This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its authentic location you possibly can go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://www.sci.news/genetics/mammoth-microbiome-14188.html
and if you wish to take away this text from our web site please contact us
In a brand new research, scientists analyzed historical microbial DNA from 483 mammoth stays spanning over 1 million years, together with 440 newly-sequenced and unpublished samples from a 1.1-million-year-old steppe mammoth. Using metagenomic screening, contaminant filtering, injury sample evaluation, and phylogenetic inference, they recognized 310 microbes related to totally different mammoth tissues.
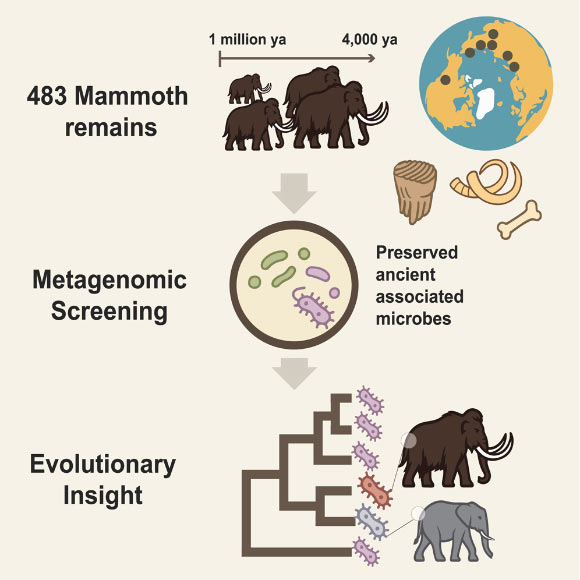
Guinet et al. reconstructed partial genomes of Erysipelothrix from the oldest mammoth pattern, representing the oldest authenticated host-associated microbial DNA thus far. Image credit score: Guinet et al., doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2025.08.003.
“Imagine holding a million-year-old mammoth tooth,” stated Dr. Benjamin Guinet, a postdoctoral researcher on the Centre for Palaeogenetics in Stockholm and the Swedish Museum of Natural History.
“What if I told you it still carries traces of the ancient microbes that lived together with this mammoth?”
“Our results push the study of microbial DNA back beyond a million years, opening up new possibilities to explore how host-associated microbes evolved in parallel with their hosts.”
The researchers recognized six microbial teams constantly related to mammoth hosts, together with kinfolk of Actinobacillus, Pasteurella, Streptococcus, and Erysipelothrix. Some of those microbes might have been pathogenic.
For occasion, one Pasteurella-related bacterium recognized within the research is intently associated to a pathogen that has triggered deadly outbreaks in African elephants.
Since African and Asian elephants are the closest residing kinfolk of mammoths, these findings increase questions on whether or not mammoths may have been weak to comparable infections.
Remarkably, the scientists reconstructed partial genomes of Erysipelothrix from a 1.1-million-year-old steppe mammoth, representing the oldest recognized host-associated microbial DNA ever recovered.
This pushes the boundaries of what researchers can be taught in regards to the interactions between historical hosts and their microbiomes.
“As microbes evolve fast, obtaining reliable DNA data across more than a million years was like following a trail that kept rewriting itself,” stated Dr. Tom van der Valk, additionally from the Centre for Palaeogenetics in Stockholm and the Swedish Museum of Natural History.
“Our findings show that ancient remains can preserve biological insights far beyond the host genome, offering us perspectives on how microbes influenced adaptation, disease, and extinction in Pleistocene ecosystems.”
Although the precise influence of the recognized microbes on mammoth well being is tough to find out resulting from DNA degradation and restricted comparative knowledge, the research offers an unprecedented glimpse into the microbiomes of extinct megafauna.
The outcomes counsel that some microbial lineages coexisted with mammoths for a whole lot of 1000’s of years, spanning each extensive geographic ranges and evolutionary timescales, from over a million years in the past to the extinction of woolly mammoths on Wrangel Island about 4,000 years in the past.
“This work opens a new chapter in understanding the biology of extinct species,” stated Professor Love Dalén, a researcher on the Centre for Palaeogenetics in Stockholm, the Swedish Museum of Natural History and Stockholm University.
“Not only can we study the genomes of mammoths themselves, but we can now begin to explore the microbial communities that lived inside them.”
The study was revealed this week within the journal Cell.
_____
Benjamin Guinet et al. Ancient host-associated microbes obtained from mammoth stays. Cell, revealed on-line September 2, 2025; doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2025.08.003
This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its authentic location you possibly can go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://www.sci.news/genetics/mammoth-microbiome-14188.html
and if you wish to take away this text from our web site please contact us



