This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its authentic location you may go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41526-025-00534-4
and if you wish to take away this text from our web site please contact us
Exposure to microgravity throughout prolonged house missions induces vital physiological adjustments that problem the physique’s cardiovascular system, vascular regulation, and mind operate. These adjustments, occurring throughout acute, subacute, and continual phases, have an effect on each the construction and performance of the vascular system, in addition to cerebral blood circulation and cerebrovascular regulation. The absence of gravitational forces alters fluid distribution, vascular tone, and autonomic regulation, resulting in profound variations. This assessment explores these phases of vascular and mind adjustments, highlighting the adaptive responses and their potential implications for astronaut well being, notably throughout long-duration missions.
Acute part
Acute publicity to microgravity triggers a cascade of cardiovascular adjustments primarily pushed by fluid redistribution10. With the absence of Earth’s gravitational forces, roughly two liters of blood and interstitial fluid shift from the decrease extremities to the thoracic cavity and head10. This cephalad fluid shift leads to a right away enhance in central blood quantity and central venous stress (CVP), which initially rises however then declines after a number of hours as a result of lowered intrathoracic stress11. The resultant enhance in preload briefly enhances stroke quantity by as a lot as 46%, resulting in a 22–36% enhance in cardiac output1. However, regardless of this enhance, imply arterial stress (MAP) and systolic blood stress (SBP) stay comparatively secure11. This paradox arises as a result of a compensatory discount in systemic vascular resistance (SVR) and a concomitant reflexive lower in coronary heart price, sustaining general perfusion with out extreme hypertensive responses11. The baroreceptor reflex performs a key function in stabilizing MAP by modulating each autonomic tone and vascular resistance, stopping extreme fluctuations in arterial stress12.
This fluid redistribution not solely causes transient facial edema and higher airway congestion but in addition influences autonomic regulation1. Initially, baroreceptors reply to the elevated central blood quantity with parasympathetic activation and lowered sympathetic outflow. However, with sustained publicity to microgravity, a progressive resetting happens as a result of sustained publicity to microgravity, resulting in an general discount in baroreceptor sensitivity12. This adaptation contributes to impaired autonomic operate and post-flight orthostatic intolerance upon return to Earth12.
Cardiac morphology quickly adapts to the altered hemodynamic atmosphere. Echocardiographic research reveal a extra spherical coronary heart, attributed to adjustments in myocardial stress and intracardiac stress gradients1. Additionally, left ventricular mass declines throughout the first few days, owing to lowered mechanical load on the guts in microgravity situations13. Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) stays preserved within the acute part, however the lower in myocardial workload results in early cardiac reworking, which can affect long-term cardiac reserve13. While these adjustments seem adaptive, the long-term penalties of myocardial atrophy and purposeful reserve upon re-entry stay unsure. Studies have proven that a few of these adjustments might be reversed upon return to regular gravity, however the restoration course of could fluctuate between the left and proper ventricles14. The proper ventricle, specifically, could take longer to get better or expertise extra persistent adjustments13.
Electrophysiological variations additionally emerge, with an elevated incidence of arrhythmias resembling untimely atrial and ventricular contractions, atrial fibrillation, and episodes of ventricular tachycardia15. These arrhythmias are sometimes transient and linked to autonomic nervous system variations, electrolyte imbalances, and adjustments in baroreceptor operate16. Although fluid shifts enhance sympathetic tone, cerebrovascular autoregulation stays intact, stopping main disruptions in cerebral perfusion15. Hypokalemia and hypercapnia could exacerbate electrical instability, and QT prolongation suggests an elevated susceptibility to repolarization abnormalities17. While no life-threatening arrhythmias have been recorded in wholesome astronauts, these findings increase issues for people with underlying cardiovascular situations or throughout prolonged missions.
Vascular variations in microgravity result in a uniform distribution of arterial stress throughout the physique, eliminating hydrostatic gradients18. Although MAP and SBP stay secure, diastolic blood stress (DBP) declines by roughly 5-12 mmHg throughout the first 24 hours19. This discount in DBP suggests a lower in whole peripheral resistance, doubtless as a consequence of each lowered gravitational hydrostatic stress and altered autonomic management20. Despite the preliminary enhance in central blood quantity, decrease limb blood circulation decreases considerably, accompanied by an increase in vascular resistance over the next days20. This vascular reworking consists of endothelial dysfunction, with early impairments in nitric oxide (NO)-mediated vasodilation as a result of altered shear stress and mechanical unloading21. Although sympathetic outflow will increase in response to microgravity, it doesn’t absolutely counterbalance the lack of gravitational stress, resulting in a blunted vasoconstrictive response which will contribute to post-flight orthostatic intolerance22. Reduced vascular easy muscle contraction, altered adrenergic responsiveness, and adjustments in oxidative stress pathways contribute to those purposeful adjustments, which can predispose astronauts to long-term vascular stiffness and elevated cardiovascular danger upon return to Earth20.
Blood composition adjustments considerably, with a fast enhance in central blood quantity resulting in suppression of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and activation of cardiac stretch receptors, erroneously signaling hypervolemia23. These triggers elevated diuresis and natriuresis, leading to a ten–20% discount in plasma quantity throughout the first 24–48 hours24. Hemoconcentration results in an preliminary rise in hematocrit and purple blood cell (RBC) rely, however because the physique adjusts, erythropoiesis is downregulated, inflicting a gradual decline in RBC mass, a phenomenon referred to as “space anemia”25.
Orthostatic regulation is considerably impaired after publicity to microgravity because of the absence of gravitational forces and the ensuing physiological variations. On Earth, gravitational forces induce a hydrostatic stress gradient that aids venous return when standing15. In microgravity, the absence of gravitational loading results in baroreceptor desensitization, decreasing their capacity to sense and reply to blood stress adjustments successfully26. This diminished sensitivity leads to a resetting of baroreflex operate to a decrease operational vary, weakening the reflexive cardiovascular changes wanted for standing postures on Earth26. Vagal baroreflex achieve decreases throughout spaceflight, additional impairing autonomic responses27.
Microgravity-induced fluid shifts result in a rise in central blood quantity, triggering diuresis and a subsequent 10–20% discount in plasma quantity24. This hypovolemia contributes to a discount in stroke quantity and cardiac output upon standing, additional exacerbating orthostatic intolerance28. Studies affirm that whereas muscle sympathetic nerve exercise (MSNA) will increase throughout spaceflight as a compensatory mechanism, it doesn’t absolutely translate into an satisfactory vasoconstrictive response as a result of endothelial dysfunction, altered adrenergic receptor sensitivity, and protracted vasodilation from lowered mechanical loading20,29. As a outcome, peripheral vascular resistance fails to extend proportionally, resulting in post-flight orthostatic intolerance20.
In abstract, the acute cardiovascular response to microgravity is characterised by fluid redistribution, elevated central blood quantity, lowered myocardial workload, and transient cardiac reworking. The paradox of secure MAP and SBP regardless of elevated preload is reconciled by a compensatory discount in SVR and autonomic changes, which finally result in long-term vascular variations. Baroreflex compensation maintains hemodynamic stability within the acute part, however the gradual desensitization of this reflex, coupled with plasma quantity depletion and impaired vasoconstrictive responses, contributes to post-flight orthostatic intolerance. Furthermore, cerebrovascular autoregulation seems to be preserved regardless of elevated sympathetic outflow, suggesting a singular adaptation of cerebral perfusion mechanisms to weightlessness. The elevated incidence of arrhythmias, endothelial dysfunction, and early vascular reworking emphasize the necessity for focused countermeasures to mitigate cardiovascular dangers throughout spaceflight.
Subacute part
During prolonged house missions, lasting weeks to months, the cardiovascular system undergoes additional variations past the preliminary acute part. One key change is the sustained discount in plasma quantity, which, together with altered vascular dynamics, results in a persistent decline in stroke quantity24. Despite this, cardiac output stays secure at relaxation as a result of a compensatory enhance in coronary heart price10. However, this adaptation limits the guts’s capacity to assist greater bodily exertion10. The myocardium undergoes structural reworking, with reductions in left ventricular mass of as much as 9.1%, mirroring the deconditioning seen in extended mattress relaxation30.
Vascular reworking continues because the unloading of gravitational forces diminishes mechanical stress on giant arteries, growing arterial stiffness and endothelial dysfunction31. This is especially evident within the femoral and carotid arteries, the place reductions in luminal diameter and intima-media layer thickening counsel accelerated vascular ageing32,33. Impaired nitric oxide (NO) bioavailability reduces vasodilation, predisposing astronauts to long-term cardiovascular issues upon return to Earth34.
Cerebrovascular variations change into extra pronounced throughout this part. Despite central blood quantity reductions, cerebral blood circulation stays secure, doubtless as a result of compensatory cerebral vasodilation35,36. However, the sustained fluid shift will increase intracranial stress, contributing to SANS, with signs resembling complications, blurred imaginative and prescient, and cognitive disturbances37,38. Prolonged publicity to elevated CO₂ ranges exacerbates these signs by inducing additional cerebral vasodilation, probably resulting in persistent neurovascular adjustments affecting cognitive operate and visible acuity35,39.
Chronic publicity to elevated CO₂ additionally impacts chemoreceptor operate within the medulla oblongata, which regulates cerebrovascular responses to fluctuations in CO₂ and pH40. Prolonged hypercapnia results in chemoreceptor desensitization, impairing the regulation of cerebral blood circulation in response to metabolic calls for40,41. This may have vital implications for astronauts on deep-space missions, the place CO₂ management is more difficult41. Further analysis is critical to know the long-term results of hypercapnia on cerebrovascular operate and to develop efficient countermeasures.
Subacute spaceflight additionally results in a decline in orthostatic tolerance. The mixed results of plasma quantity depletion, baroreceptor desensitization, and lowered vascular resistance impair the physique’s capacity to manage blood stress upon re-entry16,27,42,43. This highlights the extent of autonomic and vascular deconditioning, notably the blunted baroreflex response, which prevents mandatory vasoconstriction to take care of cerebral perfusion when standing16,43.
Despite these challenges, compensatory mechanisms assist maintain circulatory stability in microgravity, however these variations include trade-offs. Prolonged cardiovascular and neurovascular adjustments throughout spaceflight could have lasting results on astronaut well being. Understanding these mechanisms is important for growing countermeasures, together with tailor-made train regimens and pharmacological interventions, to mitigate the antagonistic results of prolonged house journey.
Chronic part
In the continual part of spaceflight, lasting a number of months or extra, vital cardiovascular variations proceed. Studies have reported cardiac atrophy throughout extended spaceflight; nevertheless, latest findings counsel that train countermeasures could mitigate these results, notably in long-duration spaceflight. A examine on 13 astronauts after 155 ± 31 days aboard the International Space Station (ISS) discovered no vital distinction in LV mass postflight, suggesting that variations to microgravity could also be extra variable than beforehand assumed44. These findings counsel that the extent and variability of cardiovascular adjustments throughout long-duration spaceflight could also be extra nuanced than beforehand assumed.
Long-duration spaceflight induces advanced cardiovascular variations with various results on left ventricular (LV) construction and performance. Left ventricular operate undergoes reworking throughout the continual part, with analysis displaying that cardiac output and stroke quantity enhance by 35-41% between 3 and 6 months on the ISS, difficult earlier beliefs that spaceflight results in a web discount in cardiac output45. This suggests an adaptive response to microgravity, because the cardiovascular system adjusts over time, probably as a result of elements like train countermeasures that assist preserve cardiovascular well being throughout prolonged missions. Thus, the impression on stroke quantity differs between the acute and continual phases. While earlier research reported cardiac atrophy, latest analysis has reported that LV mass and quantity are usually preserved45. Echocardiographic assessments have reported modest reductions in LV wall thickness and end-diastolic quantity, suggesting decreased preload and chamber dimension46. These variations mirror delicate however notable adjustments in cardiac operate throughout extended microgravity publicity.
Impairments in contractile operate are evident postflight, with astronauts exhibiting lowered left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and elevated left ventricular end-systolic quantity (LVESV)47. These adjustments, notably pronounced in long-duration missions, counsel a decline in myocardial contractility as a result of elements resembling cardiac muscle atrophy, altered protein synthesis, and adjustments in autonomic regulation48. A lower in LVEF signifies diminished effectivity in blood ejection, whereas a rise in LVESV suggests incomplete ventricular emptying, each of which can enhance cardiovascular stress upon return to Earth.
Prolonged publicity to microgravity results in vital alterations in autonomic management and vascular operate. Studies have proven a discount in baroreceptor sensitivity following prolonged house missions, impairing blood stress regulation throughout postural transitions and contributing to orthostatic intolerance upon re-entry11. While there may be proof of elevated sympathetic nervous system exercise, the connection with plasma norepinephrine ranges is advanced, with some research reporting elevated concentrations and others displaying no vital change11. Recent findings problem the belief of lowered whole peripheral resistance (TPR), suggesting as a substitute that TPR could enhance throughout long-duration missions as a compensatory mechanism to take care of blood stress regardless of lowered circulating quantity49.
Vascular reworking is one other outstanding characteristic of continual spaceflight, notably in giant elastic arteries. Long-term vascular construction and performance, evaluated by flow-mediated dilation and carotid intima-media thickness (IMT), have been noticed throughout extended spaceflight. Previous research reported a 10-12% enhance in carotid IMT after six months of spaceflight and a 20% enhance after a 12 months, indicating early vascular stiffening. This reworking was accompanied by a discount in arterial compliance, which can predispose astronauts to hypertension and atherosclerosis in the long run50. However, more moderen analysis on astronauts throughout long-duration spaceflight (>4 months) discovered no vital adjustments in imply carotid IMT or the cross-sectional space of the intima-media layer throughout or after spaceflight, suggesting that vascular reworking is probably not as pronounced or constant as initially believed.51.
During the continual part of spaceflight, lipid metabolism undergoes vital alterations, with elevated ranges of angiotensin II, aldosterone, and oxidative stress markers contributing to vascular reworking and endothelial dysfunction52. Spaceflight prompts the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), resulting in elevated ranges of angiotensin II and aldosterone52. Angiotensin II exacerbates oxidative stress, additional impairing endothelial operate53. These hormones contribute to endothelial dysfunction, vascular wall hypertrophy, and fibrosis, that are pro-atherogenic processes. This pro-atherogenic state could speed up the event of cardiovascular illnesses in the long run52. Inflammatory markers resembling C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) stay elevated even after astronauts return to Earth, suggesting extended immune responses that exacerbate endothelial dysfunction52.
Chronic spaceflight additionally impacts hematologic variations. During spaceflight, purple blood cell (RBC) destruction will increase by as much as 54%, a phenomenon referred to as “house hemolysis54. This discount in RBC mass is pushed by accelerated turnover and decreased erythropoiesis as a result of decrease erythropoietin ranges in microgravity. Upon re-entry, plasma quantity will increase, resulting in dilution of RBCs and hemoglobin focus, leading to post-flight anemia. While RBC mass begins to get better after re-entry, aided by elevated erythropoietin ranges, full restoration could take weeks, with elevated inflammatory markers contributing to endothelial dysfunction54.
The sustained cardiovascular variations in microgravity, together with cardiac reworking, vascular dysfunction, and autonomic impairment, underscore the necessity for focused countermeasures to guard astronaut well being on prolonged missions. Artificial gravity simulations, enhanced train applications, and pharmacological interventions geared toward decreasing vascular and myocardial deconditioning are essential. As house companies put together for deep-space missions, understanding these continual variations and their mitigation will likely be crucial to astronaut well being and the success of long-term house exploration missions.
Figure 1 demonstrates the important thing cardiovascular variations to microgravity throughout acute, subacute, and continual phases of spaceflight.
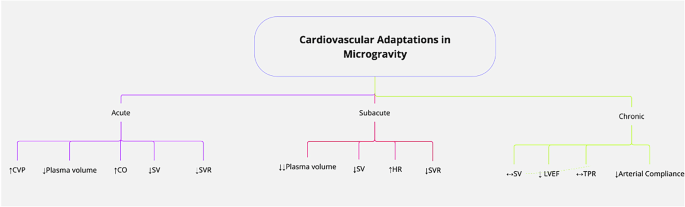
CVP central venous stress, CO cardiac output, SV stroke quantity, SVR systemic vascular resistance, HR coronary heart price, LVEF left ventricular ejection fraction, TPR whole peripheral resistance. ↑: Increases; ↓: Decreases; ↔: Remains Stable; ↑: Increases extra.
Impact of vascular adjustments as a result of microgravity on the neural operate
Vascular adjustments as a result of microgravity can considerably impression neural operate in a number of methods, primarily by means of altered cerebral perfusion, intracranial stress (ICP) dynamics, and blood-brain barrier (BBB) integrity.
Cerebral blood circulation (CBF) dysregulation
In microgravity, fluid shifts trigger an preliminary enhance in central blood quantity, together with throughout the cerebral vasculature35. Over time, the physique adapts by decreasing plasma quantity and cardiac output, which can compromise cerebral perfusion55. While autoregulatory mechanisms preserve comparatively secure CBF, extended publicity to microgravity can result in impaired cerebral vascular reactivity, decreasing the mind’s capacity to regulate blood circulation in response to metabolic calls for56,57. This may have an effect on cognitive operate, response instances, and reminiscence.
Intracranial stress (ICP) alterations
In microgravity, the absence of gravity-driven venous drainage prevents the conventional discount in ICP that happens when upright on Earth58. Lawley et al. discovered that whereas ICP in microgravity is decrease than within the supine place on Earth, it stays greater than the standard upright ICP58. This persistent elevation could clarify signs like complications, visible impairment (e.g., SANS), and cognitive fatigue59,60. Though microgravity doesn’t trigger pathological ICP will increase, the shortage of postural variations could contribute to long-term neural results.
Blood-brain barrier (BBB) disruption
The BBB is essential for regulating the passage of drugs between the bloodstream and the mind61. Microgravity-induced fluid shifts and vascular reworking could alter BBB permeability, growing the danger of neuroinflammation and oxidative stress62. Elevated CO2 ranges in house additional exacerbate this, as CO2-induced vasodilation can weaken the BBB and permit dangerous molecules to enter the mind, probably resulting in neurodegenerative adjustments over lengthy missions63.
Neurotransmitter and autonomic dysregulation
Changes in cerebral perfusion and CO2 publicity can have an effect on neurotransmitter launch, notably these concerned in autonomic regulation (e.g., norepinephrine and acetylcholine)64,65,66. This could contribute to dizziness, spatial disorientation, and temper disturbances. Astronauts typically report difficulties with stability, coordination, and sensory integration upon return to Earth, highlighting the function of vascular adjustments in neural processing67.
Impaired waste clearance (glymphatic system)
The glymphatic system, chargeable for clearing metabolic waste from the mind, depends on cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) circulation, which can be disrupted in microgravity as a result of altered ICP and vascular adjustments68,69,70. This may result in the buildup of neurotoxic proteins resembling beta-amyloid, probably growing the danger of neurodegenerative situations with extended house publicity71.
Recommendations
Mitigating the physiological results of microgravity requires a multifaceted method. Cardiovascular deconditioning might be countered with synthetic gravity coaching and high-intensity train (resistance and cardio)33. Pharmacological assist, resembling beta-agonists to forestall myocardial atrophy and vasoconstrictors like midodrine for post-flight orthostatic intolerance, must also be offered72. To preserve plasma quantity and scale back hypovolemia-related dizziness, astronauts sometimes devour a mix of water and salt tablets to create an isotonic answer earlier than re-entry73. For NASA astronauts, this includes ingesting 1–1.5 liters of water with salt tablets roughly one hour previous to re-entry73.
Vascular well being methods embody NO donors, dietary antioxidants (e.g., vitamin C, flavonoids), and compression clothes to assist endothelial operate and forestall extreme fluid shifts49,74. These measures scale back oxidative stress and vascular reworking, minimizing cardiovascular dangers post-flight.
Neurological countermeasures goal ICP and cerebrovascular operate. Lower-body adverse stress (LBNP) remedy enhances cerebral venous outflow, mitigating the danger of SANS60. Intermittent head-down tilt could assist regulate ICP by bettering CBF and dynamic autoregulation75. While improved CO₂ filtration minimizes hypercapnia-induced cerebral vasodilation76. Nanoligomers concentrating on inflammatory pathways (e.g., NF-κB and IL-6 inhibitors) have proven promise in mitigating neurodegeneration markers related to microgravity77. These medication, together with biofeedback coaching, may assist protect cognitive and autonomic operate.
Post-flight rehabilitation is important for restoration. Tilt desk coaching aids baroreceptor reconditioning whereas rehydration and electrolyte balancing speed up plasma quantity restoration. Long-term cardiovascular monitoring (echocardiography, vascular imaging) ensures early detection of residual dangers. Personalized train and dietary plans additional assist long-term cardiovascular well being.
Future instructions and limitations
Future analysis ought to deal with additional elucidating the mechanisms behind microgravity-induced vascular adjustments and their implications for neural operate. Advanced imaging strategies, resembling purposeful MRI and PET scans, may present deeper insights into cerebral blood circulation alterations. Longitudinal research monitoring astronauts earlier than, throughout, and after spaceflight can assist set up causal relationships between microgravity publicity and neural adjustments. Additionally, the event of countermeasures, resembling focused pharmacological interventions and synthetic gravity programs, must be explored to mitigate antagonistic vascular results in long-duration house missions.
Despite vital progress in understanding the impression of microgravity on vascular and neural well being, a number of limitations exist. First, the pattern sizes in spaceflight research are sometimes small as a result of logistical constraints, which limits the generalizability of findings. Second, most research depend on short-duration missions, whereas long-term results stay much less understood. Third, the extrapolation of animal mannequin findings to human physiology requires cautious interpretation, as species-specific variations could affect outcomes. Finally, technological limitations in space-based imaging and monitoring constrain the flexibility to acquire real-time, high-resolution information.
This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its authentic location you may go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41526-025-00534-4
and if you wish to take away this text from our web site please contact us

