This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its authentic location you possibly can go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://rbej.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12958-025-01490-0
and if you wish to take away this text from our web site please contact us
Participants
We performed a population-based case–management examine in Isfahan, Iran, in 2024, comprising 300 infertile males (circumstances) and 300 fertile males (controls). The pattern measurement was computed based on earlier proof suggesting that roughly 60% of Iranian males have insufficient dietary consumption (of greens and fiber) [21]. Owing to an absence of prior info on the impact measurement of the composite wholesome life-style rating (HLS), we used an odds ratio (OR) of 1.65 for infertility primarily based on this single HLS part. With 80% energy and a 5% sort I error price, a minimal of 556 individuals (278 per group) was required. Considering a 15% dropout price, 648 people had been invited (Fig. 1). The circumstances had been newly recognized infertile males (analysis throughout the final 6 months), aged 20–55 years, recruited from the Shahid Beheshti Hospital Infertility Center, Shahrak-e-Salamat Infertility Clinic, and foremost andrologists specializing in infertility therapy. Male infertility was outlined for every case primarily based on the sixth version of the World Health Organization (WHO) standards [22] by an andrologist. The topics not included within the case group of our examine had been these with a historical past of: 1) metabolic ailments or endocrine problems resembling diabetes, most cancers (together with these with a historical past of radiotherapy or chemotherapy), cardiovascular ailments, kidney problems, and osteoporosis; 2) testicular atrophy; 3) testicular torsion; 4) azoospermia; and 5) ejaculation or anatomical problems.
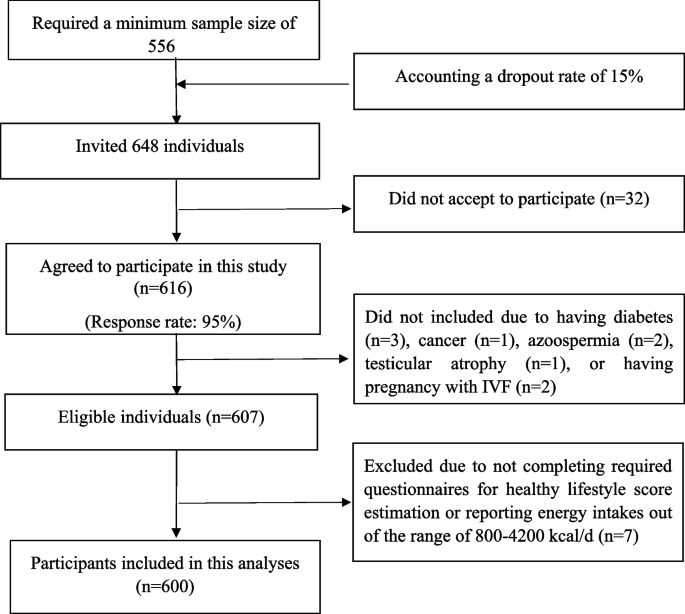
The examine participant flowchart
Controls had been wholesome males aged 20–55 attending six randomly chosen well being facilities in Isfahan for both routine development monitoring of their little one (aged < 2 years) or prenatal care for his or her naturally conceived pregnant wives. The management group non-inclusion standards mirrored the metabolic and endocrine problems standards utilized to the circumstances.
From the 616 initially enrolled individuals, 607 had been included within the examine. We subsequently excluded topics who: 1) reported vitality consumption < 800 or > 4200 kcal/day, or 2) failed to finish the required questionnaires for wholesome life-style rating estimation. The last evaluation included 600 individuals (300 circumstances and 300 controls) (Fig. 1). Our interview-based knowledge assortment protocol, with phone follow-up, ensured that there have been no lacking knowledge for life-style parts, the first consequence, or key covariates in your entire examine inhabitants (n = 600). All individuals offered written knowledgeable consent. The Ethics Committee of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences accepted the examine protocol (No. 3403573).
Assessment of life-style components
Data on dietary consumption had been gathered utilizing a validated 168-item semi-quantitative meals frequency questionnaire (FFQ), administered by an interviewer [23]. Participants had been requested to report their dietary consumption through the earlier yr when it comes to frequency of consumption (every day, weekly, or month-to-month) and amount (primarily based on the usual serving sizes). These portion sizes had been then transformed to grams per day utilizing family measures [24]. Finally, Nutritionist IV software program was used to acquire the nutrient intakes.
Dietary high quality was assessed utilizing the Healthy Eating Index-2015 (HEI-2015), which has demonstrated validity in evaluating diet-disease relationships for numerous continual circumstances [25, 26]. The HEI-2015 was chosen for its complete dietary evaluation capabilities and epidemiological relevance; nevertheless, its applicability to male reproductive outcomes requires additional investigation [27]. The HEI-2015 consists of 13 parts categorized into two domains: 9 adequacy parts and 4 moderation parts. To optimize classification accuracy, part intakes had been evaluated utilizing quintile- and decile-based distributions fairly than absolute quantitative thresholds. Six adequacy parts (complete fruits, entire fruits, greens, greens/beans, protein meals, and seafood/plant proteins) had been scored from 1 (lowest quintile) to five (highest quintile) primarily based on energy-adjusted consumption distributions. Three different adequacy parts (entire grains, dairy, and the ratio of polyunsaturated plus monounsaturated fatty acids to saturated fatty acids) had been scored from 1 (lowest decile) to 10 (highest decile) utilizing decile-based, energy-adjusted consumption classifications. The 4 moderation parts (refined grains, sodium, added sugars, and saturated fat) had been reverse-scored, with 10 assigned to the bottom consumption decile and 1 to the best. The complete HEI-2015 rating, starting from 13 to 100, was calculated by summing the scores of all particular person parts.
Information on dietary habits was collected utilizing a pre-tested, self-reported questionnaire. Although no gold commonplace exists for validating dietary behavior assessments, the predictive validity of the utilized questionnaire has been demonstrated by way of established associations with metabolic problems in Iranian populations [28,29,30]. This questionnaire evaluated meal frequency (1–3 meals/day) and regularity (by no means to at all times), consumption patterns of breakfast, lunch, and dinner (by no means to every day), fluid consumption options (timing [before/during/after meals], amount [≤ 1 to > 4 glasses], temperature), consuming behaviors (chewing thoroughness, meal length [< 5 to > 20 min]), meal-to-sleep intervals, and dietary composition relating to fats and spices, together with fatty meals consumption (animal fat, fried meals, meal fats content material [low–high], dairy/meat fats content material) and spicy meals consumption (frequency and amount). Dietary behavior domains had been derived by way of latent class evaluation (LCA), leading to six courses of diet-related practices: consuming price (sluggish/average/quick), meal sample (common/irregular), intra-meal fluid consumption (average/extra), meal-to-sleep interval (lengthy/brief), fatty meals consumption (low/excessive), and spicy meals consumption (low/excessive). Low-risk behaviors (scored 1 level every) included common meals, sluggish/average consuming price, average fluid consumption, lengthy meal-to-sleep interval, low fatty meals consumption, and excessive spicy meals consumption, primarily based on established associations with well being outcomes [28,29,30]. High-risk behaviors included irregular meals, quick consuming price, excessive intra-meal fluid consumption, brief meal-to-sleep interval, excessive fatty meals consumption, and low spicy meals consumption, which acquired 0 factors. Based on complete scores starting from 0 to six, individuals had been labeled as having wholesome dietary habits (scores of 4 to six; 1 HLS level) or unhealthy dietary habits (scores of 1 to three; 0 HLS factors) (Fig. 2).
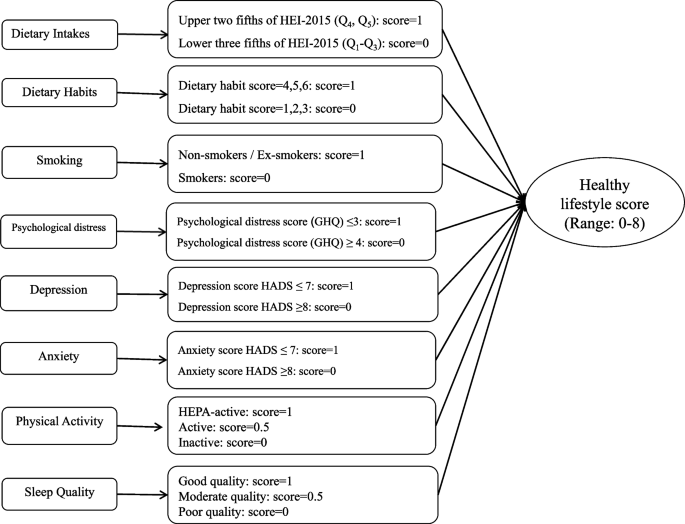
The wholesome life-style rating growth
Physical exercise ranges had been assessed utilizing the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ), a easy and legitimate screening instrument [31]. The IPAQ categorizes bodily exercise into three sorts: 1) vigorous-intensity actions (e.g., working, aggressive sports activities, heavy lifting), 2) moderate-intensity actions (e.g., brisk strolling, leisure biking), and three) strolling. For every class, individuals reported each frequency (days/week) and length (minutes/session). Using metabolic equal process (MET) coefficients—3.3 for strolling, 4.0 for average actions, and eight.0 for vigorous actions—activity-specific MET-minutes per week had been calculated as follows: MET worth × length × frequency. Total bodily exercise was decided by summing the MET-minutes throughout all classes. Based on established IPAQ thresholds, individuals had been labeled into three exercise ranges: 1) health-enhancing bodily exercise (HEPA)-active (≥ 3000 MET-min/week), 2) minimally lively (600–3000 MET-min/week), or 3) inactive (< 600 MET-min/week).
Smoking standing was assessed utilizing a pretested, self-report questionnaire. Participants reported their present cigarette use by deciding on from 5 response choices: “never smoked,” “former smoker,” “1–5 cigarettes/day,” “6–20 cigarettes/day,” or “ > 20 cigarettes/day.” Based on these responses, individuals had been categorized into three mutually unique teams: 1) present people who smoke, 2) ex-smokers, and three) nonsmokers.
The validated Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) questionnaire was used to evaluate sleep high quality. The validity and reliability of this instrument have been beforehand established [32]. The Persian model of this questionnaire has additionally been validated in Iranian adults [33]. This 19-item self-report questionnaire evaluates seven domains: (1) subjective sleep high quality, (2) sleep latency, (3) sleep length, (4) ordinary sleep effectivity, (5) sleep disturbances, (6) use of sleep medicine, and (7) daytime dysfunction. Each area is scored from 0 to three (0 = no sleep issues, 1 = average sleep issues, 2 = extreme sleep issues, and three = very extreme sleep issues), with a worldwide rating starting from 0 to 21; larger scores point out poorer sleep high quality. Participants had been categorized into three sleep high quality teams: scores of 0–3 as “good quality,” 4–5 as “moderate quality,” and ≥ 6 as “poor quality.”
The Iranian validated model of the 12-item General Health Questionnaire (GHQ-12) was used to evaluate psychological misery [34]. The GHQ-12 is a quick, validated screening instrument that evaluates latest signs of psychological misery by way of easy self-reported responses. Each merchandise is rated on a four-point scale: lower than traditional, not more than traditional, fairly greater than traditional, or rather more than traditional. We employed the usual bimodal scoring methodology (0–0–1–1), leading to a complete rating starting from 0 to 12, with larger scores indicating larger psychological misery. Participants with scores ≥ 4 had been labeled as having excessive psychological misery, whereas these with scores ≤ 3 had been categorized as having low psychological misery.
The Iranian validated model of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) was used to display screen for nervousness and despair [35]. The HADS is a quick and helpful questionnaire designed to evaluate psychological problems and measure the signs and severity of tension and despair. It accommodates 14 objects divided into two subscales: nervousness and despair. Each merchandise is rated on a four-point scale, with larger scores indicating larger severity of signs. The most rating every subscale is 21. In this examine, individuals scoring ≥ 8 on both subscale had been labeled as exhibiting signs of tension or despair, whereas these scoring ≤ 7 had been categorized as regular.
Assessment of a wholesome life-style rating
The Healthy Lifestyle Score (HLS) was calculated utilizing strategies described in earlier research [36, 37]. The rating incorporates eight modifiable life-style domains: 1) dietary consumption, 2) dietary habits, 3) sleep high quality, 4) bodily exercise, 5) smoking standing, 6) despair standing, 7) nervousness standing, and eight) psychological misery, all primarily based on established danger components for male infertility [15, 16, 20, 38]. The HLS was developed by integrating six dichotomous (0 or 1 level) and two three-level (0.0, 0.5, or 1.0 factors) life-style components, every assessed utilizing validated standards, as illustrated in Fig. 2.
Dietary high quality was assessed utilizing the HEI-2015, as beforehand described, with individuals categorized into quintiles primarily based on prior literature [36, 37]. Individuals within the higher two quintiles (This fall–Q5) had been labeled as having a healthful dietary sample and awarded 1 level within the Healthy Lifestyle Score (HLS) calculation, whereas these within the decrease three quintiles (Q1–Q3) had been assigned 0 factors. Dietary habits had been evaluated and labeled based on a longtime methodology [38]. Participants who scored 4–6 the pretested self-reported dietary behavior questionnaire had been labeled as having wholesome dietary habits and had been awarded 1 level in HLS calculation. Conversely, respondents scoring 0–3 had been recognized as exhibiting unhealthy dietary behaviors and acquired 0 factors [38]. Regarding smoking standing within the HLS development, present people who smoke had been labeled as participating in unhealthy conduct and accordingly awarded 0 factors, whereas former people who smoke and by no means people who smoke had been categorized as demonstrating wholesome conduct and allotted 1 level [37]. Psychological misery was assessed utilizing the General Health Questionnaire (GHQ). Participants scoring ≤ 3 had been labeled as having low psychological misery and awarded 1 level within the HLS, whereas these scoring ≥ 4 had been categorized as having excessive psychological misery and acquired 0 factors [34, 39]. For despair and nervousness signs, the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) was used. Participants with regular scores (≤ 7 on both subscale) had been designated as wholesome and allotted 1 level per subscale. Conversely, these exhibiting despair or nervousness signs (≥ 8 on both subscale) acquired 0 factors [35, 40].
Participants who met the HEPA-active standards had been labeled as having a wholesome exercise stage and had been awarded 1 level. Those who had been minimally lively acquired 0.5 factors, whereas inactive individuals got 0 factors within the HLS computation [41]. Participants had been assigned 1 level for good sleep high quality (PSQI rating of 0–3, indicating low-risk conduct), 0.5 factors for average sleep high quality (PSQI rating of 4–5), and 0 factors for poor sleep high quality (PSQI rating ≥ 6, reflecting high-risk conduct) [42]. By summing the scores every participant acquired for the assorted life-style parts, we constructed the full Healthy Lifestyle Score (HLS). The complete factors ranged from 0 (indicating the bottom adherence to a wholesome life-style) to eight (indicating the best adherence).
Assessment of male infertility
Semen samples had been collected from sufferers experiencing infertility after a 3-day interval of abstinence, utilizing sterile containers. The samples had been liquefied at 37 °C for 30 min earlier than evaluation. All infertility diagnoses had been performed by a board-certified andrologist, primarily based on the newest semen evaluation outcomes and the sixth version of the World Health Organization (WHO) standards [22].
Assessment of covariates
Demographic info of individuals, together with age, intercourse, schooling, length of marriage, medical historical past, alcohol consumption, and occupation, was gathered utilizing a self-reported questionnaire. Participants had been labeled as having high-risk occupations in the event that they labored in agriculture with pesticide publicity, steel smelting, battery manufacturing, plastic compound manufacturing, epoxy resin manufacturing, the oil and fuel trade, ionizing radiation, welding, or extended driving [43]. Socioeconomic standing (SES) was assessed utilizing a validated questionnaire that integrated components resembling occupation, family measurement, homeownership, variety of vehicles, possession of a pc/laptop computer, frequency of inner and worldwide journey, and household earnings. SES scores ranged from 7 to 22. All anthropometric measurements had been carried out by skilled dietitians following commonplace protocol. Body mass index (BMI) was estimated utilizing the Quetelet formulation (weight (kg) divided by the sq. of peak (m2)).
Statistical evaluation
Participants had been categorized into quartiles primarily based on their Healthy Lifestyle Score (HLS). Continuous variables are reported as imply ± SD/SE and categorical variables as frequency (share). One-way evaluation of variance (ANOVA) and the chi-square (χ2) check had been used to match steady and categorical variables HLS quartiles, respectively. Additionally, an unbiased pattern t-test and Fisher’s actual check had been employed for case–management comparisons. Multivariate logistic regression was performed to look at the affiliation between HLS and male infertility standing. As proven in Supplemental Table 1, all variance inflation components (VIFs) had been effectively under the multicollinearity threshold (VIF = 10). Odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for infertility had been calculated utilizing a crude mannequin; mannequin 1: adjusted for age and vitality consumption; mannequin 2: additional adjusted for socioeconomic standing, schooling stage, marriage length, having a high-risk occupation, and alcohol consumption; and mannequin 3: additional adjusted for BMI. Furthermore, multivariable-adjusted ORs with 95% CIs had been assessed for infertility per one-point enhance in wholesome life-style rating , modeled linearly.
We assessed the robustness of our findings to potential residual confounding utilizing E-value evaluation. The E-value quantifies the minimal energy of affiliation that an unmeasured confounder would wish to have with each the publicity and the result to totally clarify away the noticed impact estimate after adjusting for measured covariates [44, 45]. These analyses had been applied utilizing the E-value bundle (model 4.1.3) in R statistical software program (model 4.4.0). A weighted wholesome life-style rating was developed utilizing principal part evaluation (PCA) to combine the eight correlated life-style components right into a single measure. The first principal part (PC1) (or the primary issue), which defined the most important proportion of variance among the many parts, was retained to generate the rating. Weighted wholesome life-style scores had been calculated because the weighted sum of standardized life-style components, utilizing the issue loadings from PC1 as weights (Supplemental Table 2). This steady rating represents a person’s adherence to the dominant sample of wholesome life-style. For analytical functions, the rating was categorized into quartiles.
The P development throughout HLS classes was decided by treating HLS as an ordinal variable in regression fashions. Dietary habits had been characterised utilizing latent class evaluation (LCA), carried out with the free statistical software program R, model 2.15.1. All different analyses had been performed utilizing SPSS software program, model 26 (IBM, Chicago, IL). A P-value lower than 0.05 was thought-about statistically vital.
This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its authentic location you possibly can go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://rbej.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12958-025-01490-0
and if you wish to take away this text from our web site please contact us



