This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its unique location you’ll be able to go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://www.academia.edu/2997-9196/3/1/10.20935/MHealthWellB8115
and if you wish to take away this text from our website please contact us
1. Introduction
Academic efficiency, together with first-year attendance in lessons and written examination scores, is essential for college college students to have a snug expertise/life on campus [1–4]. Students’ well-being encompasses bodily, psychological, and social dimensions [5]; amongst these, psychological components similar to psychological well being, educational motivation, and sophistication motivation have been proven to be necessary contributors to educational success and well-being [6–11]. To present early help to college students experiencing difficulties with their educational efficiency, figuring out simply psychological components that affect educational success is essential for sensible causes.
One approach to help college students’ well-being via enhanced psychological functioning and educational efficiency is to assist them enhance their life-style behaviors [12–14]. Although the affect of fundamental life-style behaviors, similar to bodily exercise, weight-reduction plan, sleep habits, and psychological components, on educational efficiency has been examined [15], higher consideration should be directed towards these components in mild of recent points and analysis developments.
As for bodily exercise, we give attention to three varieties of train which have distinct results on psychological well being and cognitive perform: cardio train (AE), resistance train (RE), and adaptability train (FE) [16–21]. Additionally, constructive perceptions of participating in train are necessary for rising train participation [22–24]. Regarding weight-reduction plan, decreased breakfast skipping is important for good well being and educational efficiency [25–28]. Regarding sleep behavior, subjective sleep high quality predicts melancholy [29]. Increasing display time is a matter within the modern-day that’s related to poor bodily and psychological well being and educational efficiency [30–33]. By taking a complete perspective on these key, up to date, and more and more specialised life-style components highlighted by prior analysis, this research provides new insights into the well-being of freshman college students.
Therefore, this research comprehensively explored the psychological components that affect educational efficiency. Furthermore, it in contrast life-style traits between college students with excessive and low ranges of psychological components that considerably influenced educational outcomes, aiming to derive implications for enhancing college college students’ well-being. We hypothesized that psychological well being and motivation would have an effect on educational efficiency. Moreover, we postulated that these with larger psychological components would positively take part within the three varieties of train, have extra breakfast, and exhibit larger subjective sleep high quality and decrease display time.
2. Materials and strategies
2.1. Participants
All the contributors have been college students within the departments of dentistry, pharmaceutical sciences, nursing, social administration, scientific psychology, bodily remedy, occupational remedy, and speech–language–listening to remedy on the Health Sciences University of Hokkaido. Students within the division of dentistry participated solely within the pilot research and never in the primary research as a result of their lessons began sooner than these in some other division. The research was authorized by the Institutional Ethics Committee of the Health Sciences University of Hokkaido (protocol code 22N025026, authorized on 8 February 2023), in accordance with the rules of the most recent model of the Declaration of Helsinki. The survey was carried out in train science lessons for 1st-year college students through the second semester. Before the survey, the analysis content material was defined, and participation consent was obtained in Excel file format. To guarantee college students’ free option to take part within the analysis, it was defined that there was no drawback in not consenting to take part, and that it could not have an effect on their class efficiency. A complete of 371 respondents accomplished the survey through the specified interval and within the specified kind. Of these, 343 agreed to take part and 28 didn’t. Among those that offered consent (N = 343), 73 have been excluded from the evaluation on account of incomplete questionnaire responses. Consequently, we analyzed the info of 270 contributors (imply age: 18.73 ± 0.70 years; 183 feminine). The demographic traits of the contributors are proven in Table 1.
2.2. Measurements
This research was carried out between October 2023 and December 2023. The survey consisted of seven-day measurements and a questionnaire in a specified Excel format. Participants entered the next details about demographic traits and seven-day measurements in an Excel file. Consent for participation, intercourse (one = male, two = feminine), age, peak, and weight have been recorded. Body mass index (BMI) was calculated utilizing the next formulation: weight (kg)/peak (m)2. The train length per day (min/day) for AE, RE, and FE (actions specializing in rising muscle flexibility and vary of movement, e.g., static stretching) was recorded utilizing a questionnaire, and the entire time (min/week) for AE, RE, and FE was calculated because the frequency × each day common of train durations [32]. Perceptions of train was evaluated by a query “I am reluctant to engage in exercise,” and was rated on an 11-point scale (0: by no means; 5: impartial to 10: extraordinarily). For dietary habits, the breakfast skipping depend (counts/week) was recorded. For sleep behavior, each day sleep length (hours/day) was recorded, and each day subjective sleep high quality (feeling refreshed after awakening) was rated on an 11-point scale (0: by no means; 5: impartial to 10: extraordinarily) [32]. Daily display time (whole time spent on TV, video games, smartphones, and laptop units) was recorded (min/day) [32]. Depression ranges have been evaluated utilizing the Japanese model of the Beck Depression Inventory-II (BDI-2) questionnaire [34, 35]. Academic motivation was evaluated by a sum of 4 query gadgets referencing the ARCS mannequin [36]: “Feeling that learning is interesting,” “Feeling that learning is rewarding,” “Feeling that learning builds confidence,” and “Feeling that learning gives me satisfaction,” and every merchandise was rated on an 11-point scale (0: by no means; 5: impartial to 10: extraordinarily). A earlier research utilizing this measure reported that educational motivation was negatively correlated with breakfast skipping and display time [32]. Academic motivation refers to enthusiasm for educational pursuits generally, whereas class motivation refers to enthusiasm for college programs. Class motivation was evaluated by a sum of three query gadgets: “I try not to be absent from class,” “I try not to be late for class,” and “I try to submit my assignments on time,” and every merchandise was rated on an 11-point scale (0: by no means; 5: impartial to 10: extraordinarily). Previous research have reported associations between college students’ motivation and educational efficiency, most of which employed questionnaires with greater than ten gadgets [37, 38]. In the current research, the variety of gadgets was decreased to a few with a view to study the connection utilizing a extra sensible measure. The Cronbach’s α for the category motivation measure was 0.73.
Although universities make use of varied strategies to judge educational efficiency, evaluation via written examinations stays some of the frequent approaches. Attendance doesn’t instantly characterize college students’ educational achievement; nevertheless, it has a considerable affect on their efficiency [4, 39, 40]. Therefore, sustaining a low variety of absences and attaining excessive written examination scores are necessary for sustaining passable educational efficiency, and these variables have been used as educational indicators within the current research. The absent depend from the train science class within the first semester was recorded (counts/semester). The written examination scores for train science (content material on train habits and well being, train physiology, and protected and efficient train practices) within the first semester have been additionally recorded (factors).
2.3. Statistical evaluation
First, the technique of all measured variables have been calculated throughout all contributors. Second, a path evaluation was carried out. Third, a subgroup evaluation was carried out based mostly on class motivation. SPSS model 26 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) and R software program model 4.5 (Auckland, New Zealand) have been used for all of the statistical analyses. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
Daily or weekly averages have been calculated for AE whole time, RE whole time, FE whole time, breakfast skipping depend, subjective sleep high quality, display time, melancholy degree, educational motivation, class motivation, absent depend from class, and written examination scores for every participant.
Path evaluation was carried out utilizing the “lavaan” bundle within the R software program to deal with a attainable correlation. Model match was evaluated with root imply sq. error of approximation (RMSEA) and the comparative match index (CFI). The standards used have been CFI ≥ 0.90 and RMSEA < 0.05. Path evaluation was carried out with absent counts from the category and written examination scores as dependent variables. In the evaluation, variables associated to demographic traits, psychological well being, and motivation (intercourse, BMI, melancholy degree, educational motivation, and sophistication motivation) have been entered first after which variables that weren’t vital (p > 0.05) have been eliminated. The mannequin that totally met the mannequin match index was thought of the ultimate mannequin.
The subgroups have been divided based mostly on the worth of sophistication motivation, which was extracted as an influencing issue for educational efficiency variables within the path evaluation. Lifestyle parts have been in contrast between the subgroups. The median of sophistication motivation was 29, and contributors with a rating of 29 have been excluded (n = 24) to make sure equal group sizes [41]. The “high class motivation” group consisted of these whose class motivation was larger than the median (n = 120), and the “low class motivation” group consisted of these whose class motivation was decrease than the median (n = 126). Lifestyle behaviors, psychological well being, educational motivation, and educational efficiency have been in contrast between the subgroups utilizing unpaired t-test.
3. Results
3.1. Averages of life-style parts, psychological components, and educational outcomes
The common values for AE/RE/FE whole time, breakfast skipping depend, subjective sleep high quality, display time, melancholy degree, educational motivation, class motivation, absent depend from class, and written examination scores are proven in Table 2.
Table 2
Averages of life-style parts, psychological components, and educational outcomes.
3.2. Path evaluation
The bivariate correlation coefficient between the dependent variables, the absent depend from class and written examination scores, was −0.11 and never statistically vital (p = 0.09). In the primary mannequin, CFI = 1. 00 and RMSEA = 0.00. This yields a very good match to the info. Variables that weren’t vital (p > 0.05) have been excluded from subsequent fashions. In the ultimate mannequin (proven in Figure 1), CFI = 1. 00 and RMSEA = 0.00. This yields a very good match to the info. Table 3 lists the relative results of every variable on the dependent variable.
Figure 1
The closing mannequin of path evaluation exploring key issue for educational efficiency. Class motivation was negatively related to the variety of class absences (β = −0.30) and positively related to written examination scores (β = 0.18). ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
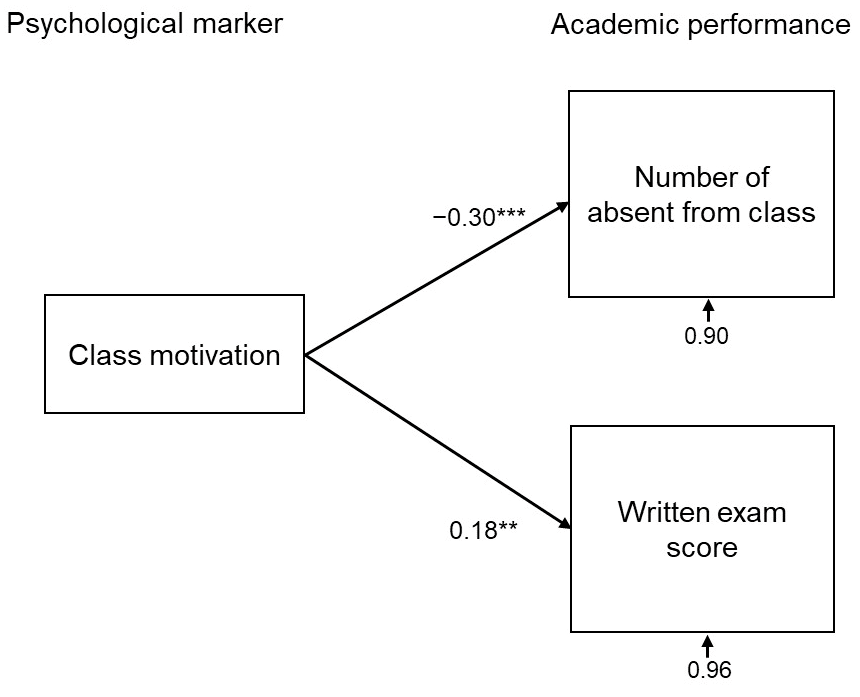
Table 3
The relative results of demographic traits, psychological well being, educational motivation, and sophistication motivation on the educational efficiency in path evaluation.
3.3. Subgroup evaluation
The excessive class motivation group confirmed considerably larger participation of FE (t(244) = 2.45, p = 0.01, d = 0.31), subjective sleep high quality (t(244) = 2.01, p = 0.04, d =0.25), educational motivation (t(244) = 6.56, p < 0.001, d = 0.83), and written examination rating (t(211) = 3.46, p < 0.001, d = 0.47) than low class motivation group. The excessive class motivation group confirmed considerably decrease reluctance to have interaction in train (t(244) = 2.89, p = 0.004, d = 0.36), breakfast skipping (t(244) = 3.93, p < 0.001, d = 0.50), display time (t(244) =2.54, p = 0.01, d = 0.32), melancholy (t(244) = 3.08, p = 0.002, d = 0.39), and absent depend from class (t(239) = 6.35, p < 0.001, d = 0.81) than low class motivation group. There was no vital distinction between teams relating to participation of AE (t(244) =0.36, p = 0.71, d = 0.04) and RE (t(244) = 1.33, p = 0.18, d = 0.16). Table 4 lists the group common of every variable.
Table 4
The comparability of life-style parts, psychological well being, motivation, and educational efficiency between subgroups based mostly on class motivation.
4. Discussion
This research aimed to comprehensively discover psychological and life-style markers that affect educational efficiency amongst college college students. We consider that class motivation is a key issue influencing educational efficiency. Subgroup evaluation revealed that the excessive class motivation group confirmed considerably larger participation in FE, subjective sleep high quality, educational motivation, written examination scores, in addition to decrease reluctance to have interaction in train, breakfast skipping, display time, melancholy, and absent depend from class than the low class motivation group.
Prior analysis has proven that motivation to check is necessary for educational efficiency [8, 9]. In this research, a easy index of sophistication motivation consisting of solely three questions was related to each class absence and examination scores. Furthermore, no vital affiliation was noticed between class absence and examination scores, indicating that methods geared toward sustaining each outcomes could also be essential somewhat than specializing in both alone. Additionally, as a result of many Japanese universities require college students to fulfill a minimal attendance requirement to be eligible for examinations, the category motivation, which confirmed relevance to each class absence and examination scores, represents a noteworthy marker. Class motivation could due to this fact function a sensible marker of college college students’ well-being via enhanced educational efficiency.
The variations in school motivation revealed variations in all kinds of life-style behaviors. First, relating to train, constructive perceptions of train and FE participation have been considerably larger within the excessive class motivation group. Positive perceptions of train may encourage train participation [22, 23]. FE, similar to static stretching, may enhance psychological well being and cognitive fatigue [20, 21]. In this research, no vital variations have been noticed between subgroups when it comes to AE and RE participation. Compared to FE, the time and gear required to implement AE and RE could have been limitations to implementation, however this stays a subject for future analysis. Although the rules of bodily exercise in Japan suggest AE and RE, they don’t present particular numerical targets for FE participation. Although FE is troublesome to quantify, and its effectiveness has not been totally verified, the present findings present the significance of FE participation.
With regard to weight-reduction plan, breakfast skipping depend was considerably decrease within the excessive class motivation group. Previous research additionally reported that breakfast skipping has unfavorable results on psychological well being and educational efficiency [25–28]. Breakfast skipping delays the rise in core physique temperature within the morning [42]. It can be related to unhealthy life-style habits (similar to smoking, playing, lack of sleep, and bodily inactivity) and psychological well being points [25]. Breakfast skipping is assumed to have a unfavorable affect on educational efficiency via its affiliation with these components.
Regarding sleep, subjective sleep high quality was considerably larger within the excessive class motivation group. Previous research additionally reported that the extent of “Feeling refreshed after awakening,” predicted melancholy and eye fatigue in cross-sectional research amongst college college students [29]. In addition to class motivation, subjective sleep high quality could also be an necessary marker of college college students’ well-being.
Regarding digital system use, display time was considerably decrease within the excessive class motivation group. Previous research reported that elevated display time negatively influences psychological well being [43] and educational motivation [32]. The use of digital display media for leisure has a unfavorable affect on educational efficiency, and this affiliation is mediated by poor sleep high quality [44]. Furthermore, the kind of digital display media used is necessary, with tv viewing and online game enjoying displaying a very unfavorable affect on educational efficiency [45].
With regard to psychological well being and motivational facets, melancholy and educational motivation emerged as variations between the subgroups. Those with excessive class motivation take note of life-style parts, similar to train, weight-reduction plan, sleep, and display time, and their best life-style could hold their psychological well being and educational motivation excessive. Although the precise causality is a topic for future research, if class motivation is low, enhancing the above life-style parts is one approach to improve class motivation and educational efficiency.
In sensible settings, an early-semester steerage session for first-year college students may inform them that class motivation is related to each educational efficiency and life-style habits by making use of the Health Belief Model [46, 47]. In this framework, instructors may clarify the mannequin’s core constructs, together with perceived susceptibility (e.g., the danger of educational underachievement through the freshman 12 months), perceived severity (e.g., the danger of educational probation or retention ensuing from early educational difficulties), perceived advantages (e.g., the advantages of sustaining excessive class motivation and wholesome life-style behaviors for educational efficiency), perceived limitations (e.g., obstacles that hinder college students from concentrating on their research), self-efficacy (e.g., profitable experiences gained via small-step behavioral adjustments), and cues to motion (e.g., steerage classes). Additionally, incorporating various tutorial codecs (e.g., peer instructing and suggestions, crossover instructing, and personalised instructing) and using digital interventions tailor-made to college students’ traits could additional improve motivation and life-style behaviors [48–50] could possibly be thought of.
This research has some limitations. First, this research used the variety of absences and take a look at scores of train science lessons as the educational efficiency measures. Paramedical college college students participated within the survey. To generalize the outcomes, additional verification is important, together with educational efficiency in different topics and amongst college students with totally different traits. Second, this research employed a sensible, unique questionnaire with a restricted variety of gadgets to cut back respondents’ burden. Future analysis ought to accumulate findings utilizing the identical instrument and additional study its validity, reliability, and utility. Third, some lacking knowledge occurred on account of incomplete questionnaire responses. Future research ought to think about additional lowering respondents’ burden and exploring approaches for dealing with lacking values. Fourth, no confounding components have been recognized. Factors similar to household atmosphere and financial standing additionally have an effect on educational efficiency and psychological well being [51, 52]. Therefore, confounding components with vital results must be thought of in future research. Finally, this research was cross-sectional in nature; due to this fact, causal relationships can’t be decided. To make clear causal relationships and mechanisms, measuring physiological indices and mixing experimental research are required in future research. For instance, it could be attainable to survey class motivation and key life-style components early within the first 12 months, implement life-style enchancment interventions for these values which might be undesirable, and confirm the consequences on educational efficiency.
5. Conclusions
Class motivation was the important thing issue influencing educational efficiency. The excessive class motivation group was in a extra favorable state than the low class motivation group in a variety of facets, together with train, weight-reduction plan, sleep habits, display time, psychological well being, motivation, and educational efficiency. This research supplies elementary data for college college students to realize well-being via enhanced educational efficiency, emphasizing the usefulness of sophistication motivation as a simple marker and the significance of enhancing their life-style behaviors.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge using DeepL Translate (DeepL SE, Cologne, Germany) and ChatGPT (GPT-5, OpenAI, San Francisco, CA, USA) for language modifying and refinement. The device was utilized to reinforce readability and scholarly tone, and all edits have been fastidiously reviewed and validated by the authors to make sure accuracy, compliance with educational requirements, and analysis integrity. The authors totally help Academia.edu Journals’ adherence to COPE pointers on AI in publication ethics and make sure that this use has been managed responsibly and ethically.
Author contributions
Conceptualization, T.F., Ok.I. and A.Y.; methodology, T.F., Ok.I. and A.Y.; software program, T.F.; validation, T.F., Ok.I. and A.Y.; formal evaluation, T.F.; investigation, T.F., Ok.I. and A.Y.; sources, T.F., Ok.I. and A.Y.; knowledge curation, T.F.; writing—unique draft preparation, T.F.; writing—evaluation and modifying, Ok.I. and A.Y.; visualization, T.F.; supervision, A.Y.; undertaking administration, A.Y. All authors have learn and agreed to the printed model of the manuscript.
Data availability assertion
The knowledge supporting the findings of this publication could be made obtainable upon request.
Institutional evaluation board assertion
The research was carried out in accordance with the rules of the Declaration of Helsinki and authorized by the Institutional Ethics Committee of the Health Sciences University of Hokkaido (protocol code: 22N025026, authorized on 8 February 2023).
Informed consent assertion
Informed consent for participation was obtained from all topics concerned within the research.
Publisher’s word
Academia.edu Journals stays impartial with regard to jurisdictional claims in printed maps and institutional affiliations. All claims expressed on this article are solely these of the authors and don’t essentially characterize these of their affiliated organizations, or these of the writer, the editors, and the reviewers. Any product that could be evaluated on this article, or declare that could be made by its producer, is just not assured or endorsed by the writer.
References
Ortiz-Lozano JM, Rua-Vieites A, Bilbao-Calabuig P, Casadesús-Fa M. University pupil retention: greatest time and knowledge to determine undergraduate college students prone to dropout. Innov Educ Teach Int. 2020;57:74–85. doi: 10.1080/14703297.2018.1502090
Kaya M, Erdem C. Students’ well-being and educational achievement: a meta-analysis research. Child Indic Res. 2021;14:1743–67. doi: 10.1007/s12187-021-09821-4
Chaudhry S, Tandon A, Shinde S, Bhattacharya A. Student psychological well-being in larger training: the position of inner workforce atmosphere, institutional, family and friends help and educational engagement. PLoS ONE. 2024;19:e0297508. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0297508
Credé M, Roch SG, Kieszczynka UM. Class attendance in school: a meta-analytic evaluation of the connection of sophistication attendance with grades and pupil traits. Rev Educ Res. 2010;80:272–95. doi: 10.3102/0034654310362998
Chemers MM, Hu L, Garcia BF. Academic self-efficacy and first 12 months school pupil efficiency and adjustment. J Educ Psychol. 2001;93:55–64. doi: 10.1037/0022-0663.93.1.55
Richardson M, Abraham C, Bond R. Psychological correlates of college college students’ educational efficiency: a scientific evaluation and meta-analysis. Psychol Bull. 2012;138:353–87. doi: 10.1037/a0026838
Fong CJ, Krou MR, Johnston-Ashton Ok, Hoff MA, Lin S, Gonzales C. LASSI’s nice journey: a meta-analysis of the training and research methods stock and educational outcomes. Educ Res Rev. 2021;34:100407. doi: 10.1016/j.edurev.2021.100407
du Toit AT, Thomson R, Page A. A scientific evaluation and meta-analysis of longitudinal research of the antecedents and penalties of wellbeing amongst college college students. Int J Wellbeing. 2022;12:163–206. doi: 10.5502/ijw.v12i2.1897
Chevrier B, Lannegrand L. The relationship between educational motivation and fundamental psychological wants throughout the freshman 12 months context: a longitudinal person-oriented method. Eur J Psychol Educ. 2022;37:921–47. doi: 10.1007/s10212-021-00569-7
La Cascia C, Maniaci G, Palummo A, Saia GF, Pinetti G, Zarbo M, et al. Healthy life and educational success in a pattern of Italian college college students. Curr Psychol. 2021;40:5115–23. doi: 10.1007/s12144-019-00401-y
Gore MN, Yeravdekar RC, Menon Ok. The affect of on-campus well being promotion actions on wholesome life-style behaviours of Indian college college students. Asia Pac J Health Manag. 2023;18:199–207. doi: 10.24083/apjhm.v18i1.1473
Roldán-Espínola L, Riera-Serra P, Roca M, García-Toro M, Coronado-Simsic V, Castro A, et al. Depression and life-style amongst college college students: a one-year follow-up research. Eur J Psychiatry. 2024;38(3):100250. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpsy.2024.100250
Trockel MT, Barnes MD, Egget DL. Health-related variables and educational efficiency amongst first-year school college students: implications for sleep and different behaviors. J Am Coll Health. 2000;49:125–31. doi: 10.1080/07448480009596294
Byun Ok, Hyodo Ok, Suwabe Ok, Ochi G, Sakairi Y, Kato M, et al. Positive impact of acute delicate train on govt perform through arousal-related prefrontal activations: an fNIRS research. Neuroimage. 2014;98:336–45. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.04.067
Wang C-C, Alderman B, Wu C-H, Chi L, Chen S-R, Chu I-H, et al. Effects of acute cardio and resistance train on cognitive perform and salivary cortisol responses. J Sport Exerc Psychol. 2019;41:73–81. doi: 10.1123/jsep.2018-0244
Tsuk S, Netz Y, Dunsky A, Zeev A, Carasso R, Dwolatzky T, et al. The acute impact of train on govt perform and a focus: resistance versus cardio train. Adv Cogn Psychol. 2019;15:208–15. doi: 10.5709/acp-0269-7
Chekroud SR, Gueorguieva R, Zheutlin AB, Paulus M, Krumholz HM, Krystal JH, et al. Association between bodily train and psychological well being in 1·2 million people within the USA between 2011 and 2015: a cross-sectional research. Lancet Psychiatry. 2018;5:739–46. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(18)30227-X
Sudo M, Ando S. Effects of acute stretching on cognitive perform and temper states of bodily inactive younger adults. Percept Mot Skills. 2020;127:142–53. doi: 10.1177/0031512519888304
Fukuie T, Inoue Ok, Yamaguchi A. Static stretching has an assuaging impact on cognitive fatigue on account of cognitive work with visible show terminal. Sport Sci Health. 2025;21:2349–59. doi: 10.1007/s11332-025-01450-6
Allender S, Cowburn G, Foster C. Understanding participation in sport and bodily exercise amongst youngsters and adults: a evaluation of qualitative research. Health Educ Res. 2006;21:826–35. doi: 10.1093/her/cyl063
Salmon J, Owen N, Crawford D, Bauman A, Sallis JF. Physical exercise and sedentary conduct: a population-based research of limitations, enjoyment, and choice. Health Psychol. 2003;22:178–88. doi: 10.1037/0278-6133.22.2.178
Fukuie T, Inoue Ok, Yamaguchi A. Influencing components and physiological parameters of psychological hurdle and motivation instantly previous to train. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2024;65:286–96. doi: 10.23736/S0022-4707.24.16055-0
Pengpid S, Peltzer Ok. Skipping breakfast and its affiliation with well being threat behaviour and psychological well being amongst college college students in 28 nations. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020;13:2889–97. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S241670
Adolphus Ok, Lawton CL, Dye L. The results of breakfast on conduct and educational efficiency in youngsters and adolescents. Front Hum Neurosci. 2013;7:425. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2013.00425
Peprah P, Oduro MS, Boakye PA, Morgan AK. Association between breakfast skipping and psychosomatic signs amongst Canadian adolescents. Eur J Pediatr. 2024;183:1607–17. doi: 10.1007/s00431-023-05392-4
Burrows T, Goldman S, Pursey Ok, Lim R. Is there an affiliation between dietary consumption and educational achievement: a scientific evaluation. J Hum Nutr Diet. 2017;30:117–40. doi: 10.1111/jhn.12407
Fukuie T, Inoue Ok, Yamaguchi A. Lifestyle parts for enhancing psychological and bodily well being in Japanese college college students: subjective sleep high quality is a standard key issue. Am J Lifestyle Med. 2024;18:303–12. doi: 10.1177/15598276231156546
Randjelovic P, Stojiljkovic N, Radulovic N, Stojanovic N, Ilic I. Problematic smartphone use, display time and chronotype correlations in college college students. Eur Addict Res. 2021;27:67–74. doi: 10.1159/000506738
Dol KS. Fatigue and ache associated to web utilization amongst college college students. J Phys Ther Sci. 2016;28:1233–7. doi: 10.1589/jpts.28.1233
Fukuie T, Inoue Ok, Yamaguchi A. Lifestyle and well-being of college college students in Japan: a cross-sectional research. Acad Ment Health Wellbeing. 2024;1:1–11. doi: 10.20935/MHealthWellB7327
Kassaw C, Demareva V. Determinants of educational achievement amongst larger training college students present in low useful resource setting, a scientific evaluation. PLoS ONE. 2023;18:e0294585. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0294585
Kojima M, Furukawa TA, Takahashi H, Kawai M, Nagaya T, Tokudome S. Cross-cultural validation of the beck melancholy inventory-II in Japan. Psychiatry Res. 2002;110:291–9. doi: 10.1016/S0165-1781(02)00106-3
Beck AT, Steer RA, Ball R, Ranieri WF. Comparison of beck melancholy inventories-IA and-II in psychiatric outpatients. J Pers Assess. 1996;67:588–97. doi: 10.1207/s15327752jpa6703_13
Keller JM. Development and use of the ARCS mannequin of tutorial design. J Instr Dev. 1987;10:2–10. doi: 10.1007/BF02905780
Bakar KA, Tarmizi RA, Mahyuddin R, Elias H, Luan WS, Ayub AFM. Relationships between college college students’ achievement motivation, perspective and educational efficiency in Malaysia. Procedia Soc Behav Sci. 2010;2:4906–10. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2010.03.793
Afzal H, Ali I, Aslam Khan M, Hamid Ok. A research of college college students’ motivation and its relationship with their educational efficiency. Int J Bus Manag. 2010;5:80–8. doi: 10.5539/ijbm.v5n4p80
Dey I. Class attendance and educational efficiency: a subgroup evaluation. Int Rev Econ Educ. 2018;28:29–40. doi: 10.1016/j.iree.2018.03.003
Lukkarinen A, Koivukangas P, Seppälä T. Relationship between class attendance and pupil efficiency. Procedia Soc Behav Sci. 2016;228:341–7. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2016.07.051
DeCoster J, Gallucci M, Iselin AMR. Best practices for utilizing median splits, synthetic categorization, and their steady options. J Exp Psychopathol. 2011;2:197–209. doi: 10.5127/jep.008310
Ogata H, Horie M, Kayaba M, Tanaka Y, Ando A, Park I, et al. Skipping breakfast for six days delayed the circadian rhythm of the physique temperature with out altering clock gene expression in human leukocytes. Nutrients. 2020;12:2797. doi: 10.3390/nu12092797
Wu X, Tao S, Zhang Y, Zhang S, Tao F. Low bodily exercise and excessive display time can improve the dangers of psychological well being issues and poor sleep high quality amongst Chinese school college students. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0119607. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119607
Mao Y, Xie B, Chen B, Cai Y, Wu J, Zhang J, et al. Mediating impact of sleep high quality on the connection between digital display media use and educational efficiency amongst school college students. Nat Sci Sleep. 2022;14:323–34. doi: 10.2147/NSS.S346851
Adelantado-Renau M, Moliner-Urdiales D, Cavero-Redondo I, Beltran-Valls MR, Martínez-Vizcaíno V, Álvarez-Bueno C. Association between display media use and educational efficiency amongst youngsters and adolescents. JAMA Pediatr. 2019;173:1058. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.3176
Li H, Zhang J, Wang L, Yang T, Yang Y. A well being promoting-lifestyle prediction mannequin for dementia prevention amongst Chinese adults: based mostly on the well being perception mannequin. BMC Public Health. 2022;22:2450. doi: 10.1186/s12889-022-14828-9
Çiftci N, Kadıoğlu H. The impact of the well being perception model-based instructional program on bodily exercise beliefs and behaviors of college college students. J Public Health. 2023;31:1981–8. doi: 10.1007/s10389-022-01776-2
Åsberg Ok, Eldh AC, Löf M, Bendtsen M. “Simply complicated”: uncovering the processes of life-style conduct change amongst school and college college students with entry to a digital a number of life-style intervention. Digit Health. 2024;10:20552076241245905. doi: 10.1177/20552076241245905
Daniel Ok, Msambwa MM, Antony F, Wan X. Motivate college students for higher educational achievement: a scientific evaluation of blended progressive instructing and its affect on studying. Comput Appl Eng Educ. 2024;32(4):e22733. doi: 10.1002/cae.22733
Torbergsen H, Utvær BK, Haugan G. Nursing college students’ perceived autonomy-support by academics impacts their intrinsic motivation, research effort, and perceived studying outcomes. Learn Motiv. 2023;81:101856. doi: 10.1016/j.lmot.2022.101856
Wintre MG, Dilouya B, Pancer MM, Pratt MW, Birnie-Lefcovitch S, Polivy J, et al. Academic achievement in first-year college: who maintains their highschool common? High Educ. 2011;62:467–81. doi: 10.1007/s10734-010-9399-2
Mofatteh M. Risk components related to stress, anxiousness, and melancholy amongst college undergraduate college students. AIMS Public Health. 2021;8:36–65. doi: 10.3934/publichealth.2021004
This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its unique location you’ll be able to go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://www.academia.edu/2997-9196/3/1/10.20935/MHealthWellB8115
and if you wish to take away this text from our website please contact us



