This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its authentic location you’ll be able to go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11274-025-04780-2
and if you wish to take away this text from our website please contact us
Genome filtering, species delimitation, and phylogeny
To allow strong comparative analyses and genetic mining, we first curated the genomic dataset, guaranteeing high quality, eradicating redundancy, and clarifying taxonomic assignments. In complete, 1,286 genomes of Pantoea spp. have been retrieved from the NCBI GenBank database (February 2025). From this preliminary set, we chosen genomes containing fewer than 500 contigs. We then assessed meeting completeness by calculating the proportion of anticipated single-copy genes, retaining solely these with > 90% completeness. In addition, we screened for a number of copies of single-copy genes and excluded genomes with > 10% contamination. After making use of these high quality filters, 1,151 genomes have been retained.
Redundancy was diminished utilizing Mash, which clustered genomes with pairwise distances beneath 0.05 (akin to 99.95% ANI), figuring out 506 duplicate assemblies. Within every cluster, the meeting with the very best contiguity (N50) was chosen because the consultant genome. This course of resulted in a remaining dataset of 645 high-quality, non-redundant genomes that have been used for subsequent analyses, Table S1 lists all downloaded genomes, indicating duplicates and causes for exclusion.
Species delimitation was carried out utilizing an all-vs-all ANI evaluation. Genomes sharing ≥ 95% ANI (Bobay 2020), the accepted threshold for bacterial species boundaries, have been grouped collectively. This evaluation recognized 189 essential reclassifications, the bulk (80.4%) akin to beforehand unclassified strains. Interestingly, some discrepancies concerned kind strains themselves—for instance, the sort pressure of P. leporis shares 98.5% ANI with P. endophytica, which additionally possesses its personal kind pressure. Additional instances of misassignment are supplied in Table S2.
A most chance phylogeny was then reconstructed utilizing single-copy orthologs genes recognized by OrthoFinder (see Methods for particulars). The reconstruction resolved 23 main teams, every containing a sort pressure. These phylogenetic clusters have been congruent with the ANI-based species boundaries, reinforcing the robustness of each approaches for taxonomic delimitation inside the genus Pantoea (Fig. 1).
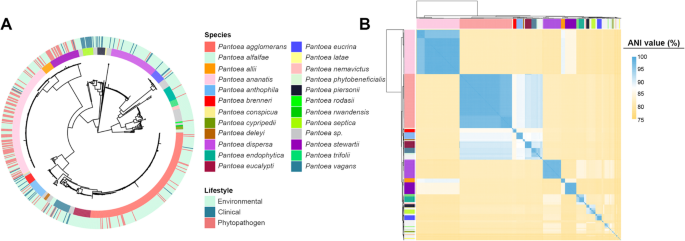
Phylogeny and variety of the Pantoea genus. (A) Maximum chance phylogenetic tree of Pantoea genomes, indicating species and their related life. Reconstruction was carried out with IQ-TREE. (B) ANI-based clustering exhibiting 23 genomic teams outlined by > 95% identification
Species distribution throughout life revealed distinct developments. The most steadily represented phytopathogenic taxa have been P. ananatis, P. stewartii, P. allii, and P. agglomerans, according to their recurrent affiliation with crop ailments. In distinction, strains remoted from medical settings have been predominantly assigned to P. septica, P. piersonii, P. brenneri, and P. anthophila. The remaining species have been largely of environmental origin, generally related to crops, and lacked data of pathogenicity or deleterious interactions (Fig. 1).
Plant growth-promoting potential of Pantoea
After defining genomic teams and reclassifying the genomes, we examined the repertoire of genes with potential biotechnological relevance, specializing in these related to plant progress promotion. Strains of Pantoea have been more and more acknowledged as candidates in agricultural biotechnology, given their documented results on plant improvement (Walterson and Stavrinides 2015). To discover this potential, we screened the genus for classical PGPB traits, together with genes concerned in nitrogen fixation, phosphate solubilization, phytohormone manufacturing, siderophore synthesis, and ethylene modulation. The genes used for genome mining and their predicted capabilities are listed in Table S3.
Figures 2 and three present presence–absence profiles of PGPB-related genes, revealing a broadly homogeneous distribution throughout Pantoea life. Notably, even phytopathogenic and medical strains harbor genes historically linked to plant progress promotion. These findings point out that the mere presence of such genes is inadequate to tell apart helpful from pathogenic life inside the genus. A extra detailed dialogue of the principal PGPB-related genes recognized is supplied beneath.
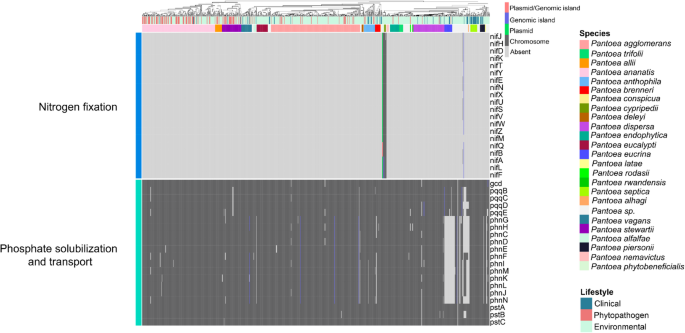
Presence–absence heatmap of genes related to nitrogen fixation, phosphate solubilization and transport. Columns correspond to particular person genomes and are annotated with species names and their respective life. The prevalence of the identical gene in numerous genomic areas is represented by distinct colours
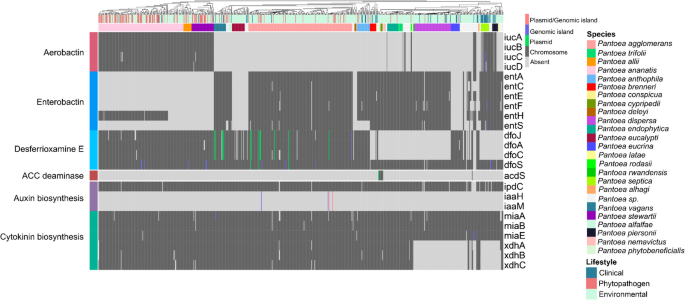
Presence–absence heatmap of genes related to siderophore biosynthesis, phytohormone manufacturing, and ethylene stage modulation. Columns signify particular person genomes and are annotated with species and their respective life. Distinct colours point out the prevalence of the identical gene in numerous genomic areas
Nitrogen fixation and phosphate solubilization
A classical trait of PGPB is the power to repair atmospheric nitrogen, changing it into types readily assimilable by crops (Sepp et al. 2023). This operate is mediated by the nif operon, which encodes roughly 20 proteins concerned in nitrogen uptake, biosynthesis of the iron–molybdenum cofactor, discount of nitrogen to ammonia, and regulatory capabilities.
All nif genes have been detected solely in P. cypripedii, P. phytobeneficialis, and two unclassified strains, forming a monophyletic group (Fig. 2). In one in all these strains, the nif cluster is situated on a plasmid that additionally harbors the genes acdS and acdR (related to ACC deaminase exercise) (Fig. 3), in addition to genes associated to iron transport, jasmonic acid biosynthesis, and glucose-1-dehydrogenase. In P. cypripedii and P. phytobeneficialis, the nif genes are chromosomally encoded and syntenic, suggesting chromosomal integration after plasmid acquisition via horizontal gene switch (HGT). Thus, nitrogen fixation in Pantoea is circumscript to a small monophyletic group that doubtless acquired such genes via a standard HGT occasion.
Phosphate solubilization represents one other essential PGPB trait, given the restricted availability of plant-assimilable phosphorus in most soils (Olanrewaju et al. 2017). Genes associated to inorganic phosphate solubilization, reminiscent of gcd (glucose-1-dehydrogenase) and its cofactor pqq (pyrroloquinoline quinone), which mediate gluconic acid (GA) synthesis, have been recognized. GA promotes soil acidification, thereby releasing phosphate ions for plant uptake. Genes related to GA manufacturing have been persistently detected in chromosomes of all Pantoea species, suggesting that phosphate solubilization is an intrinsic characteristic of the genus.
In addition, the phn operon, which encodes phosphonatase—an enzyme chargeable for the degradation of organophosphonate compounds that may additionally function phosphorus sources—was detected in most species. Notable exceptions included P. eucrina, P. coffeiphila, and a number of other unclassified strains.
Stress management, phytohormone manufacturing, and siderophore biosynthesis
Under biotic and abiotic stress, crops typically accumulate ethylene, a key hormone that regulates varied physiological processes however, at excessive ranges, inhibits root progress and root hair formation (Ahemad and Kibret 2014). Certain endophytic micro organism mitigate these results by producing 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC) deaminase, which metabolizes ACC, the direct precursor of ethylene within the Yang cycle. The gene encoding this enzyme, acdS, was recognized in solely two species, P. cypripedii and P. phytobeneficialis (Fig. 3).
Auxin, significantly indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), is one other phytohormone central to plant improvement, particularly in root progress and cell differentiation (Tang et al. 2023). Several bacterial pathways synthesize IAA, named based on their intermediates. In Pantoea, the predominant pathway is the indole-3-pyruvic acid (IPyA) route, catalyzed by indole-3-pyruvate decarboxylase, encoded by ipdC. This gene was detected in all species, situated on chromosomes, indicating an ancestral and conserved origin. In distinction, the indole-3-acetamide (IAM) pathway, depending on iaaM and iaaH, which encode tryptophan monooxygenase and indole-3-acetamide hydrolase, respectively, was discovered solely in 4 P. agglomerans strains, together with the pathogenic pathovars P. agglomerans pv. betae and pv. gypsophila, each related to gall formation. In these strains, IAM genes happen inside genomic islands and are sometimes linked to virulence determinants such because the hrp/hrc operon, which encodes elements of the sort III secretion system (T3SS) and the induction of tumor formation (Barash and Manulis-Sasson 2009). These findings are according to earlier reviews exhibiting that the IAM pathway is attribute of phytopathogens (Ahemad and Kibret 2014), whereas the IPyA route has a broader distribution throughout environmental, pathogenic, and medical strains, making its position much less particular to way of life.
In addition to auxin, genes related to the manufacturing of different phytohormones, reminiscent of cytokinin—a key regulator of cell division, seed germination, and seed improvement—have been additionally recognized (Orozco-Mosqueda et al. 2023). This pathway includes genes associated to tRNA modification and recycling (miaA, miaB, and miaE), in addition to subunits of xanthine dehydrogenase (xdhA, xdhB, and xdhC) (Rocha et al. 2023). Some species, together with P. dispersa, P. eucrina, P. latae, P. septica, and P. piersonii, lacked the xdhABC. However, these species harbor yagTSR, which additionally encodes a xanthine dehydrogenase (Neumann et al. 2009), enabling cytokinin biosynthesis (Hossain 2024).
Siderophores, iron-chelating molecules produced by rhizospheric and endophytic micro organism, improve iron availability to crops and contribute to pathogen suppression by outcompeting fungal siderophores (Olanrewaju et al. 2017). Three siderophore varieties have been detected in Pantoea: enterobactin (ent operon), desferrioxamine E (DFO-E, dfo), and aerobactin (iuc). While enterobactin and DFO-E-related genes are broadly distributed with occasional losses and no clear way of life correlation, aerobactin genes present a extra restricted sample, occurring primarily in P. ananatis, P. allii, and P. stewartii (primarily phytopathogens), and P. septica (a medical species). These outcomes assist earlier observations that an enterobactin-like cluster was current within the final widespread ancestor of the genus, with subsequent losses in sure species and impartial acquisitions of different siderophore clusters (e.g. aerobactin), through HGT (Soutar and Stavrinides 2018).
Antibiotic resistance potential
For the protected implementation of Pantoea strains with excessive biotechnological potential, it’s essential to evaluate their resistome, i.e., the set of genes related to antibiotic resistance, with a purpose to keep away from establishing genetic reservoirs that would facilitate the unfold of clinically related resistance determinants (Larsson and Flach 2022). Our evaluation revealed that the 2 predominant resistance mechanisms within the genus are efflux pump-mediated export and antibiotic inactivation by enzymes.
The distribution of resistance genes doesn’t observe a lifestyle-specific sample (Fig. 4), with medical strains not exhibiting a definite repertoire that would discriminate them from environmental, endophytic, or different isolates. It is noteworthy that though some resistance genes have been related to cell parts, no resistance islands carrying genes associated to last-generation antibiotics, reminiscent of blaCTX−M−15 (third-generation cephalosporins) (Darby et al. 2023), blaOXA−48−like (carbapenems) (Hendrickx et al. 2021), and qnr (fluoroquinolones) (Amereh et al. 2023), have been noticed.
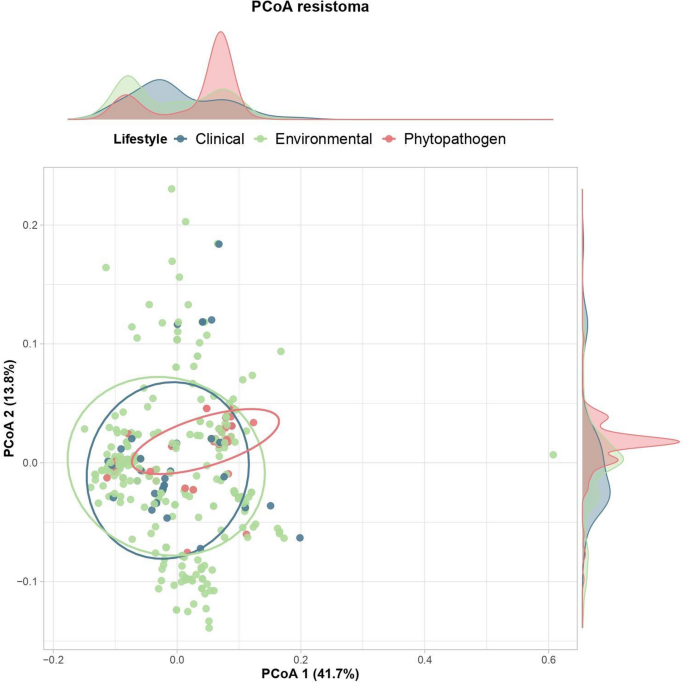
Principal Coordinate Analysis (PCoA) of dissimilarities in antibiotic resistance gene content material throughout Pantoea genomes with completely different life. Density plots alongside the axes illustrate the distribution of genomes relative to every coordinate. Ellipses signify the 90% confidence interval for every way of life group, indicating the diploma of dispersion and overlap amongst their resistome profiles
This means that the Pantoea resistome doesn’t replicate latest variations pushed by robust selective pressures in medical environments, as seen in micro organism concerned in hospital outbreaks (Sanikhani et al. 2024). Thus, the resistance repertoire discovered seems to signify intrinsic genetic traits of the genus moderately than latest acquisitions of latest mechanisms in opposition to fashionable antibiotics.
Efflux pumps and antibiotic inactivation
Efflux pumps are key bacterial protection programs that expel poisonous compounds, together with antibiotics, thereby enhancing survival in hostile environments (Huang et al. 2022). A large range of efflux pump genes is distributed throughout the analyzed strains, lots of that are linked to the export of a number of antibiotic courses (Fig. 5). This sample signifies that resistance mechanisms are intrinsic to the genus.
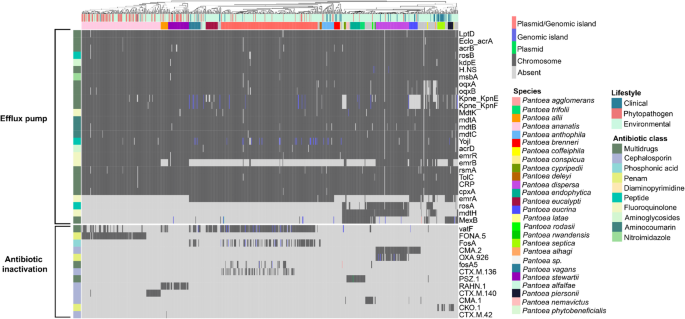
Presence–absence heatmap of genes associated to efflux pumps and antibiotic inactivation. Genes are grouped based on the antibiotic courses to which they confer resistance, whereas genomes are labeled by species and way of life
Among the efflux pump superfamilies recognized, probably the most outstanding have been RND (Resistance-Nodulation-Division), MFS (Major Facilitator Superfamily), and SMR (Small Multidrug Resistance). The acrAB and oqxAB complexes, belonging to the RND superfamily, mediate the extrusion of a number of antibiotics, significantly cephalosporins and fluoroquinolones. These programs confer resistance to second- and third-generation fluoroquinolones in addition to third- and fourth-generation cephalosporins in medical pathogens reminiscent of E. coli and Okay. pneumoniae (Huguet et al. 2013; Bialek-Davenet et al. 2015). Additional related genes have been additionally detected, together with rosAB (MFS), related to resistance to antimicrobial peptides (Bengoechea and Skurnik 2000); kpnEF (SMR), linked to resistance to cephalosporins and tetracyclines (Srinivasan and Rajamohan 2013); mdtABC (RND) (Nishino et al. 2007), concerned in resistance to aminocoumarins; and emrB-tolC (MFS), related to fluoroquinolone resistance (Gu et al. 2021).
With respect to enzymatic antibiotic inactivation, 13 genes have been recognized, however their distribution was restricted to particular species. Most of those genes correspond to β-lactamases lively in opposition to cephalosporins, present in P. ananatis, P. stewartii, P. allii, P. agglomerans, P. dispersa, and P. eucrina. Additional clinically related enzymes included fosA, conferring resistance to fosfomycin, current in P. vagans and P. agglomerans, and PSZ-1, a β-lactamase initially reported in P. endophytica and right here confirmed to be current in all genomes of this species, in addition to its sister species, P. trifolii.
Genetic determinants of Pantoea life
The genus Pantoea is well-known for its ecological versatility, comprising strains with various life, together with environmental, plant-associated, and even animal and human-associated types. We labeled the analyzed strains into three fundamental teams: environmental, phytopathogenic, and medical. Within the environmental group, endophytic species are significantly noteworthy, as they colonize plant tissues with out inflicting seen signs (Hallmann et al. 1997). However, the boundary between endophytic and phytopathogenic micro organism is commonly blurred, since each share comparable genetic repertoires, particularly virulence elements, concerned in plant colonization and an infection (Lòpez-Fernàndez et al. 2015). This genetic overlap complicates the identification of really helpful strains and represents a key problem when screening microorganisms for biotechnological purposes.
To additional discover these distinctions, we carried out a pan-GWAS evaluation to determine accent genes related to the completely different life and pinpoint genetic determinants that would function discriminators among the many classes. Genes considerably related to the phytopathogenic way of life (see Methods for particulars) included elements of the T3SS, particular T3SS effectors, and the central gene of the phosphonate biosynthetic cluster (HiVir). The restricted distribution of those determinants amongst phytopathogenic strains is proven in Figs. 6 and seven.
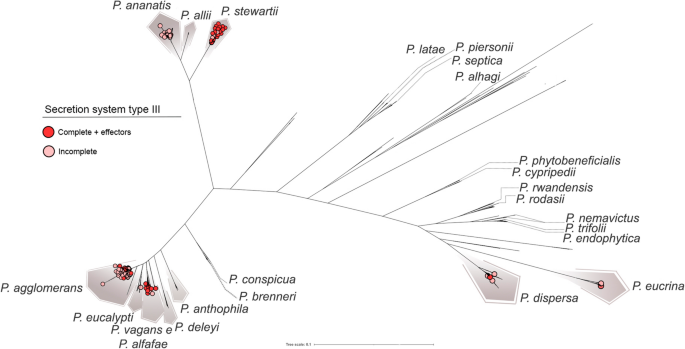
Distribution of the sort III secretion system (T3SS) of the hrp-hrc household throughout Pantoea species. Dark purple circles denote strains carrying the whole hrp-hrc cluster along with its effectors, whereas gentle purple circles signify strains missing the complete cluster and related effectors. The full system is principally present in P. stewartii, P. agglomerans, P. vagans, and P. alfalfae, which harbor all genes encoding the T3SS equipment in addition to the effectors linked to host specificity and pathogenicity—for instance, wtsE in P. stewartii (water‑soaking signs), and hsvB and hsvG (host specificity and gall formation). The restricted distribution of the T3SS amongst phytopathogenic species suggests its potential as a genetic marker to tell apart pathogenic from helpful Pantoea strains
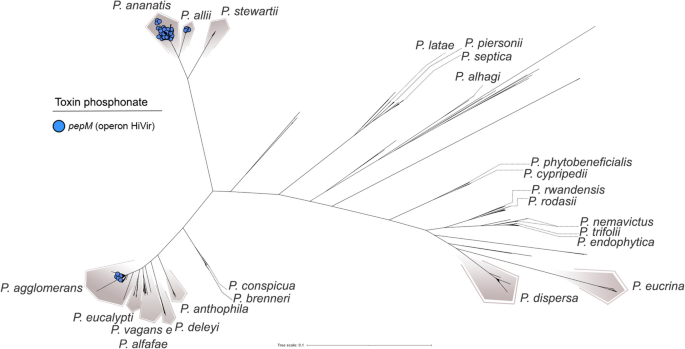
Distribution of the pepM gene throughout species of the genus Pantoea. The pepM gene is a part of the HiVir operon, which encodes enzymes for the biosynthesis of pantaphos, a phosphonate phytotoxin implicated in plant illness. Species harboring pepM are highlighted, illustrating its restricted distribution and potential affiliation with virulence and host specificity
A key determinant of pathogenicity in Gram-negative phytopathogens is the T3SS, a membrane-embedded nanomachine composed of ~ 20 structural proteins. The T3SS is encoded by the hrp/hrc gene cluster, whose distribution seems to be restricted to a restricted variety of species (Fig. 6). This system mediates the translocation of effector proteins into plant host cells via a needle-like pilus construction, often known as the Hrp pilus. Once contained in the host cells, these effectors can both set off plant immune responses or suppress host defenses to advertise illness improvement (He et al. 2025).
Among the analyzed species, P. stewartii harbored the whole hrp/hrc cluster in most genomes. The cluster was additionally detected in 5 P. vagans strains (plasmid-borne in one in all them) and within the pathovars P. agglomerans pv. gypsophila and pv. betae. P. stewartii subsp. stewartii is a well known pathogen inflicting Stewart’s bacterial wilt and leaf blight in maize (Zea mays L.), with the hrp/hrc cluster being important for its pathogenicity (Mergaert et al. 1993). In P. agglomerans, these pathovars are well-known pathogens of Gypsophila and sugar beet, respectively.
Consistent with observations on phytohormone manufacturing, the hrp/hrc operon can be related to gall formation, appearing synergistically with auxin biosynthesis genes of the IAM pathway (iaaM and iaaH). In a number of situations, these determinants have been plasmid-encoded, suggesting the horizontal acquisition of pathogenicity islands that enabled sometimes endophytic strains to undertake a pathogenic way of life.
Among the effectors, wtsE stands out as important for lesion improvement in maize by P. stewartii, the place it induces water-soaking and facilitates bacterial proliferation (Jin et al. 2016). This effector was additionally detected in P. agglomerans pv. gypsophila and pv. betae. Along with this, the effectors hsvG and hsvB have been solely detected in these pathovars, according to their specialised interactions with Gypsophila and sugar beet.
Recent reviews have additionally described plant lesions attributable to P. vagans (Rodríguez Velázquez et al. 2024; Anwer et al. 2025), a species characterised by various life. Some of its strains, reminiscent of P. vagans C9-1, are acknowledged for his or her biotechnological purposes and use as biocontrol brokers (Klein et al. 2017), additional highlighting the twin ecological roles of this species.
However, not all Pantoea phytopathogens depend on the T3SS. A notable exception is P. ananatis, broadly studied for its position in onion middle rot (Gitaitis et al. 2002; Stice et al. 2018; Shin et al. 2023). Unlike different pathogenic species within the genus, P. ananatis lacks the T3SS and as a substitute is determined by the HiVir biosynthetic gene cluster, which encodes the phosphonate phytotoxin pantaphos (Agarwal et al. 2021). Within this cluster, pepM, encoding a phosphoenolpyruvate mutase, is crucial for pathogenicity in onions (Yang et al. 2025). This phytotoxin is predominantly present in P. ananatis (Fig. 7), the place it’s situated in genomic islands, suggesting acquisition through HGT. Additionally, pepM was recognized in 4 P. allii strains (three from onion bulbs exhibiting middle rot signs), one P. vagans pressure remoted from asymptomatic Alliaria petiolata (Shin and Kvitko 2024), and 7 P. agglomerans strains additionally remoted from diseased onions. In all instances, the genes have been situated inside genomic islands, indicating attainable plasmid-mediated transmission of the HiVir cluster throughout species inside the genus.
The pan-GWAS evaluation recognized a single gene with robust organic plausibility that was considerably related to medical strains: ibeB (also referred to as cusC), encoding an invasin-related protein. In E. coli, ibeB has been described as a virulence issue concerned in human neonatal meningitis (Germon et al. 2005), whereas in Cronobacter sakazakii—an opportunistic pathogen chargeable for extreme neonatal infections reminiscent of necrotizing enterocolitis, meningitis, and sepsis—it has been equally linked to pathogenesis (Kucerova et al. 2010). The ibeB gene encodes a element of a silver and copper cation efflux system, and its exercise has been related to bacterial invasiveness. In E. coli, as an illustration, ibeB facilitates the entry of micro organism into mind microvascular endothelial cells, thereby selling penetration of the blood-brain barrier (Franke et al. 2003). This gene was most steadily detected in P. septica, significantly in strains remoted from neonatal feces. This species has been related to neonatal bloodstream infections, mirroring the pathogenic profiles of E. coli and C. sakazakii, and suggesting a recurring sample of neonatal an infection. The gene was additionally recognized in different clinically derived Pantoea species, together with P. piersonii, remoted from a bacteremia case (Howard et al. 2023) and kidney stones (Rekha et al. 2020), P. dispersa, related to bloodstream infections. Notably, ibeB was additionally detected in strains obtained from asymptomatic sufferers, underscoring its presence past overt medical illness (Fig. 8).
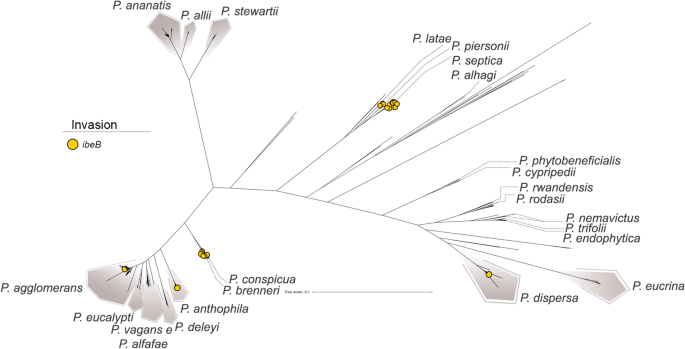
Distribution of the ibeB gene throughout Pantoea species, highlighting its prevalence in strains related to medical or pathogenic life. The presence of ibeB suggests a possible position in invasiveness and will function a marker for distinguishing pathogenic from environmental isolates
This web page was created programmatically, to learn the article in its authentic location you’ll be able to go to the hyperlink bellow:
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11274-025-04780-2
and if you wish to take away this text from our website please contact us


