This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its unique location you’ll be able to go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-025-03754-6
and if you wish to take away this text from our web site please contact us
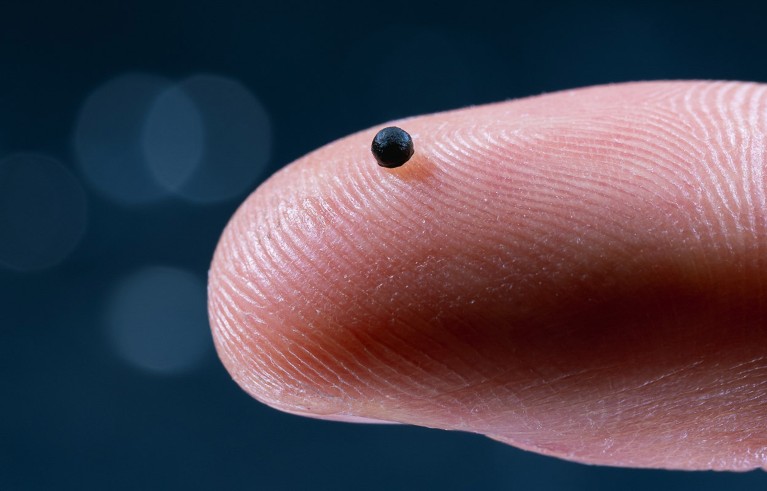
The tiny, drug-filled robots are guided by way of blood vessels utilizing magnets.Credit: Luca Donati/lad.studio Zürich
A remote-controlled robotic the scale of a grain of sand can swim by way of blood vessels to ship medicine earlier than dissolving into the physique. The expertise might permit docs to manage small quantities of medicine to particular websites, avoiding the poisonous negative effects of body-wide therapies.
The microrobots — guided by magnetic fields — work in blood vessels in pigs and sheep, researchers confirmed in a paper printed in Science on 13 November1.
The system has but to be trialled in individuals, nevertheless it exhibits promise as a result of it really works in a roughly human-sized physique, and since all its elements have already been proven to be biocompatible, says Bradley Nelson, a mechanical engineer at Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH) in Zurich, who co-led the work.
Around one-third of developed medicine that fail to come back to market achieve this as a result of they’re too poisonous2, says Nelson. The workforce says the microrobots would permit smaller quantities of medicine to be given on to the affected areas, thereby decreasing potential negative effects. The approach could possibly be used to focus on stroke-causing blockages or mind tumours.
“The demonstrations are compelling but still preclinical,” says Wei Gao, a medical engineer on the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, whose workforce has developed an alternate robotic drug-delivery system. But if additional research proceed easily, remote-controlled drug-delivery robots could possibly be used within the first medical functions inside 5 to 10 years, he says.
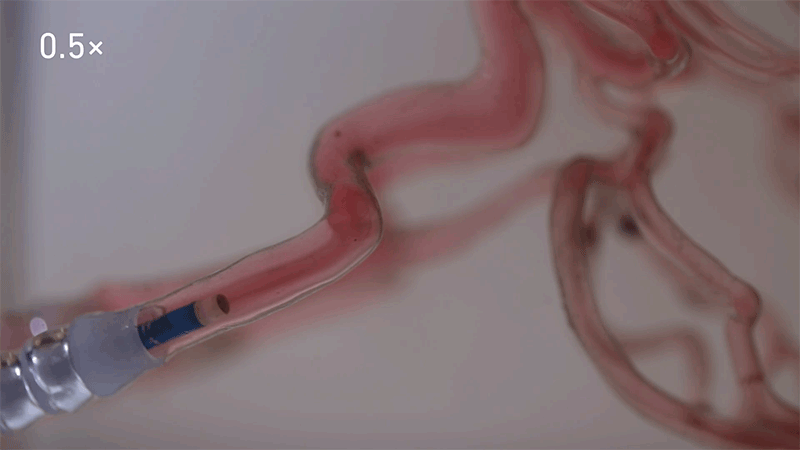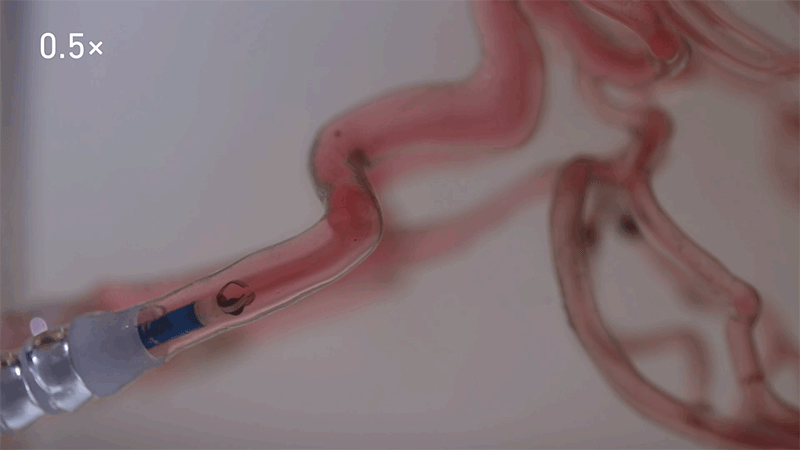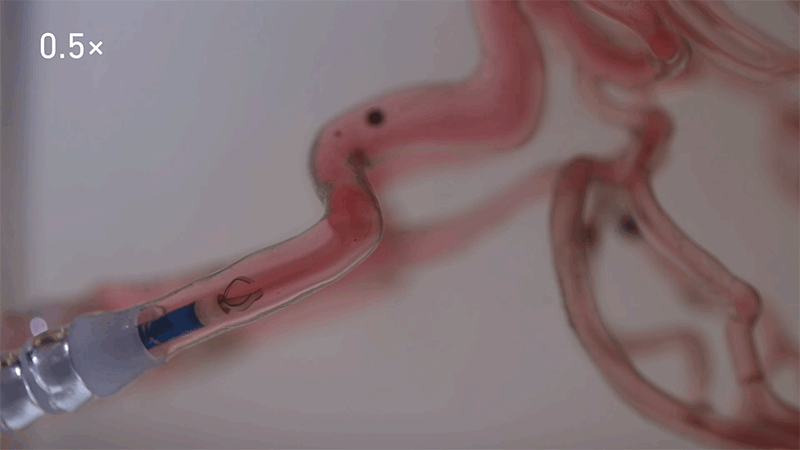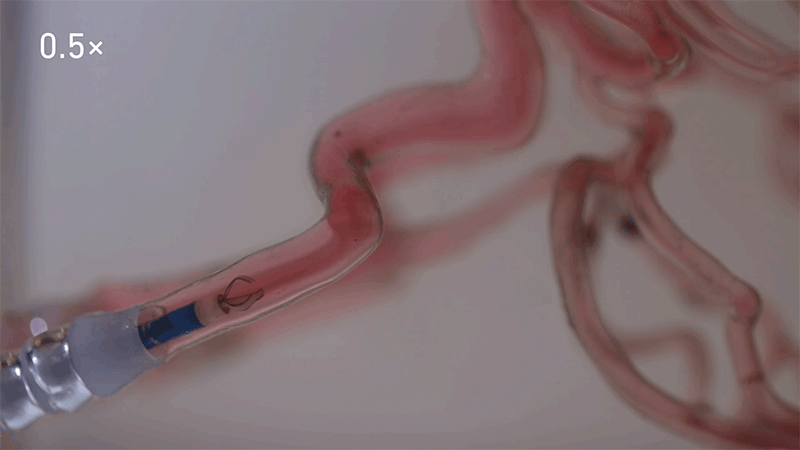
Credit: ETH Zürich
Robot-delivered medicine
Researchers have explored the way to use tiny robots to ship medicine for many years, together with by steering them utilizing ultrasound and utilizing rotating gadgets that mimic micro organism.
The system developed by the ETH workforce includes filling a tiny bead of gelatine with a drug, in addition to nanoparticles of magnetic iron oxide, which permits its motion to be managed by magnetic fields surrounding the affected person.
In trials within the brains of pigs and sheep, the workforce confirmed that they might use a catheter to insert the bots, earlier than making them roll alongside the perimeters of blood vessels, swim towards the move or navigate with the stream at speeds as quick as 40 centimetres per second. They used X-ray pictures to watch and manoeuvre the bots in actual time with millimetre-precision. In trials in pigs, the workforce confirmed that in additional than 95% of instances, the medicine had been delivered to the proper location.
This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its unique location you’ll be able to go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-025-03754-6
and if you wish to take away this text from our web site please contact us



