This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its unique location you’ll be able to go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://www.chinadailyasia.com/article/623066
and if you wish to take away this text from our web site please contact us
A Chinese Martian orbiter has noticed and photographed a uncommon interstellar comet rushing via the photo voltaic system, based on the China National Space Administration.
As a part of China’s ongoing Tianwen 1 Martian exploration mission, the orbiter noticed and captured the pictures of comet 3I/ATLAS, the third confirmed interstellar object after 1I/’Oumuamua and 2I/Borisov, when it handed close to Mars on Oct 3.
ALSO READ: China releases images of Martian dust taken by Tianwen 1 orbiter
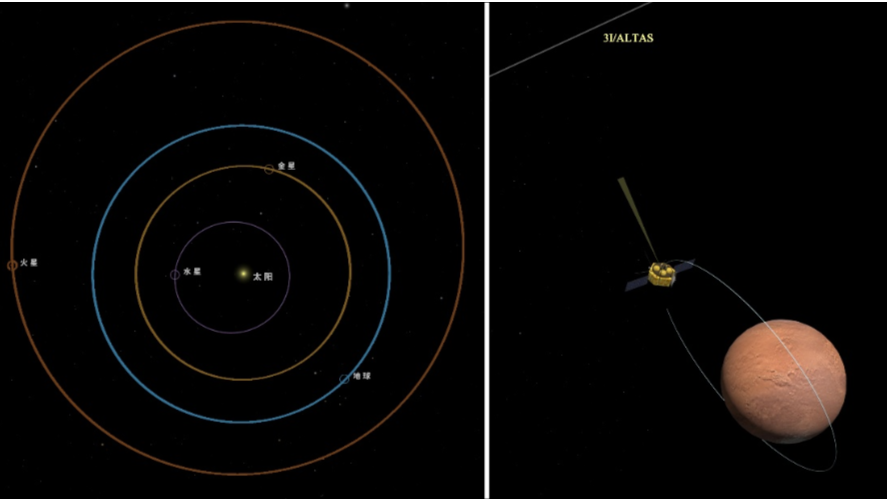
At that point, the spacecraft was about 29 million kilometers from the celestial physique, attaining one of many closest observations of this uncommon comet, the CNSA mentioned in a information launch on Thursday.
Scientists and engineers within the Tianwen 1 challenge workforce began making preparations for the 3I/ATLAS statement in early September. They carried out rounds of calculations and simulations earlier than figuring out a particular statement and imaging plan, which was based mostly on the 3I/ATLAS’ trajectory, brightness, measurement and the capabilities of the orbiter’s scientific payloads, the CNSA mentioned.
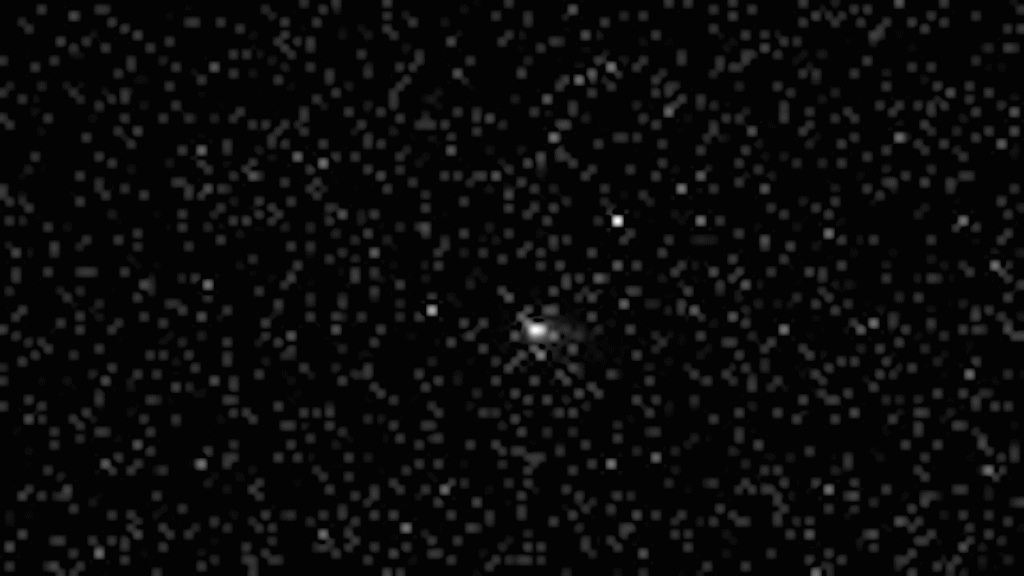

The comet was first found on July 1 by the NASA-funded Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS) survey telescope in Rio Hurtado, Chile. Since the primary report, observations made earlier than the invention had been gathered from the archives of three totally different ATLAS telescopes world wide and California Institute of Technology’s Zwicky Transient Facility on the Palomar Observatory in San Diego County, California.
According to scientists, the 3I/ATLAS could have shaped round an historic star on the middle of the Milky Way galaxy, with an estimated age of about 3 to 11 billion years, presumably older than the age of the photo voltaic system. It is a uncommon pattern for detecting the composition, evolution, and early stellar historical past of exoplanets and has essential scientific significance.
The celestial physique reached its closest level to the solar in late October, at a distance of about 1.4 astronomical models, or 210 million kilometers, simply inside Mars’ orbit.
This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its unique location you’ll be able to go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://www.chinadailyasia.com/article/623066
and if you wish to take away this text from our web site please contact us



