This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its unique location you’ll be able to go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://www.yahoo.com/news/articles/fiber-optics-breakthrough-promises-faster-180000093.html
and if you wish to take away this text from our web site please contact us
A brand new kind of hole optical fibre guarantees to spice up the quantity of knowledge that may be carried in every glass strand, and to take action over longer distances. This might assist to make telecommunications methods sooner and extra environment friendly.
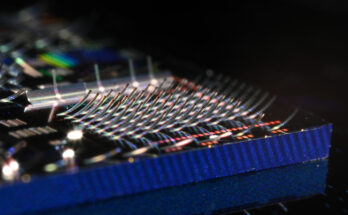
The design, described in Nature Photonics on 1 September1, replaces the hair-thin wire of stable glass that typical fibres are constructed from with a system of glass ‘straws’, during which 5 small cylinders, every containing two nested cylinders, are hooked up to the within rim of 1 fundamental cylinder. The diameter of every tube is finely tuned in such a approach that that the area can solely accommodate gentle of sure wavelengths. This implies that when a light-weight pulse of an acceptable wavelength is distributed down the hole central hole, it would keep there, relatively than escaping.
“We really think this could be transformative,” says co-author Francesco Poletti, a photonics and materials-science researcher on the University of Southampton, UK.
[Sign up for Today in Science, a free daily newsletter]
“If the new fiber can be manufactured and installed easily and proves to be durable, the result might be a faster, better classical Internet,” says Rod Van Meter, a quantum community engineer at Keio University in Tokyo.

Fibres that include hole glass tubes nested inside each other can forestall gentle from escaping.
Prof Francesco Poletti and Dr Greg Jasion, University of Southampton
The fibres shall be produced by a start-up firm referred to as Lumenisity, a spin-off from Southampton that was purchased by Microsoft in 2022. A typical glass fibre is made by melting a bit of glass, then stretching it to provide a strand of the specified thickness. To manufacture their hole fibres, the researchers begin with a bigger model of their design — measuring about 20 centimetres in diameter. The hollows are pressurized throughout stretching, in order that the configuration stays the identical as the entire construction turns into round 100 micrometres huge.
Making connections
Hollow optical fibres of varied designs exist already and have discovered area of interest functions, for instance, in connecting the various computing models in knowledge centres, the place velocity is of the essence (gentle travels 45% sooner by way of hole, air-filled tubes than by way of stable glass). Van Meter calls the rise in velocity “a dramatic change that people will pay a lot of money for.”
Poletti says he has been perfecting the design for greater than ten years, and that it’s the first one that might truly exchange fibres in mainstream functions. The optical fibres that carry a lot of the world’s Internet site visitors have improved little over the previous 4 many years. They lose half of the sunshine they transmit each 15 kilometres or so — 20 km for essentially the most superior variations — primarily as a result of it’s absorbed by the glass. Poletti and his colleagues’ design loses half of the sunshine each 33 km. This implies that the stations used to spice up and re-transmit indicators could possibly be situated farther other than one another than they’re at current. “If new technology comes along and says you can skip one building every two or three, that’s a very significant cost saving,” Poletti says.
In addition to reducing losses, the hole fibres can carry greater than 1,000 instances extra energy, and might achieve this over a broad spectrum of wavelengths — together with the single-photon pulses of visible-spectrum gentle which can be sometimes used for quantum-communication methods. Common fibres are sometimes solely environment friendly on the infrared ‘telecom wavelengths’ of round 1.5 micrometres.
“This result is very interesting for the quantum communication community,” says Tracy Northup, an experimental physicist on the University of Innsbruck in Austria. Until now, hole fibres have been prohibitively costly even for small-scale laboratory experiments, she provides. “We in the research community can hope that scaled-up production may bring prices down significantly in the future.”
This article is reproduced with permission and was first published on September 2, 2025.
This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its unique location you’ll be able to go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://www.yahoo.com/news/articles/fiber-optics-breakthrough-promises-faster-180000093.html
and if you wish to take away this text from our web site please contact us