This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its unique location you’ll be able to go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/the-physics-of-light-based-computers-can-change-the-way-ai-works/article70037081.ece
and if you wish to take away this text from our web site please contact us
Modern computing banks on standard electronics and algorithms to course of information. But as a result of the {hardware} operates in keeping with the legal guidelines of physics, information processing has a bodily velocity restrict. The availability of energy additional constrains this velocity, particularly if the software program being run is a power-guzzling synthetic intelligence (AI) mannequin. Thus one main preoccupation of scientists worldwide is arising with new sorts of computer systems that enhance the velocity restrict by working in another way.
One promising variety is light-based, a.okay.a. optical, computing. These computer systems use photons, the particles of sunshine, fairly than electrons. Because photons journey on the velocity of sunshine and photonic gadgets generate much less warmth than digital gadgets do, optical computing guarantees to be quicker, have extra bandwidth, and be extra energy-efficient.
An vital a part of an optical laptop would be the optical fibres that transmit information from one part to a different inside the machine. This specific expertise is already in use worldwide: it transmits billions of bytes of information between nations and continents and allows superfast web providers.
A brand new door
But earlier than scientists can use optical computing to supercharge AI fashions, they want some handles to manage sure bodily properties of sunshine. Light normally behaves in a daily, predictable method when it passes by media like glass or water. Scientists know this as gentle’s linear response.
However, when gentle pulses are very intense, like these issued by a strong laser, they elicit a distinct response from the fabric they’re passing by. This is the non-linear regime. Among others, gentle pulses on this regime can intrude with one another, unfold out or converge, and generate new frequencies (colors) of sunshine.
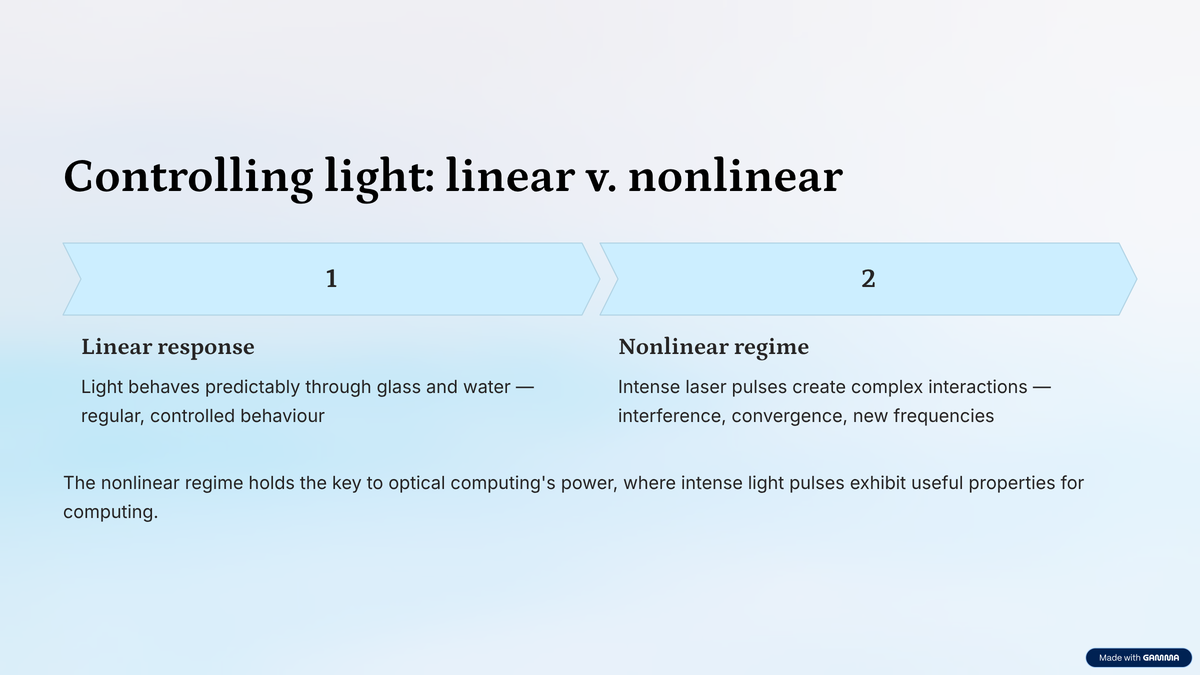
Linear v. nonlinear regimes
Recently, two analysis groups — from Tampere University in Finland and Université Marie et Louis Pasteur in France — studied nonlinear interplay between intense gentle pulses passing by skinny glass fibres and uncovered one thing uncommon. The researchers reported that it’s potential to make use of the physics of sunshine in optical fibres to carry out advanced AI duties doubtlessly a lot quicker and with much less vitality than conventional computer systems.
The work has opened a door to new kinds of AI {hardware} that can be utilized in areas the place velocity and effectivity are essential. The findings have been printed in Optical Letters in June.
Image to numbers and again
In the research, the researchers centered on an AI mannequin known as an excessive studying machine (ELM). Instead of utilizing conventional laptop chips, they used the bodily properties of sunshine travelling by optical fibres to carry out calculations. Their principal objective was to grasp how properly this method labored for recognising pictures and what components affected its accuracy.
An ELM is a kind of neural community that’s quick and easy. It has just one hidden layer (between the enter and output layers), and solely the output weights are skilled. The ELM finds these weights in a single step utilizing a mathematical methodology, fairly than studying by repeated changes like in deep neural networks.
In this setup, the enter information, like a picture, was remodeled right into a dataset of numbers. This made it simpler for the community to separate and classify various kinds of inputs. Then, the ELM used a easy linear calculation to match the remodeled information to the proper label, e.g. which digit a picture exhibits.
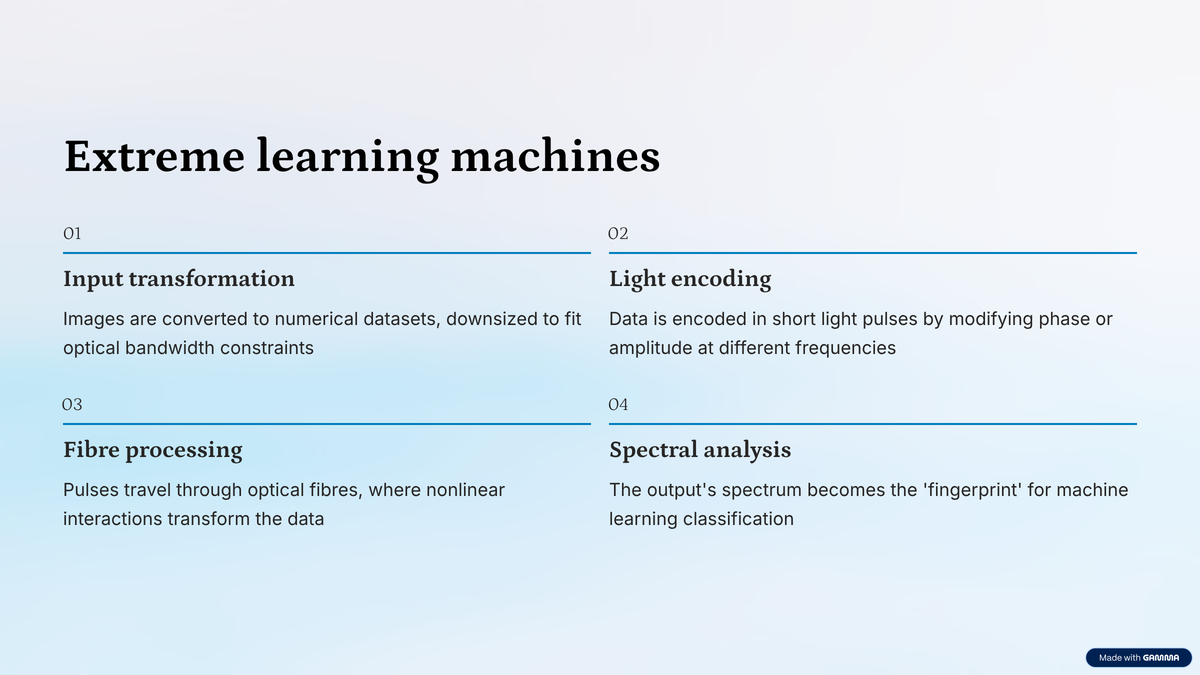
Extreme studying machines
The researchers use the distinctive properties of sunshine in optical fibres to carry out the transformation wanted for the ELM.Each picture was first downsized — like from 28 × 28 pixels to 10 × 10 — to suit the restricted bandwidth of the sunshine pulse. The picture information was then encoded onto a really quick pulse of sunshine, both by altering the section (how the sunshine wave oscillates) or the amplitude (how robust the sunshine is) at completely different frequencies.

Fingerprint within the colors
The encoded gentle pulse was then despatched by a size of optical fibre. The pulse fibre interactions have been within the nonlinear regime. The researchers tracked how the fibre responded to the pulses and the way completely different colors of sunshine journey at completely different speeds, a property known as dispersion. These modifications blended up the data within the gentle pulses in a method that was laborious to reverse — however helpful for the ELM’s transformation step.
At the tip of the fibre, the group measured how a lot gentle there was of every color. This spectrum contained a ‘fingerprint’ of the unique picture, remodeled by the fibre’s nonlinear results. The group used it because the hidden layer within the ELM — the computing layer between the enter and the output that gave rise to the machine’s ‘intelligence’.
In this manner, the group skilled the ELM on hundreds of labelled pictures. Then they examined the mannequin on new pictures to see how precisely it may classify them.
With optimum settings, the group discovered that the ELM was greater than 91% correct at recognising handwritten digits utilizing the optical fibre’s anomalous dispersion regime and greater than 93% accuracy within the regular dispersion regime. These outcomes have been near these achieved by conventional computer-based ELMs however have been achieved utilizing the physics of sunshine as an alternative of electronics.
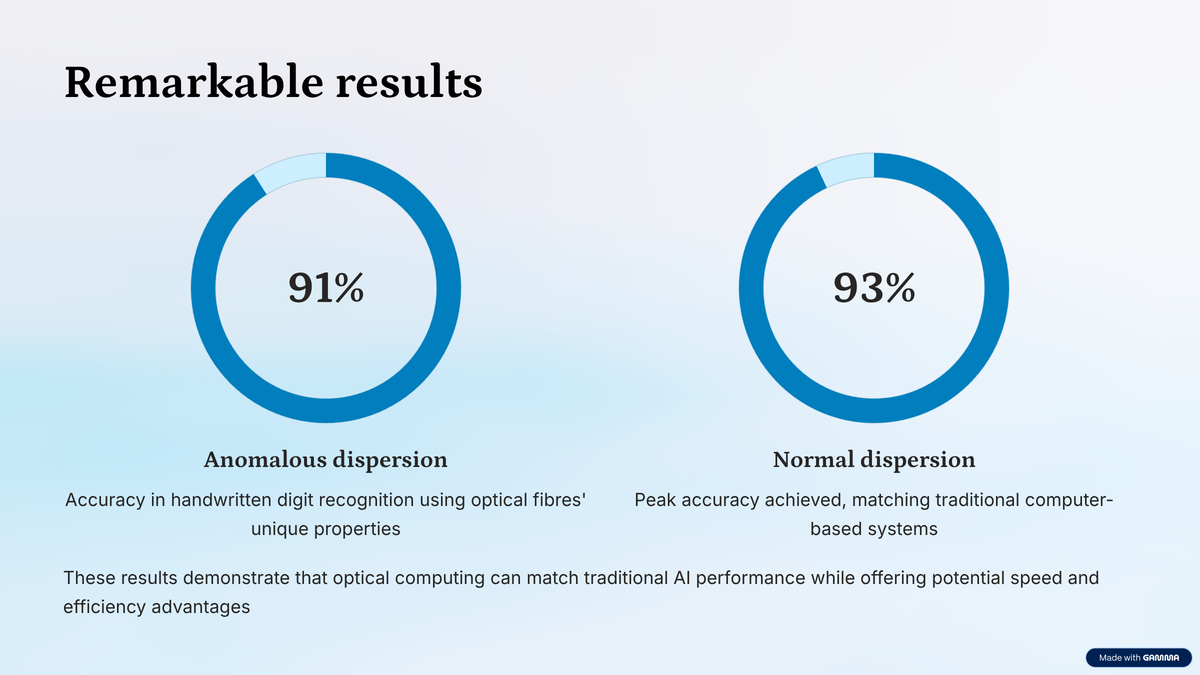
Test with pictures
Let there be gentle
According to the printed paper, growing the energy of the nonlinear results and the fibre fibre size improved accuracy, however solely up to some extent. Too a lot of a rise precipitated the system to grow to be unstable and fewer correct. There is thus an optimum vary for these parameters.
In sum, the research demonstrated that optical fibres can be utilized as highly effective instruments for machine studying, particularly for duties like picture recognition. By fastidiously tuning the system’s parameters and understanding the results of noise and encoding, it’s potential to attain excessive accuracy utilizing the pure properties of sunshine. This method may result in new, quicker, and extra environment friendly AI techniques sooner or later.
The scientists who led the groups behind the research stated in a press release: “This work demonstrates how fundamental research in nonlinear fibre optics can drive new approaches to computation.”
The research paper did notice some limitations it stated might be overcome in future analysis. For instance, the group’s mannequin didn’t embrace all potential real-world results, resembling modifications within the gentle’s polarisation (the path by which its electrical discipline oscillates). It stated future work may additionally discover encoding data on completely different polarisation states or utilizing extra advanced optical fibres. There can also be a acknowledged potential to enhance the system by measuring not simply the spectrum’s depth but in addition its section.
This stated, the research highlighted the alternatives inside light-based computing with optical fibres to satisfy the rising demand for quicker in addition to smarter AI. By utilizing the velocity and effectivity of sunshine, computer systems of the long run may assume and study in ways in which might make the AI fashions accessible to us right this moment appear crude. But it will take many extra years as specialists and businesspersons design and check new applied sciences like photonic built-in circuits and optical neural networks.

Paradigm shift
Qudsia Gani is an assistant professor within the Department of Physics, Government Degree College Pattan, Baramulla.
Published – September 12, 2025 05:30 am IST
This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its unique location you’ll be able to go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/the-physics-of-light-based-computers-can-change-the-way-ai-works/article70037081.ece
and if you wish to take away this text from our web site please contact us



