This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its authentic location you may go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://www.sciencenews.org/article/supernova-first-moments-lopsided-blast
and if you wish to take away this text from our web site please contact us
When one supernova commenced, it seemed like an olive — a minimum of earlier than it acquired shaken and stirred.
This perception, reported within the Nov. 12 Science Advances, comes from new observations taken in the wake of a massive star’s death. As a number of the most complete views ever captured of a supernova’s first moments, the findings give astronomers essential clues about how these explosions start.
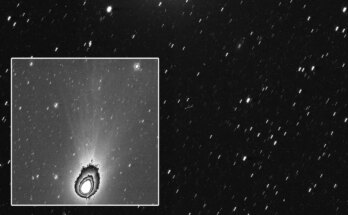
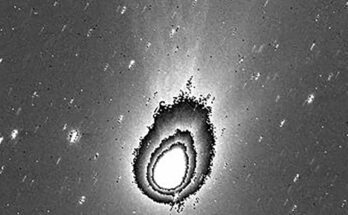
On April 10, 2024, a supernova was detected in a close-by galaxy. Over the subsequent 26 hours, a world collaboration of astronomers sprang into motion to collect further observations of the explosion earlier than it progressed too far. Their efforts produced the earliest take a look at the form of any supernova — the explosive loss of life of a large star — and revealed its blast wave breaking by means of the stellar floor.
“It’s a very important set of observations,” says astrophysicist Adam Burrows of Princeton University, who was not concerned with the examine. “The modern theory of supernova explosions seems to be validated in broad outlines by these data.”
For most of their lives, stars a minimum of eight occasions the solar’s mass generate an outward stress by means of the fusion of hydrogen and helium atoms of their core, counteracting gravity. But as soon as these stars run out of gasoline, that stress disappears and the core collapses. The higher layers of the star comply with go well with, and as they hit the core, they create a rebounding shock wave that splits the star’s floor and releases an immense quantity of power and light-weight, which we see as a supernova. How precisely the shock wave begins is a long-standing query.
Fortuitously, the shock wave’s form can reveal what initiated it. But this fleeting view have to be captured earlier than the shock wave is disrupted by the fabric surrounding the star, which may take simply hours.
To seize the snapshot of the April 2024 supernova, astronomers used the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope in Chile, which was ready to have a look at the polarization, or orientation, of the supernova’s gentle. Using a method referred to as spectropolarimetry, the researchers used the sunshine’s polarization to re-create the explosion’s form in its first moments. Their outcomes confirmed that the sunshine emanated not uniformly, like the sunshine from a typical star, however elongated, formed like an olive.
“The very first [particles of light] and matter do not shoot out spherically from the star’s surface,” says examine coauthor Yi Yang, an astronomer at Tsinghua University in Beijing. “Scientifically this is very important, because the intrinsic shape of the shock breakout tells us a lot of how it was triggered at the heart of the star in the first place.”
While the findings can’t totally clarify how any such supernova is triggered, they do slim the chances.
The observations help the idea that the shock wave is initiated by ghostly subatomic particles referred to as neutrinos being energized deep within the stellar inside, which heats the infalling higher layers like water boiling in a pot. Just as boiling water bubbles erratically, the star’s materials bubbles up in an irregular sample, which finally averages out into an uneven shock wave. This common principle appears to be confirmed by the information, Burrows says, however particular particulars nonetheless have to be labored out. And that may require extra observations.
“This is a unique set of data which may presage much better stuff for the future as we start to see, with [upcoming surveys], many, many more of these supernovas,” Burrows says. “If a fraction of them can be followed up with this type of precision, I think we will see a new era of dialogue between theoretical study of these explosions and their observational validation.”
This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its authentic location you may go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://www.sciencenews.org/article/supernova-first-moments-lopsided-blast
and if you wish to take away this text from our web site please contact us