however slowest from June to August, so the summer time months all the time carry the shortest days of the 12 months (despite the fact that we are inclined to say these are the “longest” days within the northern hemisphere, due to their higher daylight period).
These each day and seasonal adjustments are simply brief‑lived blips atop broader slowdowns. Over many years, the melting of the polar ice caps has been slowing the Earth’s rotation. To perceive why, think about a spinning ballerina retracting their outstretched arms – they start to spin a lot quicker. A spinning ball, like Earth, is not any completely different.
Earth is oblate, that means the floor on the equator is 21.5 km farther from the centre of the planet than the floor on the poles. As local weather change melts the polar ice caps, meltwater strikes from the poles to the equator through the ocean. Rising sea ranges imply water is farther from the floor, and identical to the ballerina transferring their arms again out, it aids Earth’s slowdown. Redistribution of Earth’s mass adjustments our rotation in related methods, together with by earthquakes.
Ⅱ Ⅶ Ⅻ/International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service
The Moon, whereas lovely, generally is a enormous drag over billions of years. Earth’s oceans are raised by the Moon’s gravity, however because the Earth rotates, the raised oceans are carried barely forward of the Moon in its orbit. But the Moon continues pulling on these oceans, dragging them backwards in opposition to the Earth’s anticlockwise rotation, which slows us down.
Earth’s rotational vitality isn’t misplaced, it’s transferred to the Moon, which positive aspects orbital pace and causes it to flee Earth’s gravity a bit higher – because of this it’s moving away from us at 3.8 cm a year. Our size of day has elevated from 17 hours 2.5 billion years in the past largely because of the Moon sapping Earth’s angular momentum over the eons.
Earth’s rotation has slowed yearly from 1973 to 2020 (the place exact measurements exist), with annually accumulating hundreds of milliseconds of lag, which has already been accounted for by including 27 leap seconds. Things modified from 2020 – the Earth began spinning quicker as a substitute of slower yearly, most likely the results of angular momentum exchange between the Earth’s core and mantle, however modulated by the quite a few different motions we’ve explored.
July 5, July 22 and August 5 had been singled out as a few of this 12 months’s quickest days far prematurely, as a result of on high of the Earth’s inner motions and seasonal quirks in atmospheric winds, the Moon’s place in orbit additionally slows the Earth twice per orbit (each two weeks). This is as a result of when the Moon is immediately above the equator, all of its tidal drag acts east to west, however on these dates, it’s positioned farthest north and south, weakening that impact.
You received’t discover the dawn arrive 1.33 milliseconds sooner, however to precision atomic clocks, quasar‐referenced astronomical measurements, it is going to be apparent.
This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its unique location you’ll be able to go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://theconversation.com/why-on-earth-is-the-planets-day-getting-shorter-260946
and if you wish to take away this text from our website please contact us



