This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its unique location you possibly can go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://bigthink.com/starts-with-a-bang/decline-fall-stars-universe/
and if you wish to take away this text from our website please contact us
Sign up for the Starts With a Bang publication
Travel the universe with Dr. Ethan Siegel as he solutions the largest questions of all.
Today, our Universe is illuminated, lit up primarily by stars.

This low-resolution picture reveals the total area of the COSMOS-Web survey carried out with JWST. Spanning 0.54 sq. levels within the sky, or practically three full Moons’ price of space, this represents the most important, deepest wide-field view of the Universe ever acquired.
But it wasn’t born with any stars; they wanted the appropriate circumstances to kind.
The overdense areas that the Universe was born with develop and develop over time, however are restricted of their development by the preliminary small magnitudes of the overdensities, the cosmic scale on which the overdensities are discovered (and the time it takes the gravitational drive to traverse them), and likewise by the presence of radiation that’s nonetheless energetic, which prevents construction from rising any quicker. It takes tens-to-hundreds of tens of millions of years to kind the primary stars; small-scale clumps of matter exist lengthy earlier than that, nevertheless. Until stars kind, the atoms in these clumps stay impartial, requiring ionizing, ultraviolet photons to render them clear to seen gentle.
Clumps of matter develop by way of gravity, drawing increasingly more mass into them.

An illustration of the primary stars turning on within the Universe. Without metals to chill down the clumps of fuel that result in the formation of the primary stars, solely the most important clumps inside a large-mass cloud will wind up changing into stars: fewer in quantity however better in mass than right now’s stars. Although there’s loads of light-blocking matter surrounding them, some longer-wavelength gentle (when first emitted) can nonetheless escape into the Universe past.
Eventually, they change into so large that they collapse, triggering new stellar start.
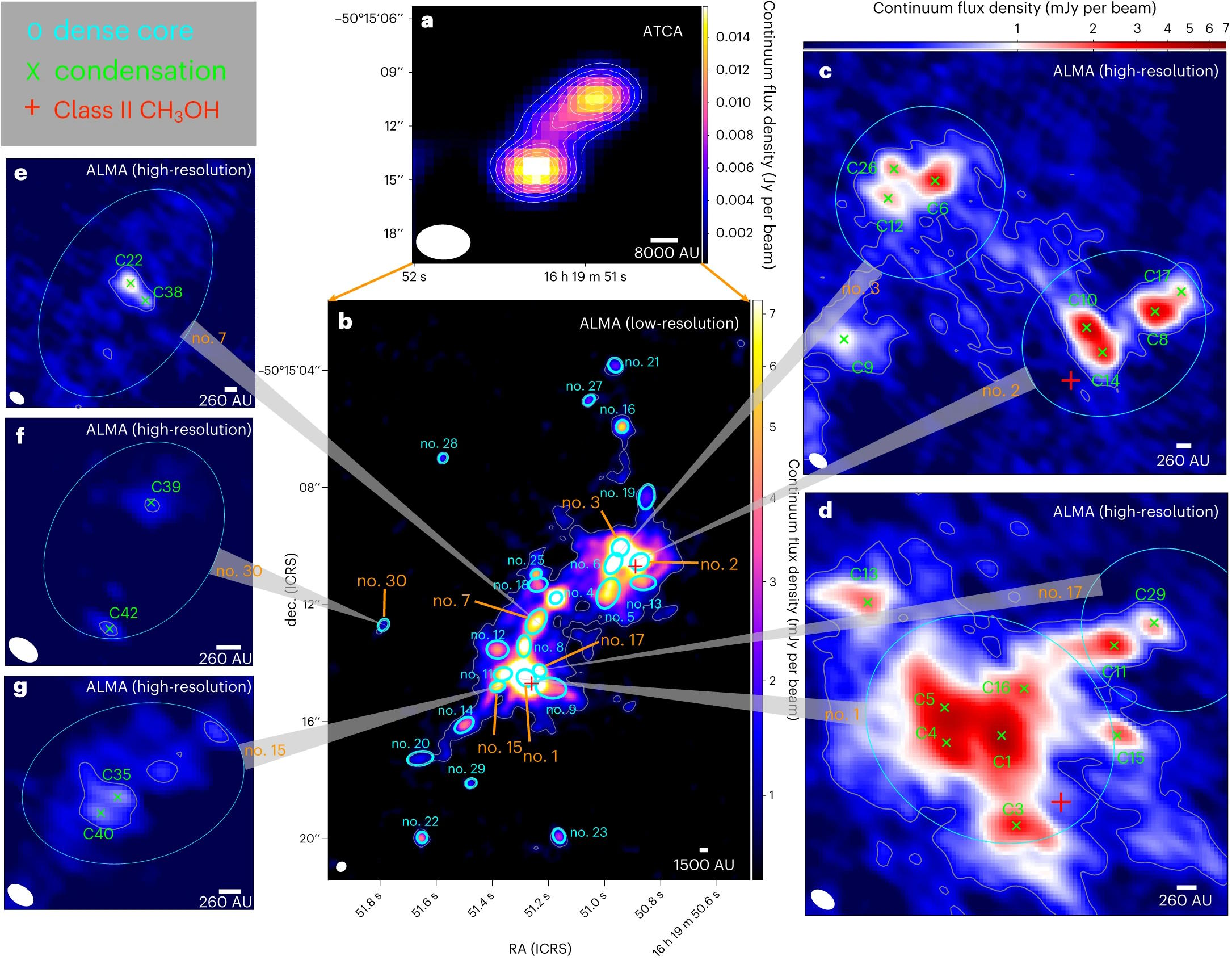
The dense cores of protostar cluster G333.23–0.06, as recognized by ALMA, present sturdy proof for giant ranges of multiplicity inside these cores. Binary cores are frequent, and teams of a number of binaries, forming quaternary techniques, are additionally fairly frequent. Triplet and quintuplet techniques are additionally discovered inside, whereas, for these high-mass clumps, singlet stars change into fairly uncommon. It is predicted that the celebrities forming in nebulae all all through the Universe, together with within the Eagle Nebula, have related clumpy, fragmented properties.
At early instances, star-formation was uncommon, occurring solely in large, fast-growing areas.
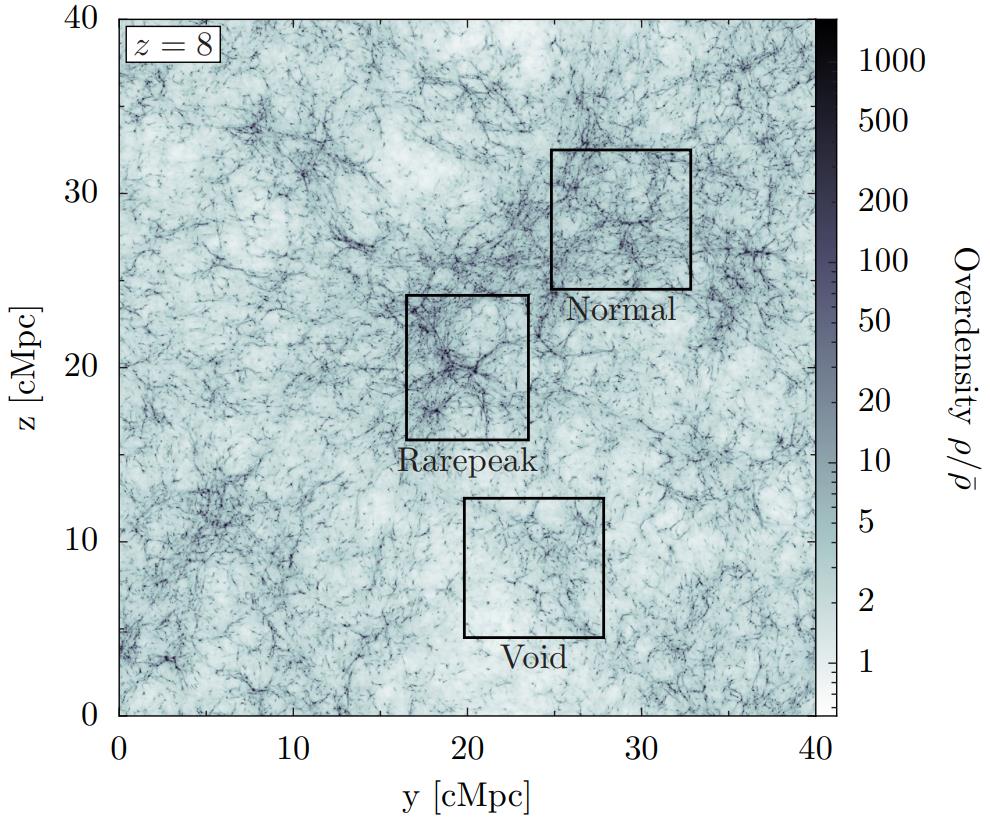
Regions born with a typical, or “normal” overdensity, will develop to have wealthy constructions in them, whereas underdense “void” areas may have much less construction. However, early, small-scale construction is dominated by probably the most extremely peaked areas in density (labeled “rarepeak” right here), which develop the most important the quickest, and are solely seen intimately to the best decision simulations.
Slightly later, development by mergers and accretion causes star-formation charges to steadily rise.

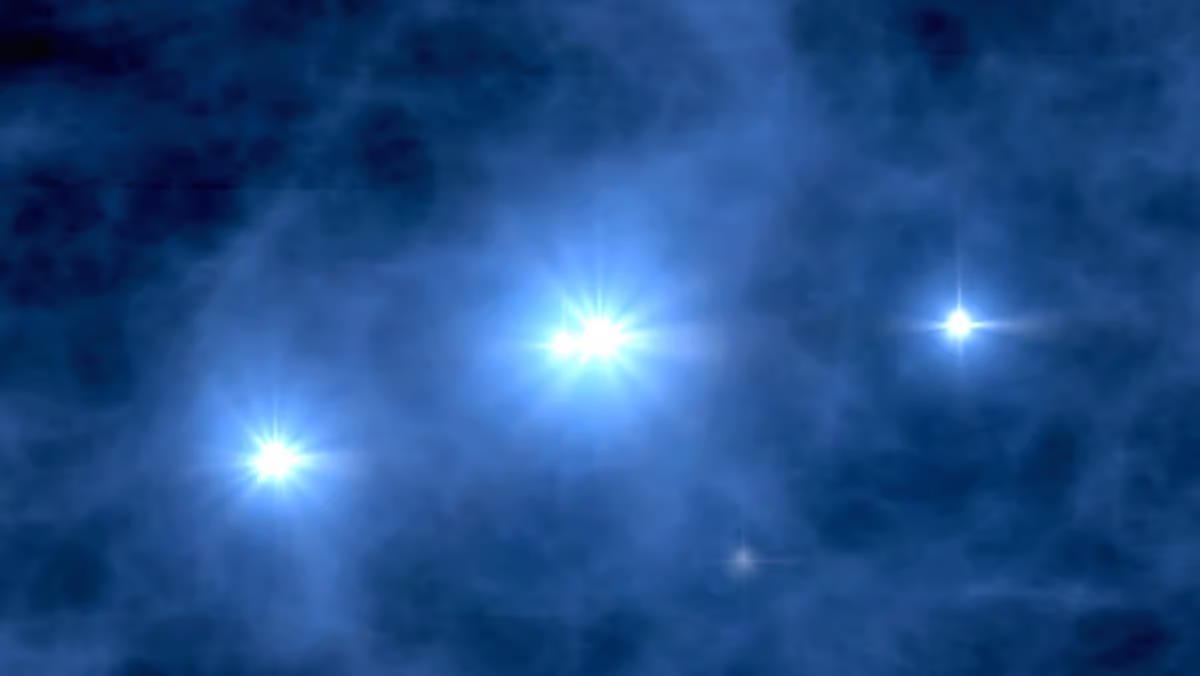
When main mergers of similarly-sized galaxies happen within the Universe, they kind new stars out of the hydrogen and helium fuel current inside them. This may end up in severely elevated charges of star-formation, much like what we observe contained in the close by galaxy Henize 2-10, positioned 30 million gentle years away. This galaxy will doubtless evolve, post-merger, into one other disk galaxy if copious quantities of fuel stays inside it, or into an elliptical if all or practically all the fuel is expelled by the present starburst. Starburst occasions like this have been way more frequent earlier in cosmic historical past than they’re right now.
After ~3 billion years, stars kind on the quickest price of all-time: what astronomers name “cosmic noon.”
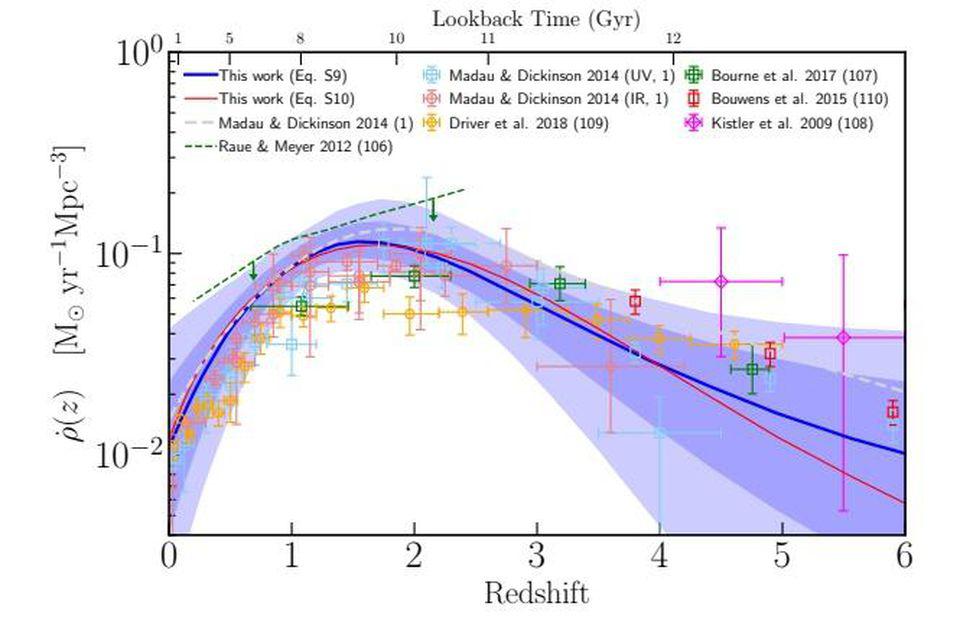
The Fermi-LAT collaboration’s reconstructed star-formation historical past of the Universe, in contrast with different information factors from different strategies elsewhere within the literature. We are arriving at a constant set of outcomes throughout many various strategies of measurement, with the best uncertainties persisting on the highest redshifts and earliest instances. These uncertainties symbolize lower than a 1% uncertainty within the complete variety of stars fashioned all through cosmic historical past.
But afterwards, the star-formation price begins to say no.
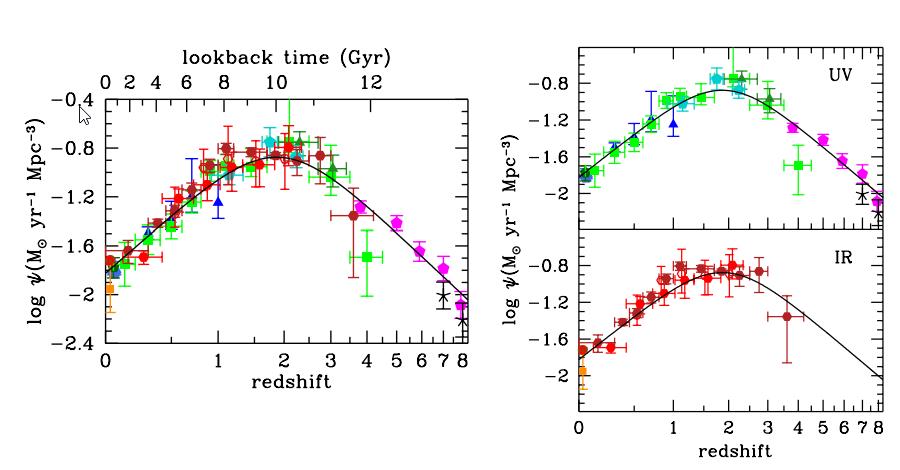
The star-formation price within the Universe is a operate of redshift, which is itself a operate of cosmic time. The total price, (left) is derived from each ultraviolet and infrared observations, and is remarkably constant throughout time and house. Note that star formation, right now, is only some % of what it was at its peak (between 3-5%), and that almost all of stars have been fashioned within the first ~5 billion years of our cosmic historical past. Only about ~15% of all stars, at most, have fashioned over the previous 4.6 billion years. Direct measures of star-formation are essential, however the technique of Fermi-LAT for measuring the full variety of photons produced by stars is superior.
The increasing Universe drives galactic teams and clusters aside.

For the primary ~3 billion years of cosmic historical past, the star-formation price rose and rose till reaching a peak, however has fallen off considerably within the ~10-11 billion years since. Although an infinite variety of photons have been cumulatively produced by stars, a good better quantity have been produced within the Big Bang.
Cosmic mergers change into rarer, occurring solely inside certain techniques.

This multiwavelength view of the 2 largest, brightest galaxies within the M81 group reveals stars, plasmas, and impartial hydrogen fuel. The fuel bridge connecting these two galaxies infalls onto each members, triggering the formation of latest stars. If every star have been shrunk right down to be a grain of sand, this group can be 36 million km away, however the two galaxies can be separated solely by a bit over 400,000 km: the Earth-Moon distance. At late instances, the one galaxy mergers that happen occur inside certain clusters and teams of galaxies, because of darkish power taking on the increasing Universe.
Credit: R. Gendler, R. Croman, R. Colombari; Acknowledgement: R. Jay GaBany; VLA Data: E. de Block (ASTRON)
Mass accretion turns into much less important, because the intergalactic medium dilutes.

In between the good clusters and filaments of the Universe are nice cosmic voids, a few of which might span lots of of tens of millions of light-years in diameter. The long-held concept that the Universe is held collectively by constructions spanning many lots of of tens of millions of light-years, these ultra-large superclusters, has now been settled, and these monumental web-like options are destined to be torn aside by the Universe’s enlargement, whereas the cosmic voids proceed to develop.
Even inside galaxies, ongoing star-formation depletes the fuel essential to create new stars.

This area of house reveals a portion of the airplane of the Milky Way, with three prolonged star-forming areas all side-by-side subsequent to at least one one other. The Omega Nebula (left), the Eagle Nebula (heart), and Sharpless 2-54 (proper), compose only a small fraction of an enormous complicated of fuel and mud discovered all via the galactic airplane that constantly result in the formation of new child stars.
The Euclid mission confirmed star-formation’s decline throughout the previous a number of billion years.

The early outcomes of the GLASS Early Release Science program reveal over 200 sources that span quite a lot of ranges in redshift and mass. This helps train us what shapes galaxies tackle over a variety of lots and levels in cosmic time/evolution, revealing quite a few very large, very early, but very evolved-looking galaxies. Data from Hubble, JWST, Fermi, Euclid, and extra all present a star-formation historical past that peaked round 10-11 billion years in the past, and has declined ever since.
Credit: C. Jacobs, Ok. Glazebrook et al., arXiv:2208.06516, 2022
Now, 13.8 billion years after the Big Bang, new stars are unusual.
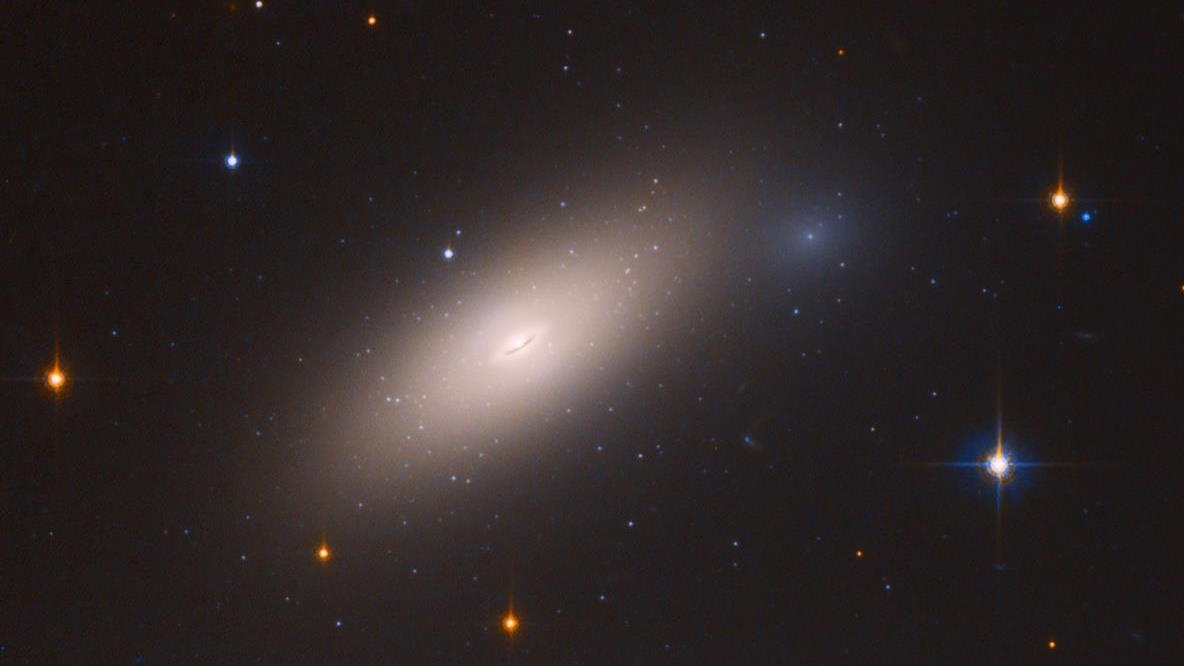

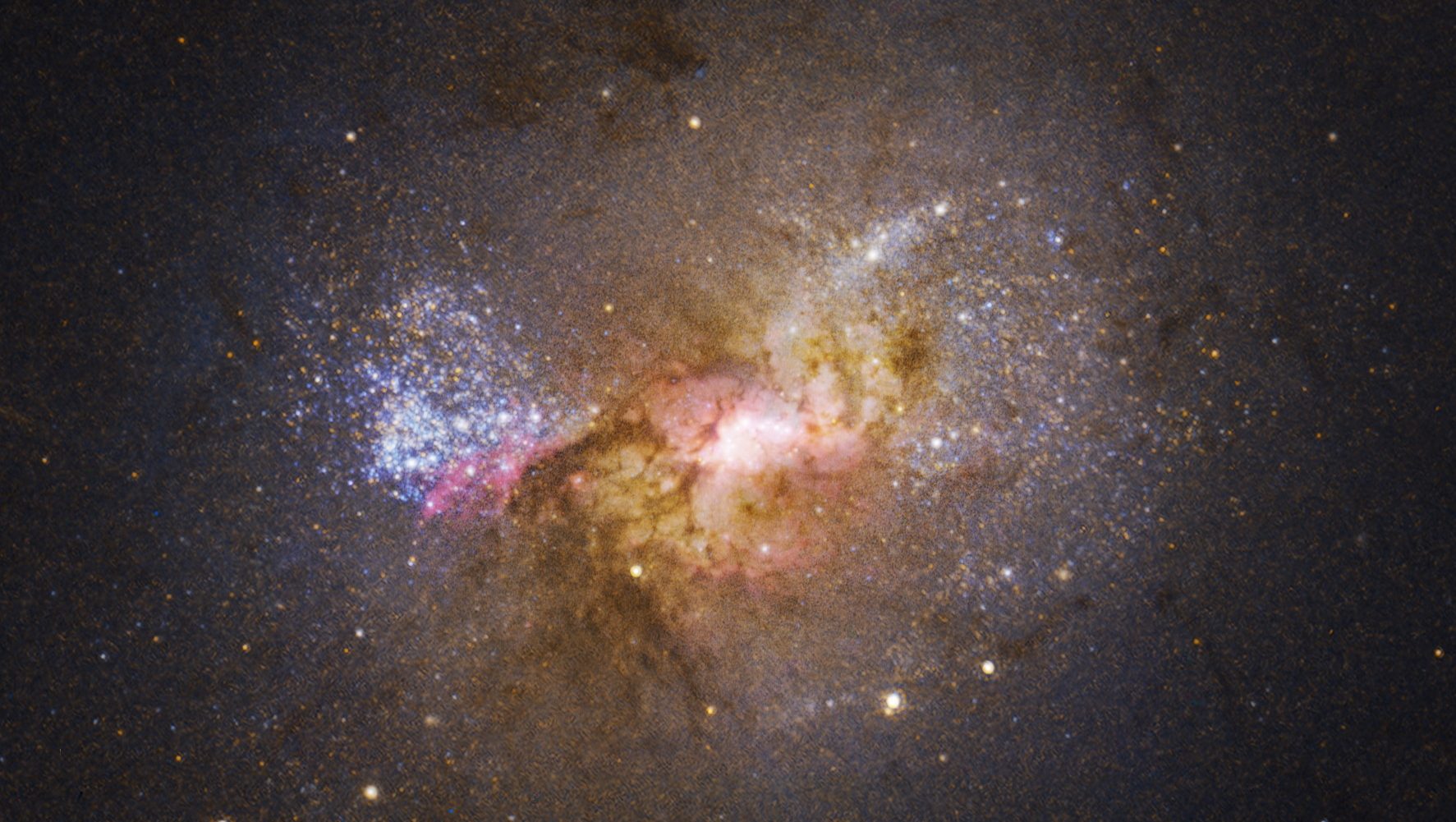
This close by galaxy, NGC 1277, though it might seem much like different typical galaxies discovered within the Universe, is exceptional for being composed primarily of older stars. Both its intrinsic stellar inhabitants and its globular clusters are all very crimson in coloration, indicating that it hasn’t fashioned new stars in ~10 billion years. When all the fuel inside a galaxy is expelled and no new fuel enters, that galaxy turns into completely “red and dead,” as no new populations of stars can kind inside it.
Today’s star-formation price, merely 3% of what it was at cosmic midday, continues to drop.

This deep-field area of the GOODS-South area comprises 18 galaxies forming stars so shortly that the variety of stars inside will double in simply 10 million years: simply 0.1% the lifetime of the Universe. The deepest views of the Universe, as revealed by house telescopes, take us again into the early historical past of the Universe, the place star-formation charges have been a lot better than right now, however the place fewer than 1% of the Universe’s cumulative stars had already fashioned. Many of probably the most distant galaxies are present in shut proximity to different foreground galaxies, whose mass distorts and magnifies the sunshine from background objects.
Someday, the final fuel reservoirs will likely be exhausted.

Galaxy clusters, like Abell S740, are the most important certain constructions within the Universe. When spirals merge, for instance, numerous new stars kind, however both post-merger or by dashing via the intra-cluster medium, fuel could be stripped away, resulting in the top of star formation in that galaxy and, finally, a red-and-dead ultimate construction. As time goes on, star formation charges gradual and increasingly more galaxies change into fuel depleted and even fuel free, resulting in “red-and-dead” big ellipticals, just like the one centrally proven right here.
Credit: NASA, ESA, Hubble Heritage Team (STScI / AURA); J. Blakeslee
Without gasoline, cosmic star-formation will stop completely, returning our Universe to darkness.
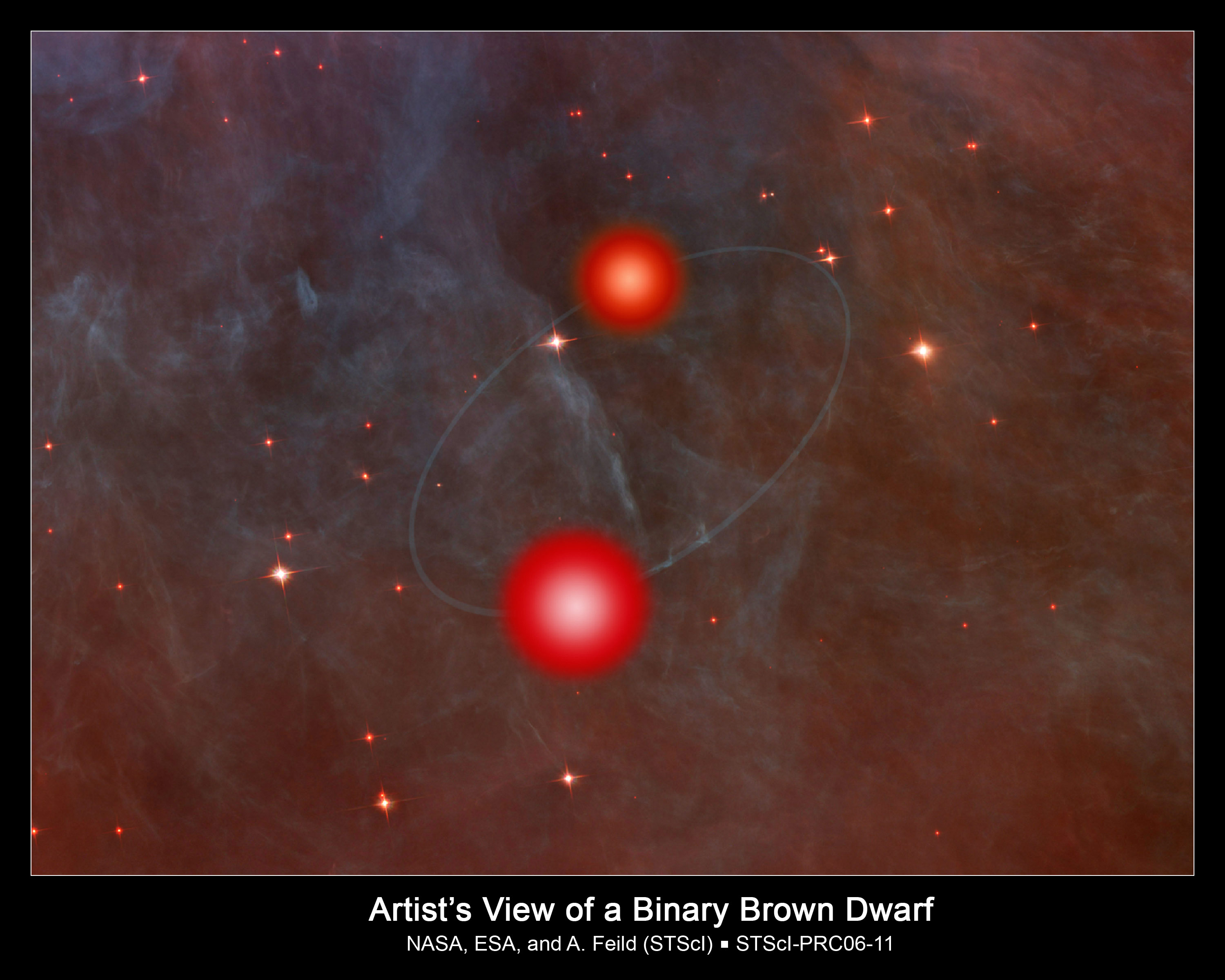

Just as stars usually exist in binary, trinary, and extra populous multi-star techniques, so too do brown dwarfs: failed stars. It’s potential that there are binary brown dwarf techniques with ample separations to allow the inspiral and merger of those elements a really very long time from now, the place they’ll ignite hydrogen fusion within the post-merger crimson dwarf that varieties: even after the host galaxy is absolutely fuel depleted and the opposite stars within the galaxy have burned out. If any orbiting worlds exist on the proper distance across the newly fashioned crimson dwarf, life might finally come up even quintillions of years into the longer term, or doubtlessly much more.
Credit: NASA, ESA, and A. Feild (STScI)
Mostly Mute Monday tells an astronomical story in photographs, visuals and not more than 200 phrases.
Sign up for the Starts With a Bang publication
Travel the universe with Dr. Ethan Siegel as he solutions the largest questions of all.
This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its unique location you possibly can go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://bigthink.com/starts-with-a-bang/decline-fall-stars-universe/
and if you wish to take away this text from our website please contact us

