This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its unique location you possibly can go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://mashable.com/article/hubble-telescope-dark-matter-galaxy-discovery-image
and if you wish to take away this text from our web site please contact us
Astronomers have noticed one thing that hardly glows but holds a good group of star clusters collectively, pointing to a hidden galaxy that nearly vanishes into the background of area.
The discovery started with 4 lonely globular clusters — dense balls of stars — sitting unusually shut to one another within the Perseus galaxy cluster, 300 million light-years away. Normally, these clusters orbit inside galaxies. Alone, they drift aside over time. Instead, this group stayed tightly packed, suggesting a robust gravitational anchor.
So the group requested a easy query: Could 4 clusters simply randomly line up in the identical spot? Scientists ran statistical exams and located that extraordinarily unlikely. Something large needed to be holding the clusters collectively.
Researchers now imagine this object, Candidate Dark Galaxy-2, or CDG-2, may very well be some of the darkish matter-dominated galaxies ever discovered. Dark matter is a mysterious materials within the universe that does not shine or work together with mild.
“This is the first galaxy detected solely through its globular cluster population,” mentioned David Li, a University of Toronto astrostatistics researcher and lead writer of the research, in a statement.
NASA will retest Artemis 2 moon rocket after discovering fueling points
The findings, which seem in The Astrophysical Journal Letters, invite the query of simply what number of different dim galaxies are on the market. Astronomers depend on seen starlight to seek out galaxies, but when galaxies will be extraordinarily faint, many might go undetected. Such an oversight might imply the estimates for what number of galaxies fill the cosmos are woefully inaccurate. But the group’s approach could enable for the invention of extra galaxies lurking within the shadows.
Mashable Light Speed
Researchers analyzed photographs of CDG-2 from NASA‘s Hubble Space Telescope, the European Space Agency’s Euclid area observatory, and the Japanese Subaru Telescope in Hawaii. At first look, they noticed no apparent galaxy. The space regarded almost empty aside from the clusters themselves.
While CDG-2 seems to have 4 globular clusters, the Milky Way has over 150. And the mysterious object dimly shines with the sunshine of solely 6 million suns, a pittance in comparison with the 20 billion or so of our personal galaxy.
Don’t miss out on our newest tales: Add Mashable as a trusted information supply in Google.
Regardless, it behaved like a galaxy, and its objects moved and clustered in a method that demanded an unseen gravitational supply.
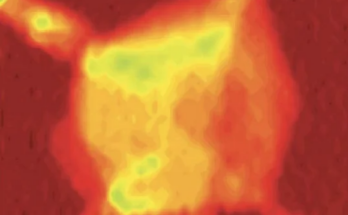
It wasn’t till astronomers stacked a number of Hubble photographs — layering them to maximise very dim indicators — that they noticed a tender glow surrounding the cluster group. The glow matched the place and form of the cluster grouping, ruling out digital camera noise or picture errors.
This Tweet is currently unavailable. It might be loading or has been removed.
Rough estimates recommend that 99 % of CDG-2’s mass — almost all of it — comes from darkish matter.
Scientists have a lot to find out about galaxies suspected of being primarily made from darkish matter. A paper revealed final 12 months on Segue 1, a dwarf galaxy considered darkish matter-dominated, discovered that it was hiding a supermassive black gap, a heavy cosmic object that can also be invisible. It’s unclear how the black gap’s results had been missed in prior research.
This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its unique location you possibly can go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://mashable.com/article/hubble-telescope-dark-matter-galaxy-discovery-image
and if you wish to take away this text from our web site please contact us