This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its unique location you possibly can go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://www.universetoday.com/articles/the-esas-mars-express-and-exomars-orbiters-catch-a-glimpse-of-3iatlas
and if you wish to take away this text from our web site please contact us
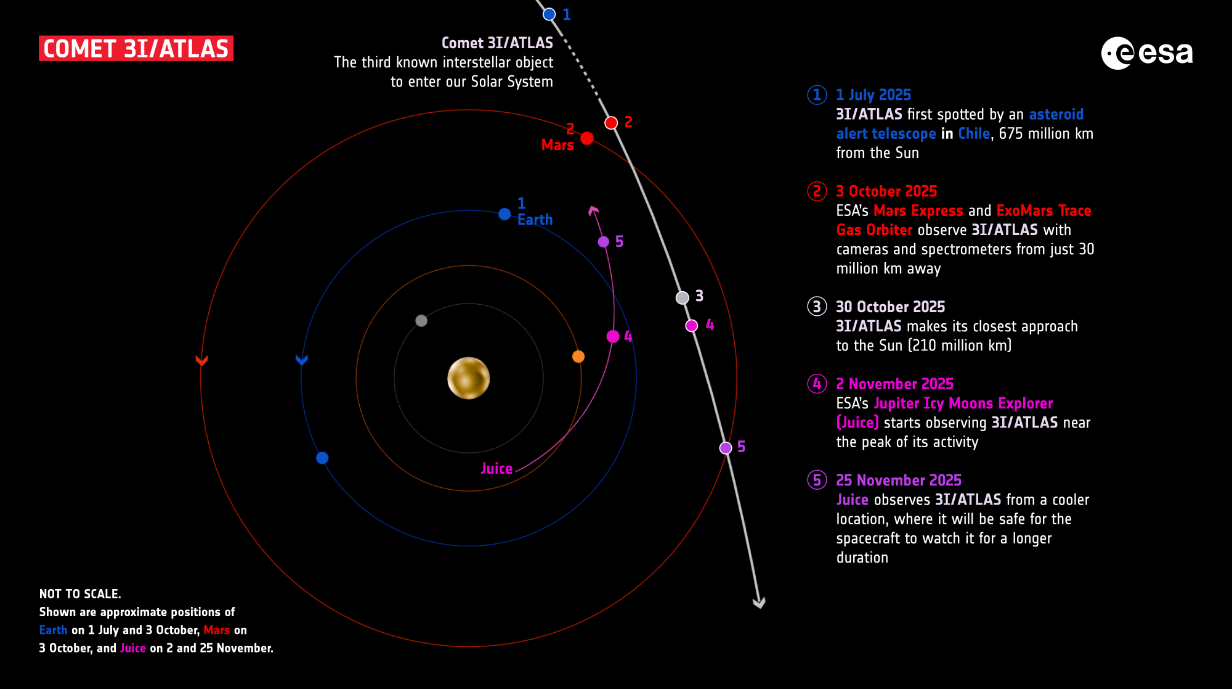
The interstellar object 3I/ATLAS has been one thing of a thriller ever because it graced our Solar System. From all outward appearances, the thing seems to be a comet that originated in one other star system and was ejected by gravitational perturbations. This was evident from the way in which it has been actively releasing water vapor because it attracts nearer to the Sun, forming a coma and a tail. Nevertheless, it has exhibited some anomalous conduct, fueling hypothesis that it might be an interstellar customer of one other sort.
It is little marvel then why scientists and most of the people have been hoping to get a better have a look at 3I/ATLAS. There have even been proposals on how energetic missions may intercept the thing to examine it extra intently. In the meantime, two Martian orbiters supplied the closest view of the thing: the European Space Agency’s (ESA) Exomars Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO) and the Mars Express. These two missions captured pictures of 3I/ATLAS with their devoted cameras because it handed inside 30 million km (18.64 million mi) from them.
The ExoMars TGO captured a collection of pictures utilizing its Colour and Stereo Surface Imaging System (CaSSIS) whereas the Mars Express orbiter snapped footage utilizing its High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC). Both devices are designed to {photograph} the floor of Mars, just some hundred to some thousand km under, when it’s brightly lit. So naturally, there was uncertainty as to what these missions would seize from a comparatively dim object tens of millions of km away.
 *ESA’s Mars and Jupiter missions observe comet 3I/ATLAS. Credit: ESA*
*ESA’s Mars and Jupiter missions observe comet 3I/ATLAS. Credit: ESA*
While CaSSIS couldn’t distinguish the nucleus of the coma, being only one km (0.62 wi) in width and so distant, the coma itself is clearly seen within the picture proven on the prime. The full measurement of the coma couldn’t be measured by CaSSIS for the reason that gasoline and dirt fade the farther it’s from the nucleus. Since the tail extends an estimated 56,000 km (35,000 mi) behind the comet (based mostly on current pictures taken by the Gemini South telescope), it’s a lot dimmer than the coma and due to this fact not seen within the CaSSIS pictures. However, it might grow to be extra seen because the comet approaches the Sun and releases extra materials.
“This was a very challenging observation for the instrument,” mentioned Nick Thomas, the Principal Investigator of the CaSSIS digital camera. “The comet is around 10,000 to 100,000 times fainter than our usual target.” The Mars Express pictures haven’t but captured 3I/ATLAS, as its digital camera has a a lot shorter publicity time of 0.5 seconds, in comparison with 5 seconds for the CaSSIS digital camera. Luckily, the mission scientists plan to investigate the info from each orbiters and mix their pictures to achieve a extra detailed view of 3I/ATLAS.
Meanwhile, Mars Express managed to gather spectra from the comet utilizing its two spectrometers – Observatoire pour la Minéralogie, l’Eau, les Glaces et l’Activité (OMEGA) and SPectroscopy for Investigation of Characteristics of the Atmosphere of Mars (SPICAM) – and the TGO’s Nadir and Occultation for MArs Discovery (NOMAD) spectrometer. It just isn’t but clear whether or not the 2 orbiters gathered sufficient mild for a correct characterization of the comet’s composition, however the mission groups will proceed to investigate the info because the comet approaches the Sun. Said Colin Wilson, a Mars Express and ExoMars venture scientist on the ESA, mentioned:
Though our Mars orbiters proceed to make spectacular contributions to Mars science, it is at all times further thrilling to see them responding to surprising conditions like this one. I look ahead to seeing what the info reveals following additional evaluation.
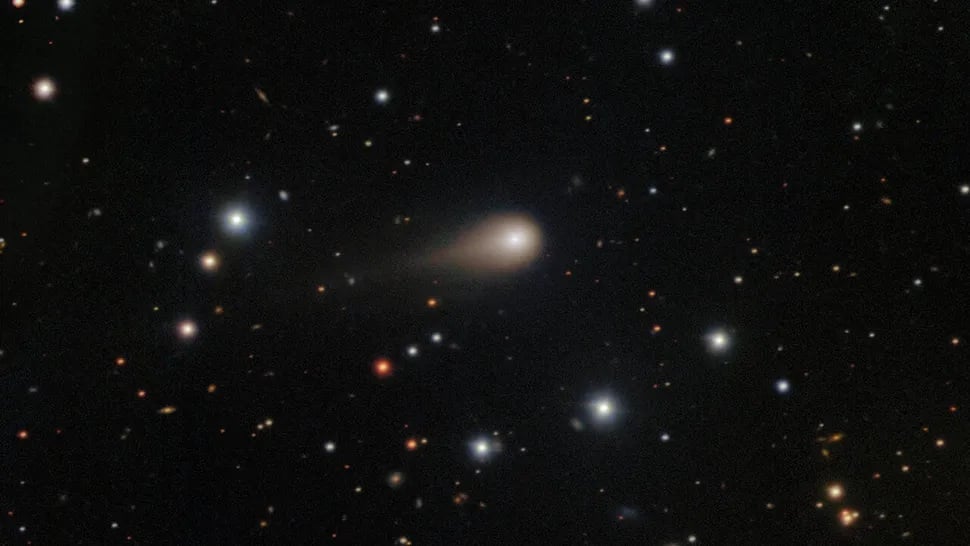 *A photograph of interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS taken in July on the Gemini South Observatory in Chile. Credit: International Gemini Observatory/NOIRLab/NSF/AURA*
*A photograph of interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS taken in July on the Gemini South Observatory in Chile. Credit: International Gemini Observatory/NOIRLab/NSF/AURA*
This coming November, the ESA’s JUpiter Icy Moons Explorer (JUICE) might be able to watch 3I/ATLAS after it makes its closest strategy to the Sun. The knowledge might be obtainable by February and is predicted to disclose extra concerning the comet, as it will likely be in a extra energetic state. More detailed pictures and spectra will enable scientists to be taught extra concerning the comet’s composition, shedding mild on its system of origin. Additionally, work is progressing on the ESA’s Comet Interceptor mission, scheduled to launch in 2029.
While not completely meant to check ISOs, this mission would be the first mission devoted to exploring comets intently and acquiring high-resolution pictures and detailed info on their conduct and composition. It can also be considered one of a number of ideas at present being explored by scientists who’re hoping to get a better have a look at interstellar guests. Once it’s positioned in a parking orbit, the Comet Interceptor will wait till one other long-period comet travels from the Oort Cloud in the direction of the Sun, or one other ISO is detected getting into our Solar System. As Michael Kueppers, a Comet Interceptor venture scientist, defined:
When Comet Interceptor was chosen in 2019, we solely knew of 1 interstellar object – 1I/ʻOumuamua, found in 2017. Since then, two extra such objects have been found, displaying [a] giant range of their look. Visiting one may present a breakthrough in understanding their nature.
Given that comets and asteroids are primarily materials left over from the formation of planetary methods, learning these objects is the subsequent neatest thing to sending missions to distant photo voltaic methods. It can also be significantly cheaper and quicker, and is certain to offer worthwhile insights into different planetary methods in our galaxy inside our lifetimes.
Further Reading: ESA
This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its unique location you possibly can go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://www.universetoday.com/articles/the-esas-mars-express-and-exomars-orbiters-catch-a-glimpse-of-3iatlas
and if you wish to take away this text from our web site please contact us



