This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its unique location you may go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-99536-1
and if you wish to take away this text from our website please contact us
Participants and research design
This research used information from UK Biobank, which is an ongoing potential cohort research of over half one million individuals aged 40–69 years at recruitment (5.5% response fee out of round 9,000,000 eligible people)15. The research protocol of the UK Biobank, detailed in eText 1, was authorised by the North West Multicentre Research Ethics Committee (11/NW/0382). The conduct of the current research was authorised by the Institutional Review Board of The University of Hong Kong / Hospital Authority Hong Kong West Cluster (UW 21–542). All measurements and experiments had been carried out in accordance with related tips and rules, and all individuals supplied written knowledgeable consent previous to participation15.
The current research included 291,151 people who met the next inclusion standards: (1) having self-reported as European descendants (‘white British’) with verification by principal part evaluation of genetic ancestry, (2) having constant self-reported and inferred gender data, (3) having no prevalence of cardiovascular occasions at baseline (i.e., CHD and stroke; based mostly on hospital admission, deaths registries and self-report information), and (4) having no lacking values for any predictors and PRS (eFigure 1).
Polygenic danger rating (PRS)
In the UK Biobank research, genotyping of all individuals was carried out with the UK Biobank Axiom Array and UK BiLEVE Axiom Array, with imputation to a haplotype reference panel of the Haplotype Reference Consortium mixed with UK10K16. Specifically, the calculation of weighted PRS was based mostly on 300 Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) recognized to be related to the chance of CHD, consisting of genome-wide important and non-significant SNPs uncorrelated with one another at a false discovery fee of 5% (eTable 1), as utilized in a earlier research by Ntalla et al.3 Weighted PRS for CHD danger was then derived by summing the merchandise of the variety of risk-increasing alleles at every of the loci and the corresponding impact measurement recognized from the literature2,3.
Derivation of the Lifestyle-Based Model (LBM)
The LBM was developed utilizing the next variables as predictors, based mostly on the established associations with the chance of CHD:4 age, intercourse, physique mass index (BMI), dietary consumption rating (0–3; generated based mostly on self-reported meals classes), smoking standing (present, earlier, by no means), and bodily exercise (wrist-worn wearable-device-derived Euclidean Norm Minus One; ENMO, a composite worth of three axes’ acceleration values).
Information on weight-reduction plan and smoking standing was collected by the self-reported touch-screen questionnaire. A dietary consumption rating (starting from 0 to three) was constructed based mostly on the rules from the AHA,17 following a longtime process18. Both calibrated ENMO and uncooked ENMO had been used as indicators of bodily exercise. Information on the era of dietary consumption scores and bodily exercise variables might be present in eText 2 and eText 317,18.
Pooled Cohort Equations (PCE) and Systematic COronary Risk Evaluation 2 (SCORE2)
Following the really helpful procedures,12,19 we recalibrated the PCE and SCORE2 so as to match the PCE and SCORE2 predictors to the variables of the UK Biobank database incorporating data on age, intercourse, smoking standing (sure or no), whole and high-density lipoprotein ldl cholesterol (mmol/l), blood stress (mmHg; handled with medicines or untreated), and diabetes (sure or no). We re-estimated the rescaling weights obtained from regressing the anticipated danger towards noticed danger utilizing the unique PCE printed in 2013 and SCORE2 formulation for low danger area (the United Kingdom)10. Detailed data on the definition and quantification of PCE and SCORE2 danger predictors is supplied in eTable 2.
Incidence of CHD
CHD incidence was ascertained by the linkage of UK Biobank individuals’ measured information with their hospital admission information and loss of life registry15. Codes of International Classification of Diseases (ICD) and operative procedures had been used to categorise CHD occasions (ICD-9: 410, 411,412.X, ICD-10: I21, I22, I23, I24, I25.2, OPCS: K40 – K46, K49, K50.1, K50.2, K50.4). Incident CHD was outlined as the primary commentary of CHD occasions that occurred till ninth December 2022 for people in England and Wales and nineteenth December 2022 for people in Scotland.
Statistical analyses
The full information pattern was randomly cut up into 5 sub-groups with an roughly equal variety of people allotted per group (See Fig. 1) for mannequin growth and cross-validation of LBM and LBM + PRS. To develop the LBM, we match Cox proportional hazard fashions incorporating age, intercourse, BMI, dietary consumption rating, smoking standing, and bodily exercise. Following the established methodology for PCE mannequin growth,10 interactions of age with every lifestyle-based predictor had been examined, and retained as predictors within the mannequin if the p-value was lower than 0.01; or the p-value was between 0.01 and 0.05, with a steady internet reclassification enchancment (NRI) for non-events ≥ 15% or a statistically important built-in discrimination index (IDI) within the full pattern.
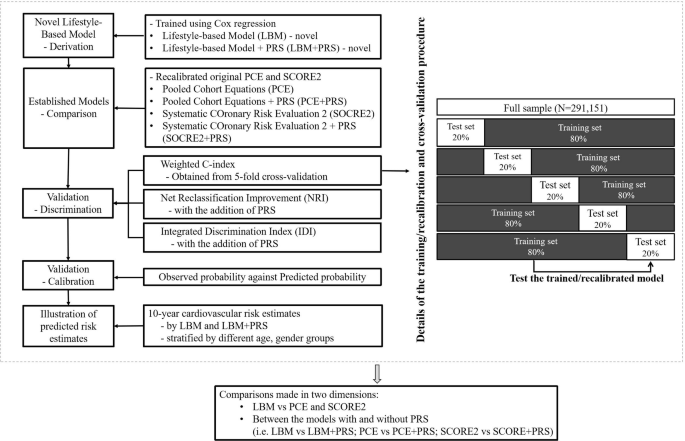
Study design, mannequin derivation, and mannequin validation course of. Notes: LBM: utilizing age, intercourse, physique mass index (BMI), dietary consumption rating, smoking standing (present, earlier, by no means), and bodily exercise (mg). LBM + PRS: including polygenic danger scores to the LBM. PCE: utilizing age, intercourse, smoking standing (sure or no), whole and high-density lipoprotein ldl cholesterol (mmol/l), handled or untreated systolic blood stress (mmHg), and diabetes (sure or no). PCE + PRS: including polygenic danger scores to the PCE. SCORE2: utilizing age, intercourse, smoking standing (sure or no), whole and high-density lipoprotein ldl cholesterol (mmol/l), systolic blood stress (mmHg), and diabetes (sure or no). SCORE2 + PRS: including polygenic danger scores to the SCORE2. Abbreviations: CHD = coronary coronary heart illness; CI = confidence interval; IDI = Integrated Discrimination Index; LBM = Lifestyle-Based Model; LBM + PRS = Lifestyle-Based Model plus polygenic danger rating; NRI = Net Reclassification Improvement; PCE = Pooled Cohort Equations; PCE + PRS = Pooled Cohort Equations plus polygenic danger rating; PRS = polygenic danger rating; SCORE2 = Systematic COronary Risk Evaluation 2; SCORE2 + PRS = Systematic COronary Risk Evaluation 2 plus polygenic danger rating.
For cross-validation of prediction fashions (LBM, PCE, SCORE2, LBM+PRS, PCE+PRS and SCORE+PRS), a complete of 5 iterations of coaching/cross-validation had been carried out, with every 20% sub-group used as a cross-validation set and the remaining 80% subset (i.e., 4 20% sub-groups) as a coaching set in every iteration20. Cox regression was match to estimate the C-index (starting from 0.5 for no discrimination to 1.0 for good discrimination, on common) together with 95% confidence interval (CI) values for every mannequin throughout the 5 iterations21 We then weighted every of the 5 C-index values relative to the corresponding variety of CHD incidence instances to acquire the weighted common C-index. A paired t-test was carried out to judge the modifications within the C-index between the prediction fashions with and with out the inclusion of the PRS.
To additional look at the added worth of PRS to the LBM and established algorithms, we evaluated the chance reclassification potential by calculating the continual NRI (calculated because the sum of “NRI+” [event NRI] and “NRI-” [non-event NRI]), categorical NRI (based on the brink of seven.5% for LBM and PCE and 10% for SCORE2), and IDI (calculated based mostly on the sum of the built-in sensitivity and built-in specificity, indicative of enhancements within the slopes of the discrimination curves) as extra parameters of discrimination22.
To look at the calibration of the LBM and established prediction fashions, calibration plots had been created by plotting the imply noticed Kaplan-Meier estimates (noticed likelihood) towards the imply predicted likelihood inside every decile of the anticipated chances from every mannequin. We additionally calculated the corresponding calibration slopes (with a “slope value = 1” indicating good calibration, on common), and Greenwood-Nam-D’Agostino (GND) P-values23.
To exhibit how incidence CHD charges fluctuate by 10-year absolute CHD danger estimates predicted by the six fashions (LBM, PCE, SCORE2, LBM + PRS, PCE+ PRS and SCORE2 + PRS), we estimated cumulative CHD incidence charges for 4 danger reclassification teams outlined based on 10-year CHD danger estimates, making use of the cut-off level of seven.5% for PCE and LBM; and 10% for SCORE2.
A complete of three units of sensitivity analyses had been carried out with particulars supplied in eText 4. Statistical analyses had been carried out utilizing Stata/MP Version 17.0 (StataCorp LP, College Station, TX) and R (Version 4.4.3).
This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its unique location you may go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-99536-1
and if you wish to take away this text from our website please contact us