This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its authentic location you may go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://scitechdaily.com/x-ray-radio-go-hand-in-hand-in-new-nasa-image/
and if you wish to take away this text from our web site please contact us
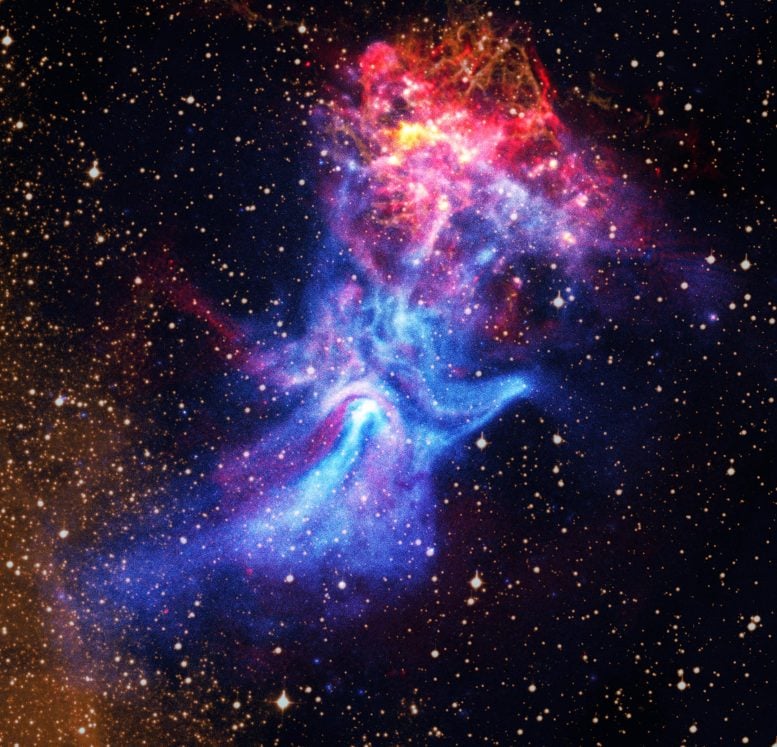

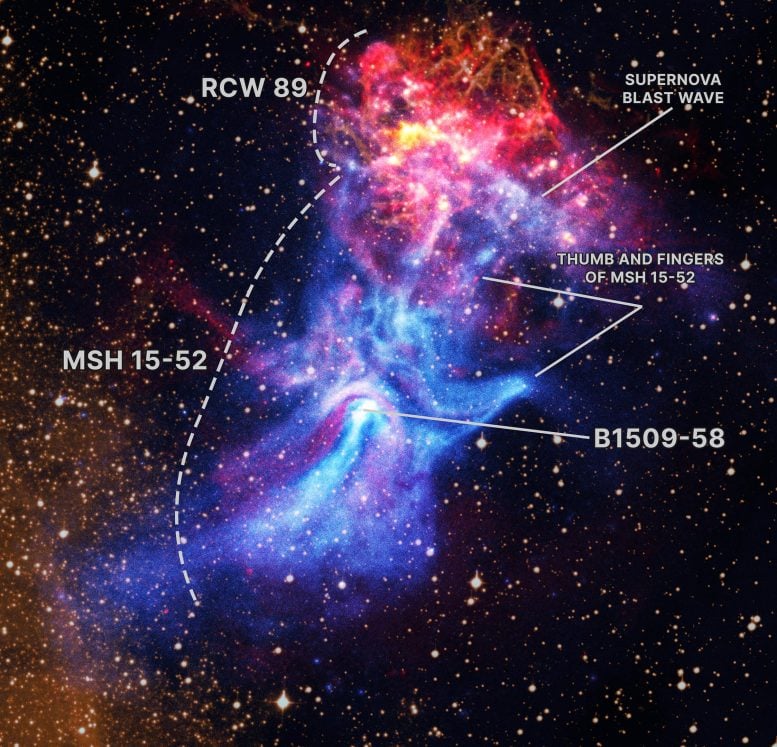
- A shocking new composite picture captures the hand-shaped nebula MSH 15-52 together with the stays of the supernova that shaped it.
- Astronomers mixed X-ray information from NASA’s Chandra Observatory with radio observations from the Australia Telescope Compact Array, uncovering fresh details and hidden structures.
- At the center lies a pulsar, an ultra-dense neutron star spinning rapidly, which fuels the creation of the nebula.
- This extraordinary system began when a massive star used up its nuclear fuel, collapsed inward, and then exploded in a brilliant supernova.
A Cosmic Hand in Space
In 2009, NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory unveiled a striking image of a pulsar surrounded by a nebula shaped like a giant hand.
Since that first release, astronomers have continued to track the object using Chandra along with other powerful telescopes. Most recently, scientists paired new radio observations from the Australia Telescope Compact Array (ATCA) with Chandra’s X-ray data, creating a more detailed portrait of the aftermath of this stellar explosion and offering new clues about its unusual appearance.
Fresh Insights from Radio and X-Ray Data
At the center of this dramatic view is pulsar B1509-58, a quickly rotating neutron star that measures solely about 12 miles throughout. Despite its small dimension, it produces a sprawling nebula (often called MSH 15-52) that stretches greater than 150 light-years, or roughly 900 trillion miles. This huge cloud of energetic particles takes on the eerie form of a human hand, with a glowing palm and outstretched fingers reaching upward to the appropriate in X-ray gentle.
The pulsar itself was born when a large star collapsed after exhausting its provide of nuclear gasoline. The inward crash triggered a supernova, blasting the star’s outer layers into house and abandoning the dense remnant.
Today, B1509-58 rotates almost seven instances per second and carries a magnetic area estimated to be about 15 trillion instances stronger than Earth’s. This extraordinary mixture of pace and magnetism makes it one of many galaxy’s strongest pure dynamos, driving a fierce outflow of electrons and different particles that type the nebula.
One of the Galaxy’s Most Powerful Generators
In this new composite picture, the ATCA radio information (represented in crimson) has been mixed with X-rays from Chandra (proven in blue, orange and yellow), together with an optical picture of hydrogen gasoline (gold). The areas of overlap between the X-ray and radio information in MSH 15-52 present as purple. The optical picture reveals stars within the area of view together with elements of the supernova’s particles, the supernova remnant RCW 89. A labeled model of the determine reveals the principle options of the picture.
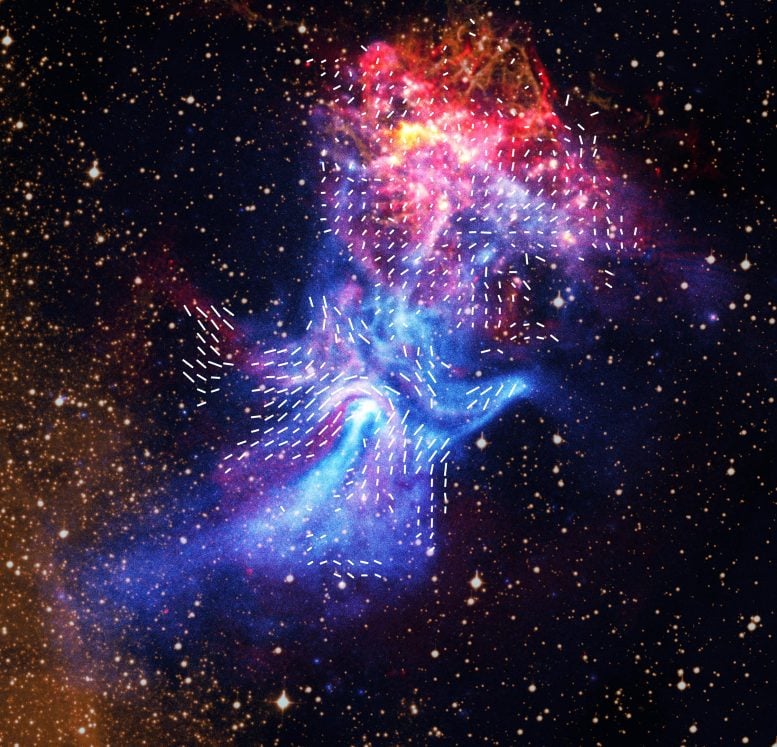
Radio information from ATCA now reveals advanced filaments which are aligned with the instructions of the nebula’s magnetic area, proven by the quick, straight, white traces in a supplementary picture. These filaments may outcome from the collision of the pulsar’s particle wind with the supernova’s particles.

Mysterious Filaments and Magnetic Fields
By evaluating the radio and X-ray information, researchers recognized key variations between the sources of the 2 varieties of gentle. In specific, some outstanding X-ray options, together with the jet in the direction of the underside of the picture and the internal elements of the three “fingers” in the direction of the highest, aren’t detected in radio waves. This means that extremely energetic particles are leaking out from a shock wave — much like a supersonic aircraft’s sonic increase — close to the pulsar and transferring alongside magnetic area traces to create the fingers.
The radio information additionally reveals that RCW 89’s construction is completely different from typical younger supernova remnants. Much of the radio emission is patchy and intently matches clumps of X-ray and optical emission. It additionally extends nicely past the X-ray emission. All of those traits assist the concept that RCW 89 is colliding with a dense cloud of close by hydrogen gasoline.
However, the researchers don’t absolutely perceive all that the info is exhibiting them. One space that’s perplexing is the sharp boundary of X-ray emission within the higher proper of the picture that appears to be the blast wave from the supernova — see the labeled characteristic. Supernova blast waves are normally vivid in radio waves for younger supernova remnants like RCW 89, so it’s shocking to researchers that there isn’t any radio sign on the X-ray boundary.
Perplexing Boundaries and Missing Signals
MSH 15–52 and RCW 89 present many distinctive options not present in different younger sources. There are, nevertheless, nonetheless many open questions relating to the formation and evolution of those constructions. Further work is required to supply higher understanding of the advanced interaction between the pulsar wind and the supernova particles.
A paper describing this work, led by Shumeng Zhang of the University of Hong Kong, with co-authors Stephen C.Y. Ng of the University of Hong Kong and Niccolo’ Bucciantini of the Italian National Institute for Astrophysics, has been printed in The Astrophysical Journal.
Reference: “High-resolution Radio Study of Pulsar Wind Nebula MSH 15–52 and Supernova Remnant RCW 89” by S. Zhang, C.-Y. Ng and N. Bucciantini, 20 August 2025, The Astrophysical Journal.
DOI: 10.3847/1538-4357/adf333
NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the Chandra program. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory’s Chandra X-ray Center controls science operations from Cambridge, Massachusetts, and flight operations from Burlington, Massachusetts.
Never miss a breakthrough: Join the SciTechDaily e-newsletter.
This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its authentic location you may go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://scitechdaily.com/x-ray-radio-go-hand-in-hand-in-new-nasa-image/
and if you wish to take away this text from our web site please contact us