This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its authentic location you possibly can go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://oncodaily.com/oncolibrary/total-body-photography
and if you wish to take away this text from our website please contact us
Skin most cancers is the commonest and quickest rising most cancers kind globally, with melanoma inflicting nearly all of pores and skin most cancers deaths. Each 12 months, hundreds of thousands are identified, and the frequency continues to rise, presenting a significant public well being burden. According to the American Cancer Society, in 2025 greater than 100000 new melanoma instances can be identified within the United States alone, and about 8000 identified sufferers are anticipated to die, majority of them being males. Alarmingly, each hour, almost two individuals die of melanoma within the U.S. These statistics spotlight the important want for improved surveillance and early detection methods (American Cancer Society, Key Statistics for Melanoma Skin Cancer, 2025).
Total Body Photography and Automated Lesion Mapping are rising as highly effective instruments to reinforce early detection and steady monitoring of pores and skin most cancers, enhancing affected person outcomes.

Photo:Depositphotos
How to Improve Survival Outcomes in Melanoma?
As with many cancers, early detection is the cornerstone of efficient melanoma administration. When caught in its earliest levels, melanoma has a five-year survival charge of as much as 99%. (American Cancer Society, Key Statistics for Melanoma Skin Cancer, 2025). There are two primary approaches used for early detection: population-based screening and focused screening. Population-based screening contains everybody no matter particular person threat. While complete, this technique can impose a considerable monetary burden on healthcare techniques because of the giant variety of low-risk people screened. In distinction, focused screening focuses on people at elevated threat of creating melanoma, reminiscent of these with a household historical past, quite a few or atypical moles, or truthful pores and skin—leading to a better prevalence of identified instances.
This method is extensively used and prioritized, as it could enhance early melanoma detection charges, improve affected person outcomes, and optimize the usage of healthcare assets (Hornung A, et al. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021).
What is Skin Surveillance and Why is it Important?
Skin surveillance facilitates the well timed identification and monitoring of suspicious or altering lesions. This is particularly important in melanoma, the place early prognosis could be lifesaving. The 5-year relative survival charge for melanoma pores and skin most cancers is roughly 95% total, reaching almost 100% when detected at a localized stage earlier than spreading. However, survival drops considerably with regional or distant unfold, underscoring the important function of early detection via systematic surveillance (SEER Cancer Stat Facts: National Cancer Institute, 2025).
Certain populations—together with people with lighter pores and skin tones, these with intense or repeated solar publicity or sunburns, individuals with private or household historical past of pores and skin most cancers, sure racial and ethnic teams, and immunosuppressed sufferers—are at increased threat for aggressive pores and skin malignancies, making surveillance important for these susceptible teams (Erdmann et al.,Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2021).
Moreover, proof reveals that melanoma detected throughout routine pores and skin checks by healthcare professionals reduces mortality threat by 32% in comparison with self-detection, highlighting the life-saving influence of proactive pores and skin monitoring (Melanoma Institute Australia, 2021). As pores and skin most cancers charges proceed to rise, with over 212,000 new instances of melanoma anticipated within the U.S. in 2025 alone, pores and skin surveillance stays a necessary public well being measure for early intervention and improved outcomes.
What’s Missing in Traditional Skin Exams?
Traditional visible examination and dermoscopy are key parts of detecting pores and skin most cancers and have been used as a main diagnosing instrument for a few years. Despite the provision of assorted detection strategies, routine pores and skin surveillance nonetheless relies on visible assessments, however these strategies have their limitations.
Visual exams are sometimes step one, however they’ll range quite a bit relying on the physician’s expertise and judgment. Dermatologists assess lesions based mostly on options reminiscent of form, shade, and dimension adjustments, however the refined resemblance between benign and malignant lesions typically makes it difficult to distinguish between the 2. This results in variability in diagnostic accuracy, potential missed diagnoses of early or atypical cancers, and pointless biopsies of benign lesions, rising affected person burden and healthcare prices.

Photo:Depositphotos
Dermoscopy is a more moderen technique, which boosts the medical examination by magnifying lesion particulars and revealing sub-surface constructions, enhancing diagnostic precision. However, this diagnostic technique requires a skilled specialist with important expertise in sample recognition. Deramoscopy could not image deeper constructions because it permits visualization of a given pores and skin lesion solely to the extent of the papillary dermis. Furthermore, dermoscopy is time-consuming and could also be much less sensible for sufferers with quite a few lesions and restricted mobility (Arige S. et al., Biomed Pharmacol J. 2025; Jennifer Y. Chen et al, JAMA Dermatology, 2025).
This is why the sector is quickly advancing in new diagnostic applied sciences like whole physique images and automatic lesion mapping, which promise to rework pores and skin most cancers screening and follow-up by rising accuracy, reproducibility, and effectivity.
What is Total Body Photography (TBP)?
Total Body Photography, also called Whole-Body imaging or mole mapping, is a sophisticated, non-invasive diagnostic instrument used to detect pores and skin most cancers. This method creates a complete visible file of a affected person’s pores and skin, from head to toe, by taking high-resolution photographs of your complete pores and skin floor. These data are sometimes saved, permitting clinicians to match subsequent photographs to the baseline to determine adjustments.
TBP is completed by skilled nurses, who information sufferers to standing in standardized poses whereas the machine takes the images. This step takes usually 15-Half-hour and supplies high-resolution photographs which are saved to create a digital map of pores and skin, the place each mole and discoloration is sized and saved. Review of this map is completed by dermatologists and AI applied sciences (Melanoma Institute Australia, 2022; The Woods Medical Centre, 2025).
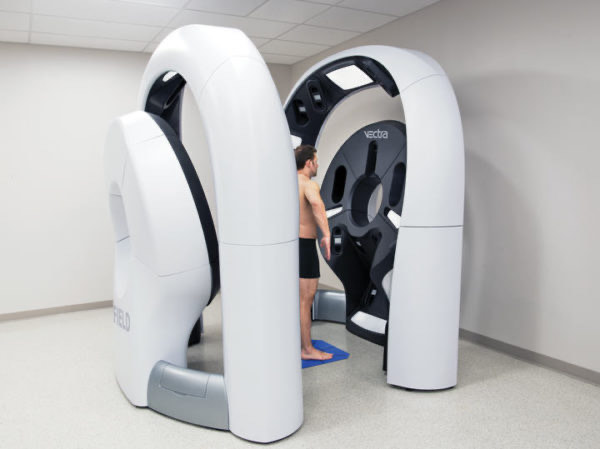
Photo of TBP process -(Machine by Canfield Scientific)
Total Body Photography (TBP) could be carried out for almost anybody, however it’s notably really helpful for individuals with a excessive variety of moles (typically over 100), moles which are unusually giant, irregular in form or shade, or situated in areas which are exhausting to observe, such because the again. TBP provides a visible and goal method to monitoring pores and skin adjustments.
How have TBP Machines Progressed?
The origins of Total Body Photography (TBP) date again to the Nineties, when imaging concerned a affected person standing in opposition to a plain wall whereas a specialist manually captured pictures utilizing a flash digicam. These photographs have been saved in sufferers’ medical data for longitudinal evaluation by dermatologists (DermEngine, 2019). Over time, TBP developed from this 2D medical images method, which required guide posing that was time-consuming, difficult for sufferers with restricted mobility, and labor-intensive (A. Ferreirinha et al., Actas Dermosifiliogr, 2025).
Future developments led to 3D TBP techniques that quickly and routinely seize high-resolution, standardized whole-body photographs inside seconds, overcoming many limitations of conventional 2D images. For instance, the VECTRA WB360 system makes use of 92 cameras organized across the affected person to provide an in depth 3D pores and skin floor mannequin inside a couple of seconds, whereas 2D techniques may take as much as an hour. (Clare A Primiero et al., Frontiers in Medicine, 2024). These fashionable 3D techniques seize each shade photographs and depth information concurrently, enabling correct illustration of pure pores and skin contours and folds, which enhance lesion visualization and monitoring, notably in difficult-to-photograph areas.
More not too long ago, automated whole physique mapping built-in with synthetic intelligence (AI) has emerged to reinforce lesion detection accuracy and cut back diagnostic variability (A. Ferreirinha et al., Actas Dermosifiliogr, 2025).
Can AI Detect Skin Cancer?
Artificial intelligence (AI), notably via convolutional neural networks (CNNs), has turn out to be an efficient instrument throughout medical specialties—together with radiology, cardiology, ophthalmology, and dermatology (Bohr et al., Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare, 2020). Sometimes, AI use in dermatology has even outperformed particular person specialists in figuring out melanoma, as a research from 2017 counsel:
“A single deep convolutional neural network, trained end-to-end on a large dataset of clinical images, can classify skin lesions—including keratinocyte carcinomas and melanoma—with accuracy comparable to that of 21 board-certified dermatologists.” – Andre Esteva et al., Nature, 2017.
Recent analysis has additionally more and more supported the usage of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and its algorithms in enhancing pores and skin most cancers detection, notably when mixed with Total Body Photography (TBP). A notable 2024 research carried out throughout two medical facilities gathered complete medical information, together with hundreds of TBP photographs alongside detailed patient-level metadata reminiscent of particular person threat components and phenotypic traits. This wealthy dataset was annotated to facilitate the event and validation of AI-based instruments able to offering a holistic evaluation — not solely of particular person pores and skin lesions but additionally of total affected person threat profiles (Clare A Primiero et al., Frontiers in Medicine, 2024).
The research outcomes confirmed that AI help considerably improved diagnostic accuracy in pores and skin most cancers detection throughout healthcare practitioners of all ranges, rising each sensitivity and specificity. Practitioners utilizing AI steering identified pores and skin cancers with about 81.1% sensitivity and 86.1% specificity, in comparison with 75% sensitivity and 81.5% specificity with out AI. The biggest profit was noticed in non-specialists reminiscent of main care medical doctors and nurse practitioners, who improved diagnostic accuracy by roughly 11-13 proportion factors with AI assist. These outcomes display AI’s potential to reinforce pores and skin most cancers detection accuracy, cut back diagnostic errors, and assist clinicians in early melanoma identification and monitoring when built-in with superior TBP imaging (Krista Conger, Stanford Medicine, 2024).
FDA-Approved AI Devices For Skin Cancer Detection
The first AI-enabled medical gadget approved by the FDA for pores and skin most cancers detection in main care is DermaSensor. This gadget assists non-specialists in assessing suspicious pores and skin lesions for melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma in sufferers aged 40 and older. It has a sensitivity of about 95.5%, increased than main care physicians alone, however comparatively decrease specificity (~20.7%), which can lead to extra false positives (Laura Okay Ferris et al., J Prim Care Community Health. 2025; Kaushik P. Venkatesh et al, npj Digital Medicine, 2024).
Other FDA-approved AI dermatology gadgets embody MelaFind and NeviSense, that are specialised instruments primarily utilized by dermatologists. MelaFind, permitted through the Premarket Approval (PMA) pathway, was discontinued because of low specificity inflicting pointless biopsies. NeviSense stays in the marketplace with excessive sensitivity but additionally comparatively low specificity (Nahm WJ et al., Int J Dermatol., 2025; Useini V et al., Sci Rep., 2024).
What Are the Challenges with AI in Dermatology?
While synthetic intelligence provides beneficial alternatives for dermatology, a number of necessary challenges stay. One main difficulty is bias within the coaching datasets, lots of which underrepresent individuals with darker pores and skin tones and may result in decreased diagnostic accuracy and widen present disparities in care. Another concern is the dearth of transparency in how most AI techniques truly work. Deep studying fashions typically operate like “black boxes,” making it exhausting for clinicians to know or clarify why a specific advice was made.
This could make it tougher to construct belief and slows down medical adoption. Generalizability can be an actual problem. AI instruments that carry out properly in a single setting won’t work as precisely in one other—particularly if the inhabitants, pores and skin sorts, or imaging strategies differ. Even past the expertise itself, there are sensible limitations to utilizing AI in on a regular basis observe.
These embody the necessity for giant, well-annotated datasets, affected person privateness issues, excessive growth prices, and the issue of integrating new instruments into present medical workflows. Moving ahead, it will likely be necessary to give attention to constructing AI techniques that aren’t solely correct, but additionally moral, clear, and simple to make use of. That means coaching fashions on various populations, making them interpretable for clinicians, and guaranteeing they are often easily built-in into real-world care (Farheen Tafti et al., IP Indian Journal of Clinical and Experimental Dermatology, 2025; Andrzej Grzybowski et al., Clinics in Dermatology, 2024).
What is Automated Lesion Mapping?
Automated lesion mapping (ALM) refers to the usage of software program instruments to determine, label, and observe pores and skin lesions—reminiscent of moles—throughout your complete physique. It is commonly carried out via whole physique images or different imaging strategies. These techniques generate a visible “map” of pores and skin lesions, both on a digital physique mannequin or 2D schematic, enabling clinicians to observe the quantity, dimension, form, and site of lesions over time. This visible documentation helps early detection of suspicious adjustments and enhances long-term follow-up care (Bell Raj Eapen et al., JMIR Dermatol 2020; Zhouxiao Li et al., J Clin Med. 2022).
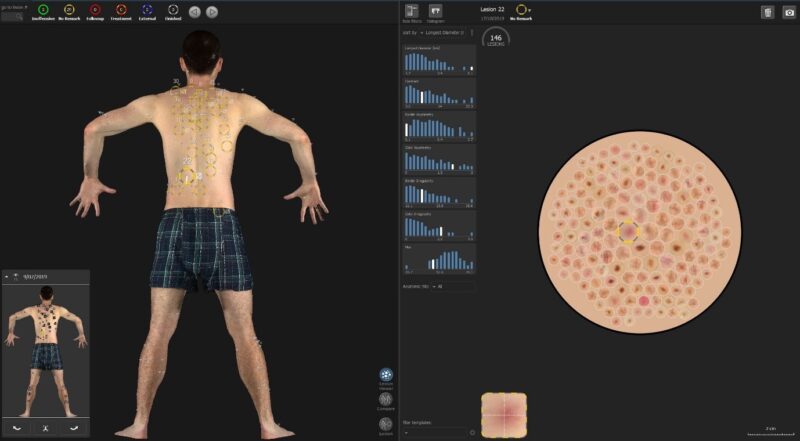
Images from the Vectra 3D Skin Imaging System, supply The University of Queensland , Australia.
To higher perceive the worth of ALM in whole physique imaging, it’s useful to contemplate how pores and skin most cancers is usually identified with out such expertise. Dermatologists depend on a variety of descriptive phrases to categorise pores and skin lesions, assessing traits reminiscent of shade, form, dimension, location, and distribution. In the case of melanoma, prognosis typically follows the extensively adopted ABCDE rule: A for asymmetry, B for border irregularity, C for shade variation, D for diameter (usually >6mm) and E for Evolving (American Cancer Society, 2025).
While this technique is efficient, it’s time-consuming—particularly contemplating that the typical particular person has as much as 40 moles (National Cancer Institute, 2022). For a single affected person, manually documenting and evaluating every lesion throughout the physique can take hours, even for skilled dermatologists.
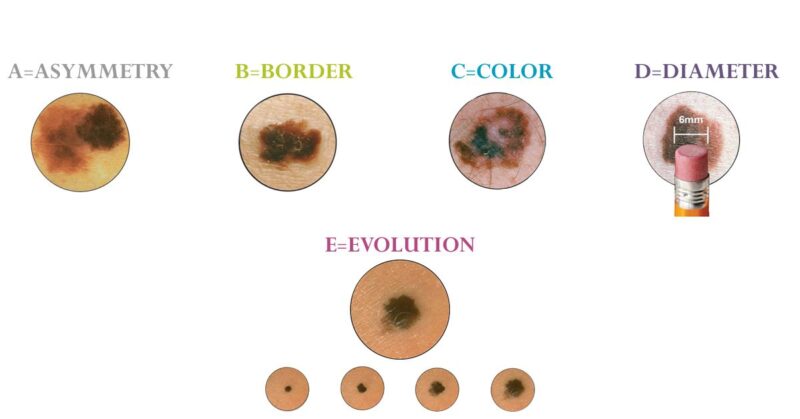
Photo: Iamatmelanoma.org
This is the place synthetic intelligence (AI) performs a transformative function. A latest literature evaluation by Zhouxiao Li and colleagues (2022) systematically analyzed research throughout a number of databases specializing in AI-assisted picture evaluation in dermatology. Authors observe that AI techniques can analyze pores and skin lesion options extra effectively and objectively than human observers. Morphological phrases generally utilized by dermatologists could be annotated and fed into specialised databases permitting AI instruments to acknowledge and retrieve details about beforehand documented lesions inside seconds (Zhouxiao Li et al., J Clin Med. 2022).
What are the Benefits of TBP over Traditional Skin Exams?
The integration of Total Body Photography (TBP) with Automated Lesion Mapping (ALM) provides many medical advantages, making it a extremely beneficial instrument for pores and skin most cancers detection and monitoring in dermatology practices.
- Early detection: This is the important thing issue figuring out survival charge of melanoma sufferers. By analyzing the entire physique, TBP facilitates the early detection of quiet killers in a non-invasive stage. Multiple research present that detection of melanoma charges have elevated with the usage of Total physique images (Annkathrin Hornung et al., Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021).
- Improved Monitoring: By capturing and storing photographs after every process, Total Body Photography (TBP) helps to note the adjustments in suspicious lesions and helps ongoing monitoring (Annkathrin Hornung et al., Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021).
- Minimization of unneeded procedures: TBP helps keep away from pointless procedures by lowering the variety of biopsies and removals of benign (non-cancerous) lesions, saving prices and minimizing affected person stress. (Melanoma Institute Australia, 2022)
- Comfortable Examinations: TBP is a fast and non-invasive process that primarily causes no disruption to sufferers bodily and psychological well-being. (On level pores and skin most cancers clinic)
- High Accuracy: Automated whole physique mapping techniques detect over 90% of clinically related melanocytic lesions recognized by knowledgeable dermatologists, together with all new or modified lesions throughout follow-up (Julia Okay Winkler et al., Elsevier, 2024).
- Efficiency and time-saving: These techniques can full a full baseline examination in about 14 minutes, considerably sooner than conventional guide strategies, lowering clinician workload whereas sustaining thorough pores and skin protection (Julia Okay Winkler et al., Elsevier, 2024).
What Role Can Total Body Photography Play in Rural Areas?
3D Total Body Photography (TBP) has the potential to considerably enhance entry to dermatology companies in distant and rural areas, the place melanoma charges are excessive however entry to care is restricted. This is especially related in international locations like Australia, the place many high-risk people stay in underserved communities with minimal entry to dermatologic care (Li et al., Frontiers in Medicine, 2018).
By enabling skilled native healthcare suppliers like nurses or common practitioners to seize standardized pores and skin photographs, these pictures could be transmitted securely to distant dermatologists for analysis through teledermatology. This mannequin helps lighten the scarcity of dermatology specialists in rural settings, providing sufferers knowledgeable evaluation with out the necessity for long-distance journey (Coustasse et al., Telemedicine and e-Health, 2019). In this manner, TBP successfully bridges the entry hole created by geographic isolation.
While challenges reminiscent of tools prices, digital infrastructure, and information privateness issues stay, profitable integration of TBP into rural healthcare techniques may drastically improve early pores and skin most cancers detection and monitoring, making specialist-level care extra equitable and accessible (The University of Queensland, 2024).
What are the Limitations of TBP?
Total Body Photography (TBP) with AI integration brings necessary advantages, but it surely additionally comes with a number of limitations that may make widespread use difficult. Cost is without doubt one of the primary issues—particularly for most cancers facilities with restricted budgets. High-end TBP techniques, notably these with 3D imaging, are costly, take up plenty of area, and require robust IT infrastructure to retailer and handle the big picture recordsdata they produce (Li et al., Frontiers in Medicine, 2018). There are additionally privateness and information safety issues, since TBP entails taking full-body photographs, typically whereas sufferers are sporting minimal clothes. This raises questions on affected person consent, safe storage, and the sensitivity of medical picture information (Primiero et al., Frontiers in Medicine, 2024).
Another limitation is that some areas of the physique—just like the scalp, genital areas, palms, soles, pores and skin folds, and different hard-to-photograph spots—are tough to seize precisely. As a end result, melanomas in these places could also be missed (Melanoma Institute Australia, 2022). TBP may wrestle with detecting hypopigmented melanomas, which account for round 2–8% of instances. These lighter or non-pigmented lesions might not be picked up as simply by the imaging techniques as darker ones (Li et al., Frontiers in Medicine, 2018). In youthful sufferers, one other difficulty is the upper charge of pointless biopsies, since regular mole progress is perhaps mistaken for a malignancy (Melanoma Institute Australia, 2022).
Finally, TBP normally requires common follow-up—yearly or biannually for most individuals, and each 3 to six months for these at excessive threat. These ongoing appointments demand time and assets, each from sufferers and clinics, and are sometimes missed because of busy schedules or sensible limitations (The Woods Medical Center, 2025).
What’s Next in AI and Skin Surveillance?
Future developments in pores and skin surveillance are more likely to give attention to making synthetic intelligence extra clear and simpler to know. By combining genetic information and medical historical past researchers hope to construct smarter, extra customized instruments for pores and skin monitoring. New applied sciences, reminiscent of smartphone-compatible whole physique images (TBP) and teledermatology platforms, may additionally play essential roles for individuals in distant or underserved areas to entry care. At the identical time, strategies like federated studying, which permit algorithms to study from information with out shifting it from safe places, could assist shield affected person privateness whereas nonetheless enhancing the accuracy of those techniques.
Photo: Depositphotos
Smartphone-Compatible Total Body Photography (TBP)
A rising variety of cellular purposes at the moment are being developed to help within the early detection of pores and skin most cancers. One such instance is SkinVision, a CE-marked medical gadget in Europe that makes use of machine studying to evaluate photographs of pores and skin lesions and categorize threat ranges (low, low with monitoring, or excessive). The app permits customers to observe adjustments over time and at the moment helps greater than 2 million customers globally. Recent research report that SkinVision detects roughly 95% of pores and skin most cancers instances (SkinVision – Skin most cancers detection app., 2025).
Similarly, instruments reminiscent of SkinScreener, MoleMapper, and SkinIO supply comparable options. SkinIO, for instance, employs whole physique images to seize complete pores and skin imagery, which is then reviewed remotely by board-certified dermatologists who notify customers if follow-up is really helpful.
While these purposes can empower customers and assist early detection, it’s important to notice that neither of them are FDA-approved but and shouldn’t be thought-about a substitute for medical dermatological analysis.
The Future Vision of Skin Cancer Monitoring
Ultimately, the way forward for pores and skin most cancers monitoring will should be centered round sufferers’ wants and experiences. This means designing applied sciences that incorporate person suggestions, present clear directions, and are accessible throughout completely different socioeconomic and geographic backgrounds. Tools that mix pores and skin imaging with particular person medical historical past—reminiscent of household historical past of melanoma or identified genetic mutations—may assist medical doctors supply extra customized threat assessments and follow-up plans (Nahm et al., Int J Dermatol, 2025).
For these applied sciences to be safely built-in into medical care, they need to undergo rigorous analysis, not solely in managed trials but additionally in real-world settings. Regulatory companies just like the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) are beginning to undertake structured frameworks that assist the protected rollout and long-term monitoring of AI-powered instruments in healthcare. For occasion, fashions such because the AI-Medical Device Risk Stratification Framework have been proposed to categorize the danger stage of various digital instruments and information regulatory oversight (FDA, EMA regulatory tips, 2024-2025).
Yet, equity stays a significant concern. Many present pores and skin picture datasets embody principally lighter pores and skin tones, which might result in decreased diagnostic accuracy for individuals with darker pores and skin. This imbalance may widen present well being disparities if not addressed (Courtney M. Heldreth et al., ACM Journal on Responsible Computing, 2024). Global efforts—just like the Skin Image Database for Equity (SIDE) and the Global Skin Image Dataset Project—at the moment are working to construct extra various and consultant datasets to make sure that new applied sciences serve all populations successfully (Ghorbani et al., MICCAI, 2024).
Importantly, these instruments aren’t meant to interchange medical professionals. Instead, they’re designed to assist clinicians by dealing with routine duties like figuring out adjustments in moles or organizing follow-up suggestions. This approach, dermatologists can focus their time and a focus on advanced instances, decision-making, and connecting with their sufferers. If designed and carried out thoughtfully, these applied sciences may enhance each the effectivity of pores and skin most cancers screening and the standard of care delivered to sufferers (Nahm et al., Int J Dermatol, 2025).
You Can Also Read Melanoma (Skin Cancer): Symptoms, Causes, Stages, Diagnosis and Treatment by OncoDaily
You Can Also Listen 50¢ Soap, Skin Cancer, and TIME’s Kid of the Year – Myths & Facts: OncoDaily DeepDive
Renaissance Portraits as Early Dermatological Records
Renaissance portraits function among the earliest unintended lesion maps, capturing visible data of pores and skin circumstances centuries earlier than fashionable dermatological instruments like dermoscopy and whole physique images existed. Artists of that period painted detailed human topics, inadvertently documenting varied pores and skin lesions and circumstances that as we speak’s dermatologists can interpret via a medical lens (Amit Om et al., J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2018).
For instance, Renaissance artwork typically depicted infectious pores and skin illnesses reminiscent of erysipelas (“St. Anthony’s fire”) and smallpox, with seen plaques or lesions proven on topics’ pores and skin. Artists additionally unintentionally captured neoplastic (tumor) circumstances like benign nevi (moles), malignant growths, and pigmentary adjustments. Here are few examples:
Charles IV of Spain and His Family” by Francisco Goya
In this royal group portrait, Goya depicts the King’s sister, Infanta María Josefa (fourth from the left), with a darkish pigmented mark on her brow that seems suspicious. While many artists of the period may need hid such an imperfection, Goya’s dedication to realism meant capturing each element. In doing so, he inadvertently created one of the crucial lifelike examples of an unintended “lesion map” in artwork. Though it’s unimaginable to substantiate whether or not the mark was melanoma or one other pores and skin situation, historic data observe that she died in 1801, solely six months after the portray was accomplished.
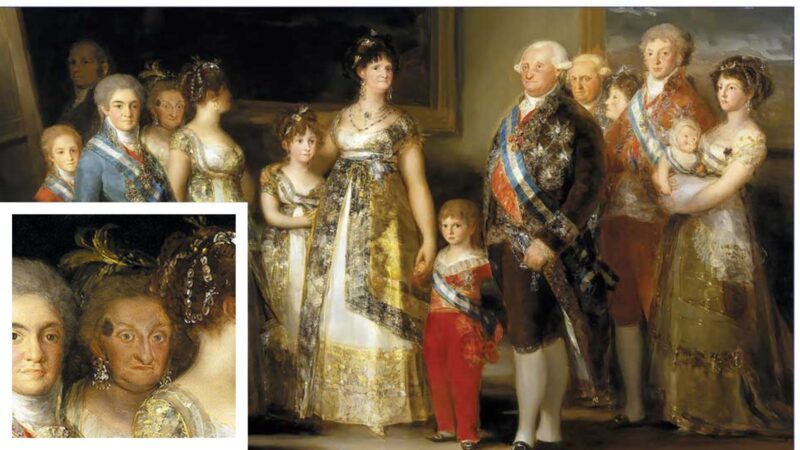

Picture from FranciscoGoya.com
The Temptation of St. Anthony” by Matthias Grünewald

This portray is part of the Isenheim Altarpiece (1512–1516), is acknowledged for its correct and full depiction of a halo naevus (also called a halo nevus or Sutton nevus). This lesion consists of a pigmented mole surrounded by an space of depigmentation, making a “halo” impact across the nevus. Grünewald’s illustration is taken into account one of many earliest and most exact visible data of this dermatological phenomenon in artwork historical past.
(Happle, R. Grünewald-Nävus. Hautarzt 45, 882–883, 1994)
Duke and Duchess of Urbino” by Francesca P.
In the portrait, the Duke is captured with benign intradermal nevi (moles).

All examples from (Amit Om et al., J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2018).
Written by Ina Khachatryan
FAQ
What is Total Body Photography and the way does it work?
TBP is a non-invasive technique that captures high-resolution photographs of your complete pores and skin floor to observe moles and lesions over time for early pores and skin most cancers detection.
Who ought to get Total Body Photography?
TBP is really helpful for individuals at excessive threat of melanoma, reminiscent of these with many moles, atypical lesions, or a household historical past of pores and skin most cancers.
How typically ought to Total Body Photography be carried out?
TBP is usually repeated each 6 to 12 months, with higher-risk sufferers generally needing follow-up each 3 to six months.
How does Total Body Photography assist in early detection of pores and skin most cancers?
By offering a visible baseline, TBP permits clinicians to detect new or altering lesions early, enhancing melanoma survival charges.
What is the distinction between Total Body Photography and dermoscopy?
TBP captures full-body photographs for broad monitoring, whereas dermoscopy magnifies particular person lesions for detailed examination.
What is Automated Lesion Mapping and the way is it used?
Automated Lesion Mapping makes use of AI software program to determine and observe pores and skin lesions on TBP photographs, supporting environment friendly lesion monitoring over time.
How correct is Automated Lesion Mapping in comparison with guide mapping?
Automated Lesion Mapping is very correct, detecting over 90% of related lesions with much less variability than guide strategies.
What applied sciences or algorithms energy Automated Lesion Mapping?
ALM depends on deep studying algorithms, particularly convolutional neural networks, skilled to research lesion options in pores and skin photographs.
Can Automated Lesion Mapping detect all varieties of pores and skin lesions?
While efficient for a lot of pigmented lesions, ALM could have limitations in detecting hypopigmented or hard-to-image lesions.
How is Automated Lesion Mapping built-in with different imaging strategies like Total Body Photography?
ALM analyzes the excellent photographs captured by TBP to create detailed lesion maps for improved pores and skin surveillance.
How correct is synthetic intelligence in diagnosing pores and skin most cancers in comparison with medical doctors?
AI can diagnose pores and skin most cancers with accuracy corresponding to or generally higher than dermatologists, enhancing sensitivity and specificity.
Can AI enhance early detection and prognosis of melanoma and different pores and skin cancers?
Yes, AI enhances early detection by analyzing pores and skin photographs effectively and supporting clinicians in figuring out suspicious lesions sooner.
What challenges does AI face in turning into a dependable instrument for pores and skin most cancers prognosis?
AI nonetheless faces challenges like biased coaching information which will miss various pores and skin tones, restricted transparency in how choices are made, inconsistent accuracy throughout completely different populations, and sensible difficulties integrating into on a regular basis medical workflows.
Is self-diagnosing pores and skin most cancers practical or dependable?
While smartphone apps and on-line assets can increase consciousness, self-diagnosing pores and skin most cancers isn’t dependable and will by no means exchange skilled analysis, as even skilled dermatologists use superior instruments like dermoscopy, TBP, and AI to detect refined or harmful lesions.
This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its authentic location you possibly can go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://oncodaily.com/oncolibrary/total-body-photography
and if you wish to take away this text from our website please contact us



