This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its authentic location you’ll be able to go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://www.mccormick.northwestern.edu/news/articles/2025/08/a-scalable-probabilistic-computer/
and if you wish to take away this text from our web site please contact us
“By proposing a scalable path for the implementation of PIMs using digital transistor-based technology and further enhancing it by the physics of magnetic devices, we believe that this work brings PIMs much closer to adoption for real-world computing problems,” stated Khalili, AT&T Research Professor and professor {of electrical} and laptop engineering on the McCormick School of Engineering. “This can impact many industries and applications where hard optimization problems are frequently encountered.”
Importantly, in contrast to another rising approaches to computing, Khalili defined that these PIMs may be manufactured utilizing transistor-based know-how that’s commercially accessible right now, they usually function at room temperature.
Athas and Duffee developed the 130nm application-specific built-in circuit (ASIC), which was fabricated in a complementary metal-oxide silicon (CMOS) know-how accessible from a semiconductor foundry.
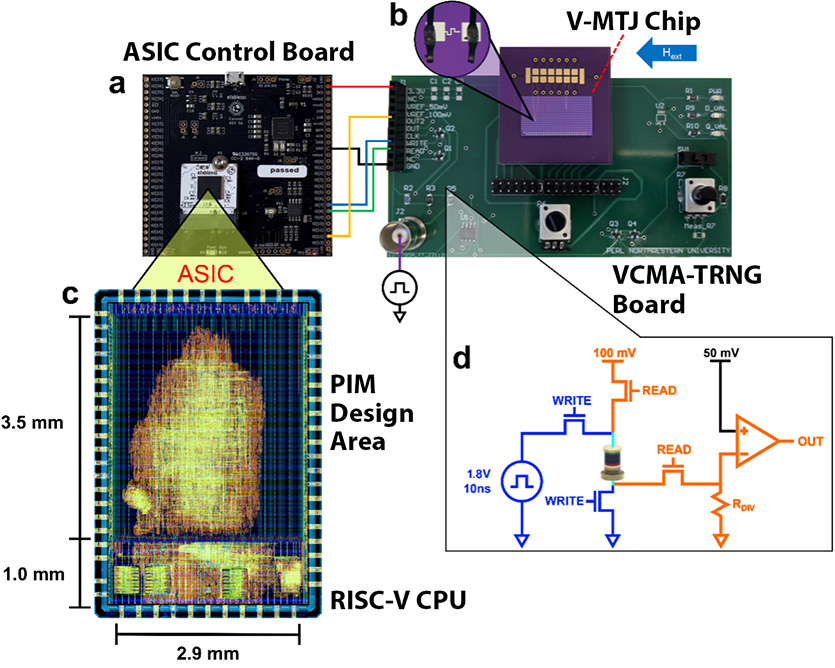
Inherent randomness, or entropy, is required for a PIM to look by way of its resolution house, so the workforce additionally designed a real random quantity generator utilizing V-MTJs addressed with an entry printed circuit board.
 “We leverage the intrinsic randomness of magnetic tunnel junctions, combined with clever circuit design, to inject high-quality randomness into our probabilistic computing hardware,” Athas stated. “Unlike pseudorandom number generators, our MTJ-based design delivers real entropy at the hardware level, which is essential for the exploration of the Ising machine’s energy landscape.”
“We leverage the intrinsic randomness of magnetic tunnel junctions, combined with clever circuit design, to inject high-quality randomness into our probabilistic computing hardware,” Athas stated. “Unlike pseudorandom number generators, our MTJ-based design delivers real entropy at the hardware level, which is essential for the exploration of the Ising machine’s energy landscape.”
MTJ-based random quantity mills are considerably smaller and extra energy-efficient than transistor-based ones, Khalili defined.
“An MTJ-based entropy source can therefore deliver similar or higher-quality entropy to the probabilistic computer using only a few transistors, where a conventional approach would require using thousands of transistors that take up a lot of chip area,” Khalili stated.
“The use of MTJs with voltage-controlled magnetic anisotropy-based random number generation enables better scalability due to an intrinsic compensation of device-to-device variation, while keeping the area occupancy smaller than full CMOS random number generation,” stated Finocchio, a professor {of electrical} engineering on the University of Messina, Italy.
As a consultant onerous optimization downside, the workforce examined the potential of the ASIC and voltage-controlled MTJ system with integer factorization issues. They additionally made estimates primarily based on simulated designs in additional superior CMOS nodes with increased transistor density that present how some large-scale issues may be mapped on future generations of the chip.
 “The infrastructure exists to scale these designs to very interesting, large-scale problems. The next step is to identify these problems, and codesign probabilistic algorithms and hardware to tackle them” stated Duffee.
“The infrastructure exists to scale these designs to very interesting, large-scale problems. The next step is to identify these problems, and codesign probabilistic algorithms and hardware to tackle them” stated Duffee.
“Probabilistic computers are being explored today using many different strategies,” stated Çamsarı, an affiliate professor {of electrical} and laptop engineering on the University of California, Santa Barbara. “In this work, the team achieved two exciting milestones: first, we showed that using voltage to control magnetism can produce highly efficient probabilistic bits. Second, we demonstrated that a carefully synchronized architecture —where all bits update together like dancers moving in lockstep — can match the performance of conventional designs where each bit updates independently and unpredictably.”
Building on this preliminary demonstration, the analysis workforce is engaged on an improved design utilizing a course of know-how with increased transistor density, enabling the computation of bigger issues. They are additionally engaged on algorithmic enhancements and designs focusing on issues aside from factorization, which can have extra real-world business significance.
This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its authentic location you’ll be able to go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://www.mccormick.northwestern.edu/news/articles/2025/08/a-scalable-probabilistic-computer/
and if you wish to take away this text from our web site please contact us