This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its unique location you possibly can go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://www.news-medical.net/health/Alzheimere28099s-Disease-and-Oral-Health.aspx
and if you wish to take away this text from our web site please contact us
Introduction
Oral Health and Systemic Inflammation
Pathways Linking Periodontal Pathogens to Neurodegeneration
Evidence from Research Studies
Implications for Prevention and Management
Challenges and Knowledge Gaps
Future Directions
Conclusions
Related video
References
Further reading
This article explores how continual periodontitis could contribute to Alzheimer’s illness by means of systemic irritation, oral pathogens, and neurodegenerative mechanisms. It highlights prevention, therapeutic methods, and analysis instructions linking oral well being with mind ageing.
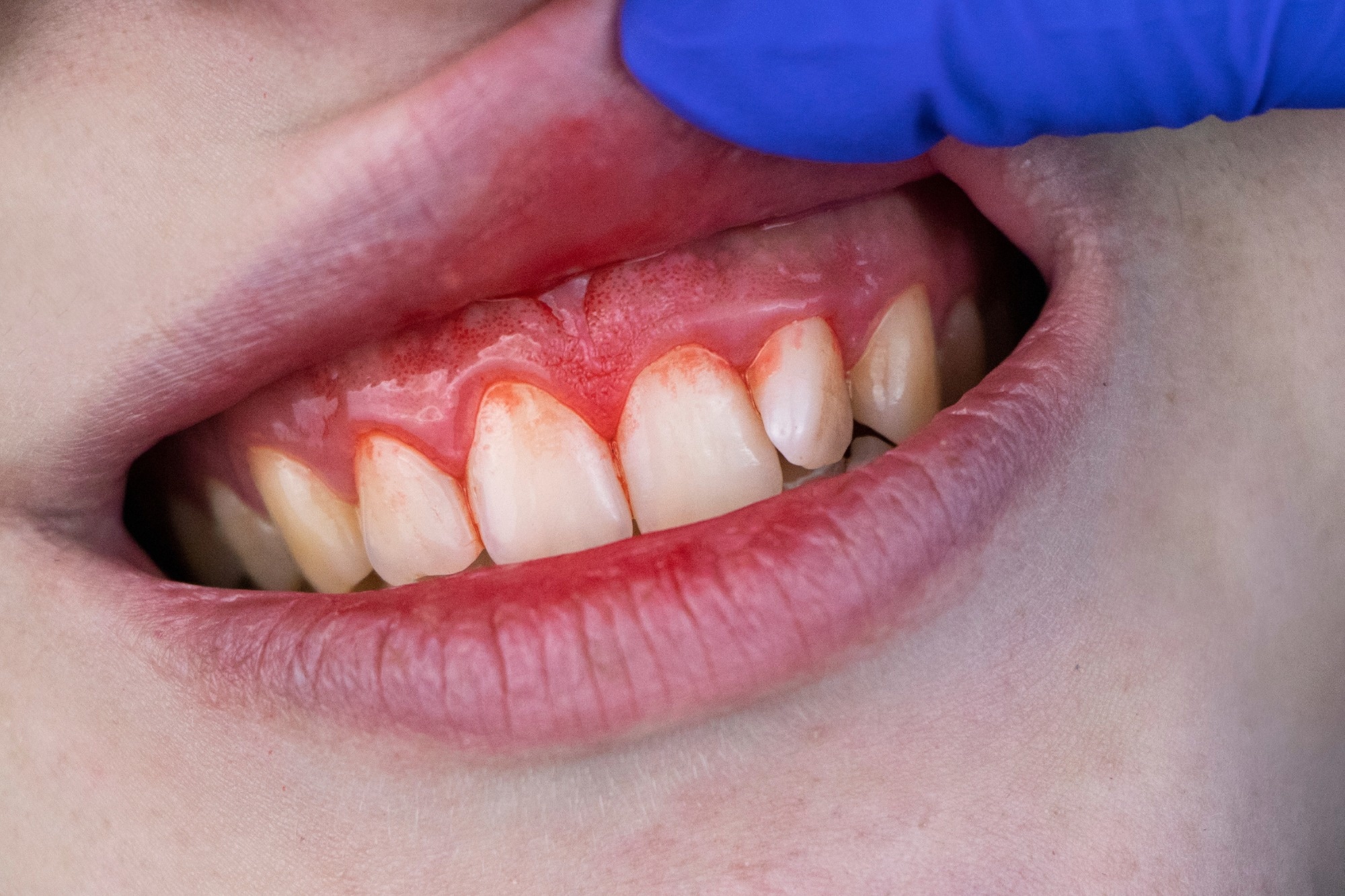 Periodontitis is usually generally known as ‘Gum Disease’ and is a quite common situation during which the gums and deeper periodontal buildings turn out to be infected. Image Credit: design_cam / Shutterstock
Periodontitis is usually generally known as ‘Gum Disease’ and is a quite common situation during which the gums and deeper periodontal buildings turn out to be infected. Image Credit: design_cam / Shutterstock
Introduction
Oral well being is more and more linked to systemic illness and mind ageing. Periodontitis (a continual inflammatory destruction of tooth-supporting tissues) raises systemic inflammatory load by means of dysbiotic biofilms and host responses. Alzheimer’s illness (AD) is characterised by progressive cognitive decline with neuroinflammation, amyloid plaques, and neurofibrillary tangles.
Converging scientific, epidemiological, and experimental work means that periodontal infections could amplify Alzheimer’s threat by means of systemic cytokines, microglial activation, and the potential translocation of oral pathogens, reminiscent of Porphyromonas gingivalis, into the mind. The detection of periodontal micro organism and their merchandise in Alzheimer’s cohorts underscores the organic plausibility. Recent narrative and mechanistic critiques point out that periodontitis is related to a heightened threat of cognitive decline and dementia, with some experiences approaching a ~2-fold elevation in AD threat.1,2,3,6
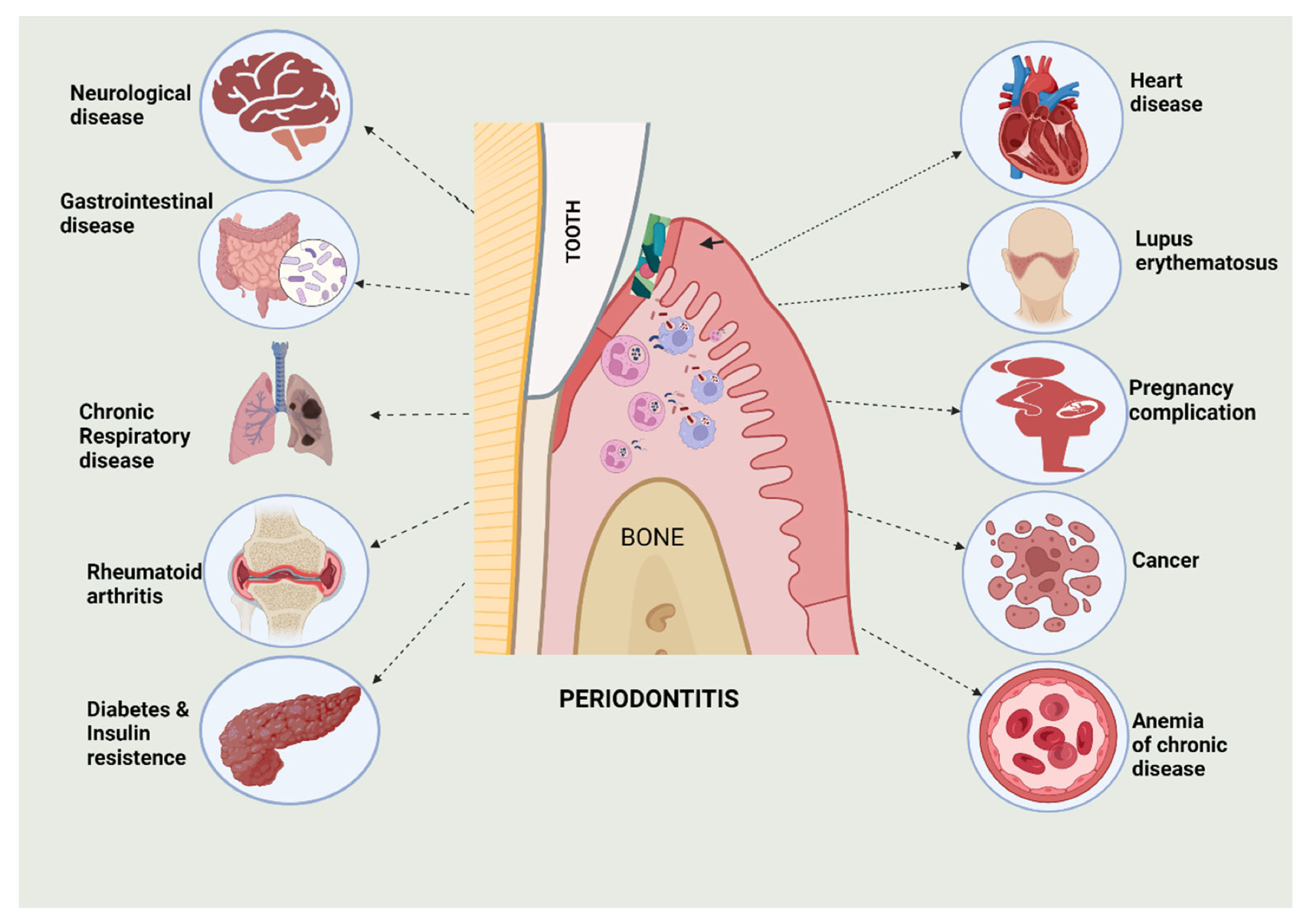
Representation of numerous systemic ailments and their relationship with periodontitis.2
Oral Health and Systemic Inflammation
Periodontitis begins as a dysbiotic plaque biofilm. Persistent plaque triggers continual irritation, deepening sulci into periodontal pockets that harbor anaerobes. Keystone pathogens reminiscent of Porphyromonas gingivalis, Tannerella forsythia, and Treponema denticola launch lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and proteases that elevate interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), IL-6, and tumor necrosis issue alpha (TNF-α).3,4
These mediators activate the receptor activator of nuclear issue kappa-B (NF-κB) (RANK) ligand-osteoprotegerin (OPG) axis and promote connective-tissue and alveolar-bone loss. Bacteria and toxins enter the blood (transient bacteremia), invade the endothelium, and disseminate, amplifying neuroinflammation related to AD. Elevated systemic biomarkers reminiscent of alkaline phosphatase (ALP) have been reported to strengthen the affiliation between extreme periodontitis and decrease cognitive efficiency.2,5
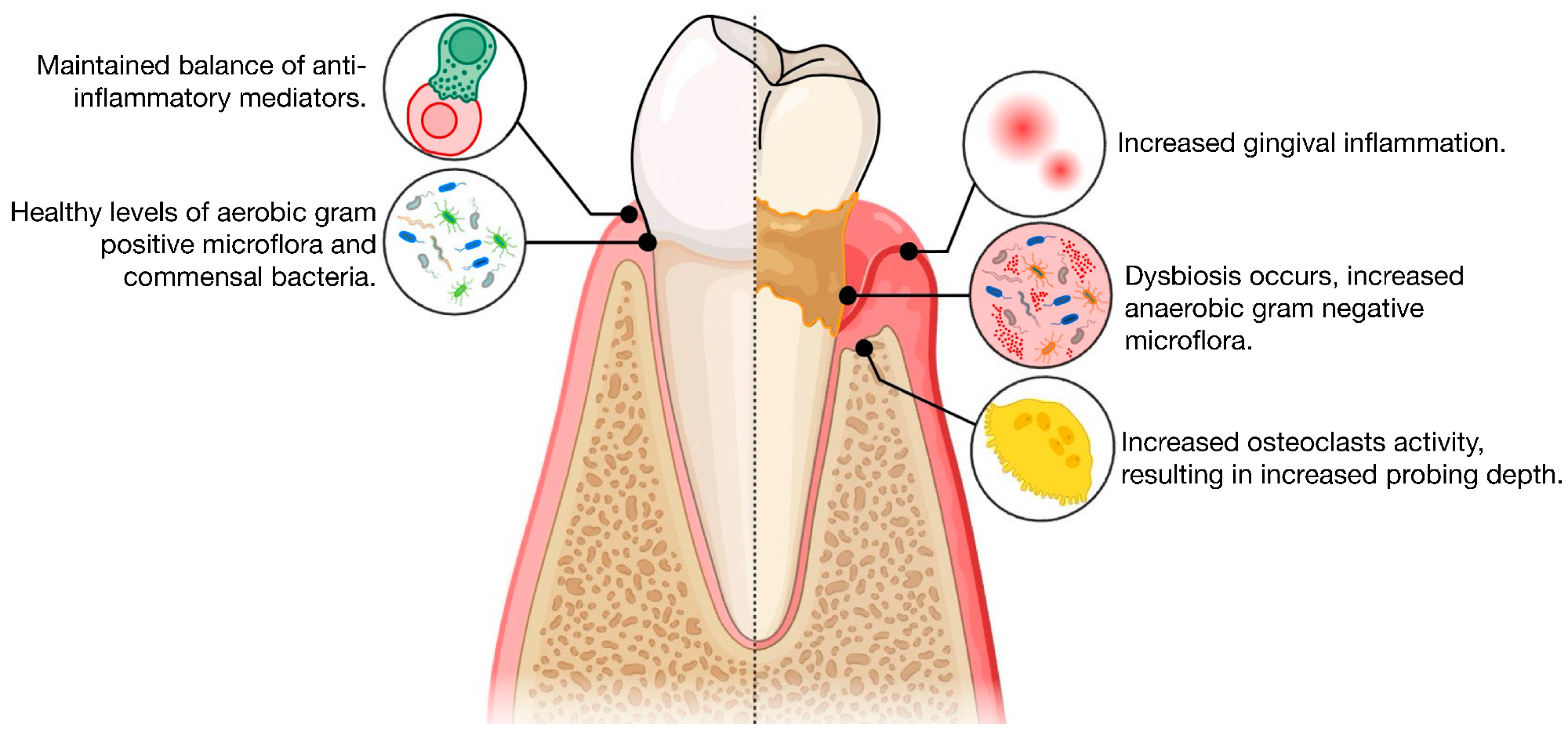
Illustration of the pathogenesis of periodontitis, evaluating well being with periodontitis.
Pathways Linking Periodontal Pathogens to Neurodegeneration
Periodontal pathogens can entry the mind immediately by breaching the blood–mind barrier (BBB) or touring alongside cranial nerves. Virulence components (e.g., gingipains) and outer membrane vesicles from P. gingivalis can have an effect on BBB integrity and activate meningeal and parenchymal immune cells, with potential unfold by way of trigeminal pathways.3,4
Indirectly, continual systemic irritation primes resident immune cells. LPS prompts Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 (TLR2/4), driving NF-κB and sign transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) signaling. These cascades assemble NLRP3 inflammasomes and complement element 1q (C1q), elevating IL-1β and TNF-α.3,4
These inflammatory alerts intersect AD biology: LPS and gingipains promote amyloid-beta (Aβ) accumulation, whereas outer membrane vesicles and gingipains improve tau phosphorylation by means of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK-3β). Spirochetes reminiscent of Treponema denticola and LPS from red-complex micro organism have been linked to tau hyperphosphorylation and neuronal apoptosis in experimental methods.3,4
Evidence from Research Studies
Converging proof hyperlinks continual periodontitis to AD. Large epidemiological cohorts report larger dementia and AD incidence in individuals with periodontitis, even after accounting for life-style components. Population research and critiques recommend elevated AD threat amongst people with periodontitis and decrease cognitive scores in these with extreme illness.1,5,6
Experimental work demonstrates organic plausibility: oral an infection with Porphyromonas gingivalis accelerates Aβ42 manufacturing, triggers neuroinflammation, and causes hippocampal neurotoxicity in animal fashions. Gingipain inhibitors directed at Kgp/Rgp have been proven preclinically to cut back mind bacterial load, inflammatory responses, and Aβ42 ranges, with neuroprotective results.3,4
Additional periodontal species (e.g., Fusobacterium nucleatum) and endotoxin challenges additional amplify neuroinflammation and Aβ accumulation, supporting a mouth-to-brain inflammatory axis.3,4
Clinical and neuropathological findings complement these knowledge. Autopsy research have detected microbial signatures in AD brains, together with Porphyromonas gingivalis. Gingipains, cysteine proteases central to P. gingivalis pathogenicity, have been recognized in AD mind tissue.3,4,6
Taken collectively, population-level associations, mechanistic animal research, and scientific detection of periodontal pathogens in autopsy AD tissue triangulate on a coherent mannequin: continual periodontal an infection could contribute to AD pathogenesis. Nonetheless, observational designs, variability in periodontal and cognitive case definitions, and residual confounding imply causality stays beneath lively investigation.1,6
Implications for Prevention and Management
Prioritizing lifelong oral hygiene is a low-cost, high-yield technique for mind well being. Twice-daily brushing with fluoride, each day interdental cleansing, tobacco cessation, and biannual skilled cleanings assist restrict periodontal irritation all through the lifespan.
For sufferers with established periodontitis, early, focused periodontal remedy, together with scaling and root planing, risk-based upkeep each 3–4 months, and short-course adjuncts when indicated, reduces each native and systemic inflammatory masses. Adjunctive methods beneath exploration embrace probiotics, oral microbiota alternative, and host-targeted anti-inflammatory approaches.7
Primary care and neurology clinics ought to combine oral well being screening into midlife and late-life prevention visits. Ask about bleeding gums or tooth mobility, examine for tooth loss, and refer for a complete periodontal examination. Including dental standing and inflammatory markers in threat stratification builds shared care pathways between dentists, geriatricians, and reminiscence clinics. In cohorts with extreme periodontitis, consideration to systemic inflammatory markers (e.g., ALP) could assist establish people at greater threat.5
For people residing with dementia, simplify hygiene practices (reminiscent of utilizing an electrical brush and high-fluoride paste, and caregiver-assisted routines), deal with lively illness promptly, and preserve frequent reminders. Preserving periodontal well being is a sensible and modifiable lever for dementia prevention.
Challenges and Knowledge Gaps
Despite rising alerts linking periodontal illness and AD, key uncertainties stay. First, most proof is observational, leaving the path of impact unresolved: does continual periodontal illness heighten neuroinflammation and speed up Aβ pathology, or does prodromal AD impair self-care, worsening oral hygiene (reverse causation)?
Second, human research fluctuate broadly. Definitions of periodontal illness, cognitive endpoints, sampling websites, and microbial assays differ. Many depend on small, clinic-based cohorts susceptible to choice bias, quick follow-up, and insufficient management of confounders reminiscent of age, diabetes, smoking, socioeconomic standing, and drugs.
Third, decisive longitudinal designs are scarce. Field priorities embrace harmonized periodontal case definitions, adjudicated AD diagnoses supported by biomarkers, serial oral-microbiome and inflammatory profiling, and pragmatic trials testing periodontal remedy throughout the AD spectrum.1,3,6
Future Directions
Future work ought to prioritize precision antimicrobials that disrupt periodontal virulence with out collapsing the commensal microbiota. Lead candidates embrace inhibitors of Porphyromonas gingivalis gingipains (lysine-specific Kgp and arginine-specific Rgp), in addition to biofilm- or quorum-sensing blockers that cut back pathogenicity and antibiotic resistance.3,7
The parallel growth of topical or regionally delivered formulations may maximize pocket-level efficacy whereas minimizing systemic publicity. Host-immune modulators (e.g., matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors and anti inflammatory brokers) are additionally being explored for his or her potential twin advantages in periodontitis and neuroinflammation.7
Progress would require interdisciplinary groups, together with dentists and periodontists to stage illness and ship care, neurologists and geriatricians to trace cognition and neuroinflammation, microbiologists and pharmacologists to optimize anti-virulence brokers, and public well being researchers to guage implementation and outcomes. Together, these instructions goal to revive oral ecological stability and cut back systemic sequelae.
Conclusions
Oral well being is a modifiable consider AD threat. Chronic periodontitis sustains systemic irritation and should allow periodontal pathogens, particularly Porphyromonas gingivalis, Treponema denticola, and Fusobacterium nucleatum, to entry the mind. Once there, they activate microglia, amplify cytokine cascades, and speed up amyloid-β and tau pathology.3,4,6
These inflammatory and infectious routes make gum care a prevention goal. Priorities embrace prevention and early intervention, reminiscent of lifelong plaque management, well timed periodontal remedy, and oral screening in midlife clinics. Further analysis ought to make clear the causal mechanisms, validate biomarkers, and take a look at focused therapies (e.g., gingipain inhibitors, probiotics, anti-virulence methods) in randomized managed trials to find out the brain-health advantages.1,3,7
What Does Gum Disease Have to Do With Alzheimer’s?
References
- Seyedmoalemi, M. A., & Saied-Moallemi, Z. (2025). Association between periodontitis and Alzheimer’s illness: A story overview. IBRO Neuroscience Reports, 18, 360–365. DOI: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2024.12.004.
- Bhuyan, R., et al. (2022). Periodontitis and Its Inflammatory Changes Linked to Various Systemic Diseases: A Review. Biomedicines, 10(10). DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10102659.
- Li, R., et al. (2024). The oral-brain axis: can periodontal pathogens set off Alzheimer’s illness? Frontiers in Microbiology, 15. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1358179.
- Cichońska, D., et al. (2024). Periodontitis and Alzheimer’s illness—a story overview. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(5). DOI: 10.3390/ijms25052612.
- Brahmbhatt, Y., et al. (2024). Association Between Severe Periodontitis and Cognitive Decline. Life, 14(12). DOI: 10.3390/life14121589.
- Barbarisi, A., et al. (2024). Periodontitis and Alzheimer’s illness: A overview. Dentistry Journal, 12(10). DOI: 10.3390/dj12100331.
- Haque, M. M., et al. (2022). Advances in novel therapeutic approaches for periodontal ailments. BMC Oral Health, 22(1). DOI: 10.1186/s12903-022-02530-6.
Further Reading
Last Updated: Sep 10, 2025
This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its unique location you possibly can go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://www.news-medical.net/health/Alzheimere28099s-Disease-and-Oral-Health.aspx
and if you wish to take away this text from our web site please contact us